Objective Structured Practical Examination – Nursing is a profession within the healthcare sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other healthcare providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialisms with differing levels of prescriber authority.
Many nurses provide care within the ordering scope of physicians, and this traditional role has shaped the public image of nurses as care providers. However, nurses are permitted by most jurisdictions to practice independently in a variety of settings depending on training level. In the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced and specialized credentials, and many of the traditional regulations and provider roles are changing.
Nurses develop a plan of care, working collaboratively with physicians, therapists, the patient, the patient’s family, and other team members, that focus on treating illness to improve quality of life. Nurses may help coordinate the patient care performed by other members of an interdisciplinary healthcare team such as therapists, medical practitioners, and dietitians. Nurses provide care both interdependently, for example, with physicians, and independently as nursing professionals.
Objective Structured Practical Examination
STETHOSCOPE
Identification:
The following supplied item is a stethoscope.
Function /Uses/ Importance:
1. To measurement of blood pressure.
2. To measurement of heart sound. E.g. Systolic murmur.
3. To examine the lung sound. E.g. Crebs, ronchi, wheezing.
4. To detect bowel movement.
5. During insertion of ryles tube/ NG tube
6. Examine the foetal movement.
7. To measurement of carotid bruit. E.g. Thyrotoxicosis.
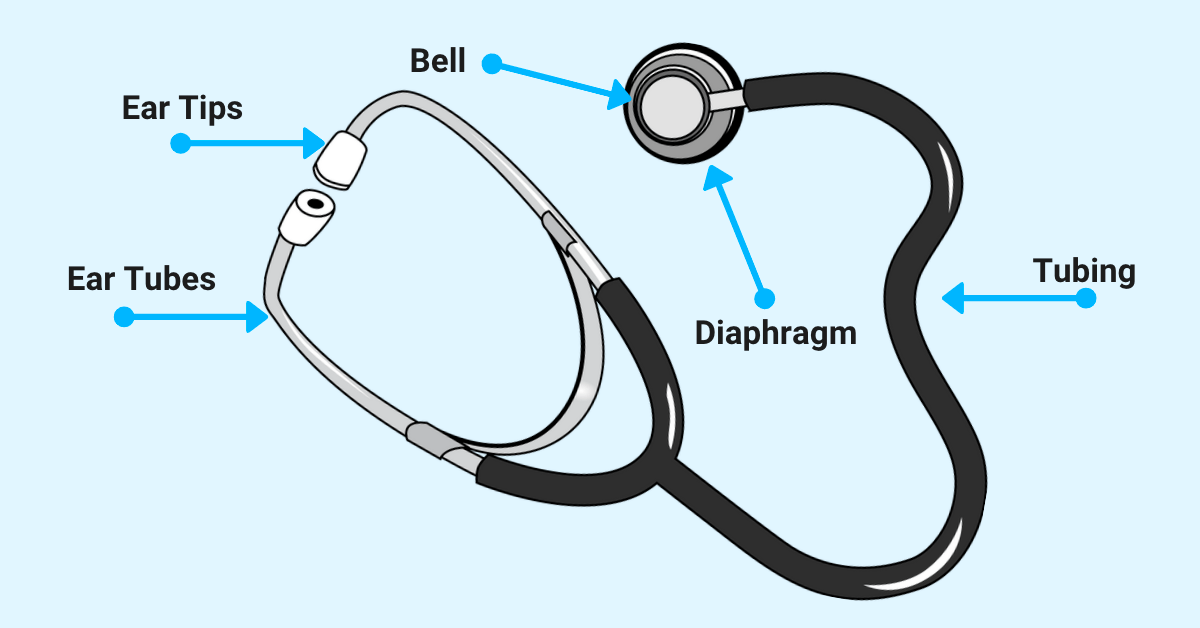
Parts:
A. Two end pieces:
a) Ear piece.
b) Chest piece
- Diaphragm
- Bell
B. Metallic connecting tube
C. Connecting rubber tube.
SPHYGMOMANOMETER
Identification:
The following supplied item is a sphygmomanometer.
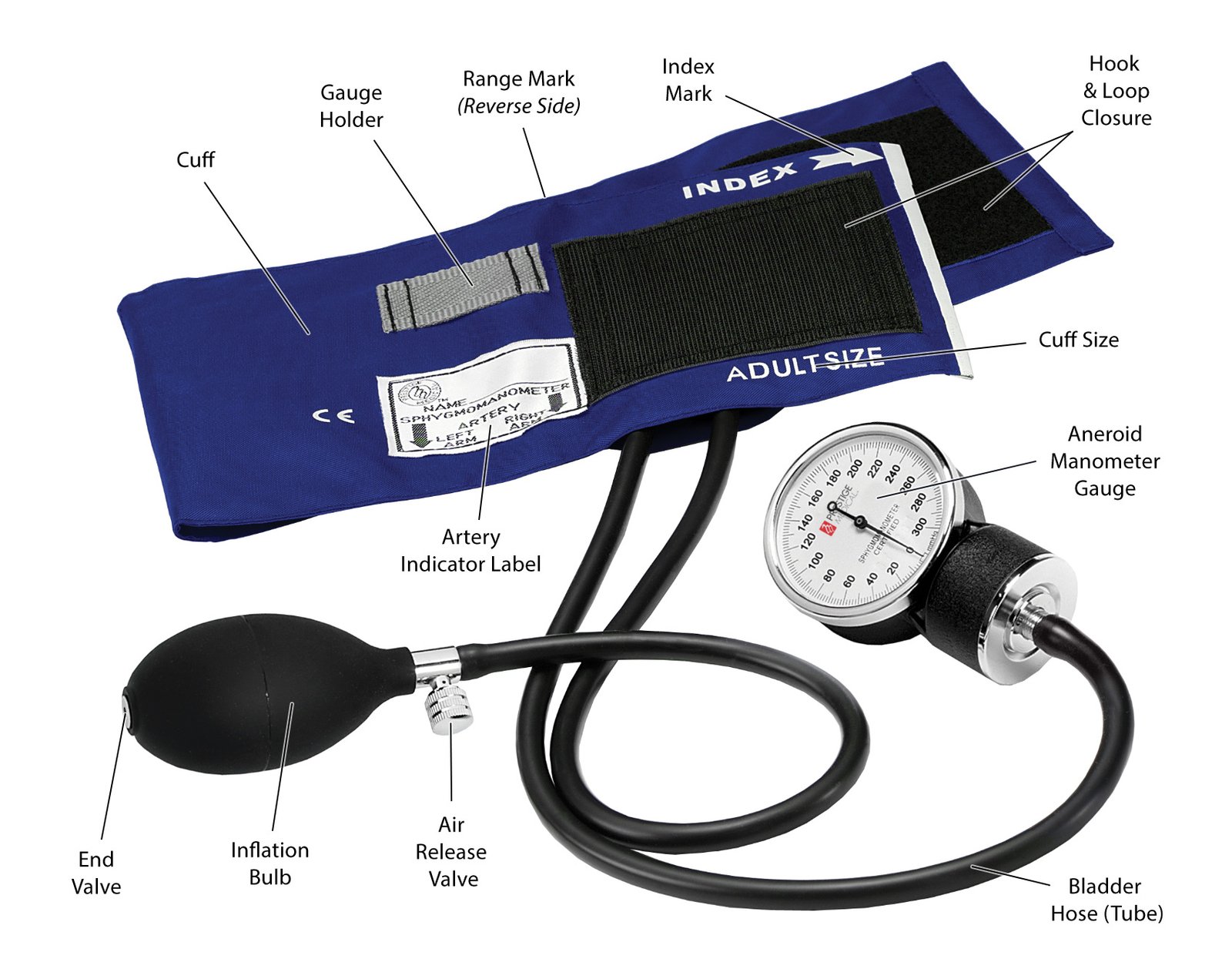
Parts of Sphygmomanometer:
A. Mercury manometer
B. Rubber tube or plastic tube.
C. Inflatable cuff/armlet/inflatable bag
D. Hand pump with screw/Air pump.
Function /Uses/Importance of Sphygmomanometer:
1. It is used to measure systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
2. To assess physical examination.
3. To detect any abnormalities
DISPOSABLE SYRINGE
Identification:
The following supplied item is a plastic disposable syringe.
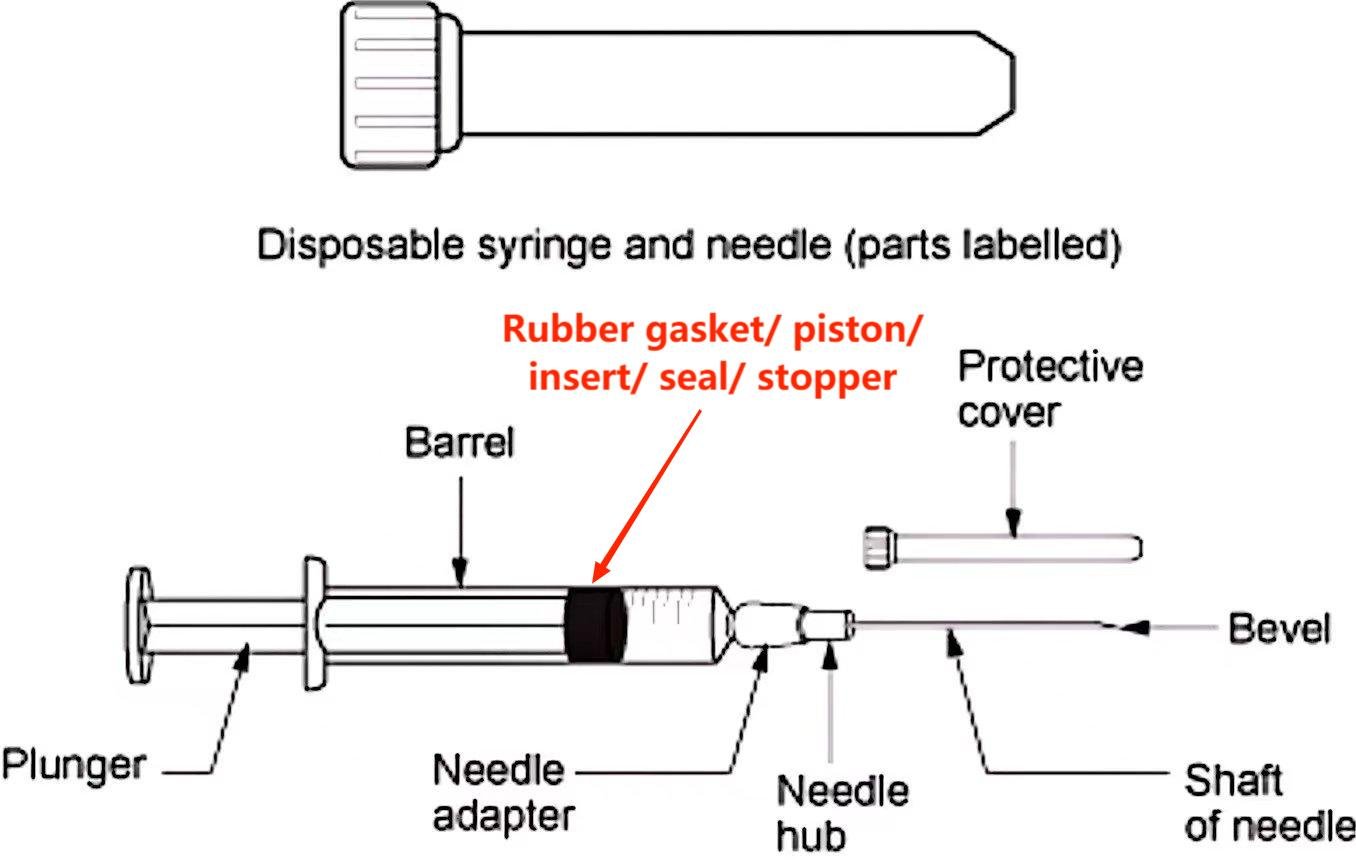
Parts of syringes and needle:
A. Barrel with scale
B. Piston/plunger
C. Adaptor
D. Needle with cover:
a. Adaptor/Needle hit/ hub.
b. Shaft of needle
c. Bevel
d. Lumen
E. Connector.
Uses/Importance/ Function of a Disposable Syringe:
- To give intravenous injection
- To give intramuscular injection
- To blood draw
- To give NG feeding
- To give NG suction
- To ballooning during catheterization/insert endotracheal tube.
Made:
- It is made by plastic.
Cleanliness Method:
- Wash with running water
Sterilization:
- Ethylene oxide gas
- Lionizing radiation
MICRO BURETTE WITH INFUSION SET
Identification:
The following supplied item is a micro burette with infusion set.
Parts:
1. Perforator (Nozzle)
2. Drip chamber
3. Connecting tube
4. Drop regular
5. Connector
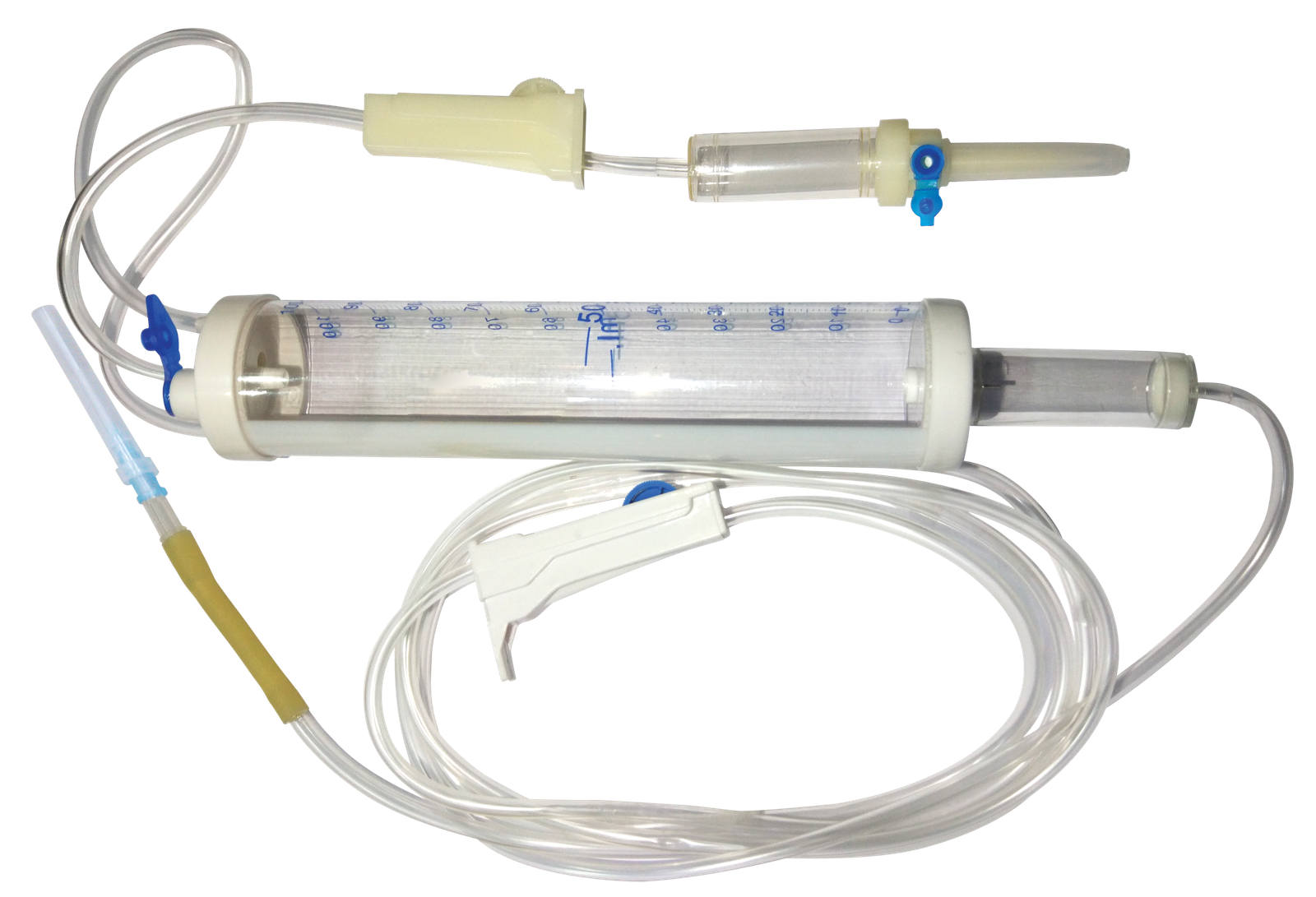
Figure: Micro burette with infusion set
Function /Uses/ Importance:
1. To give intravenous infusion (I/V) in neonate and infants.
2. For correction of dehydration.
3. To give neonates nutrition
4. To give neonates medicine.
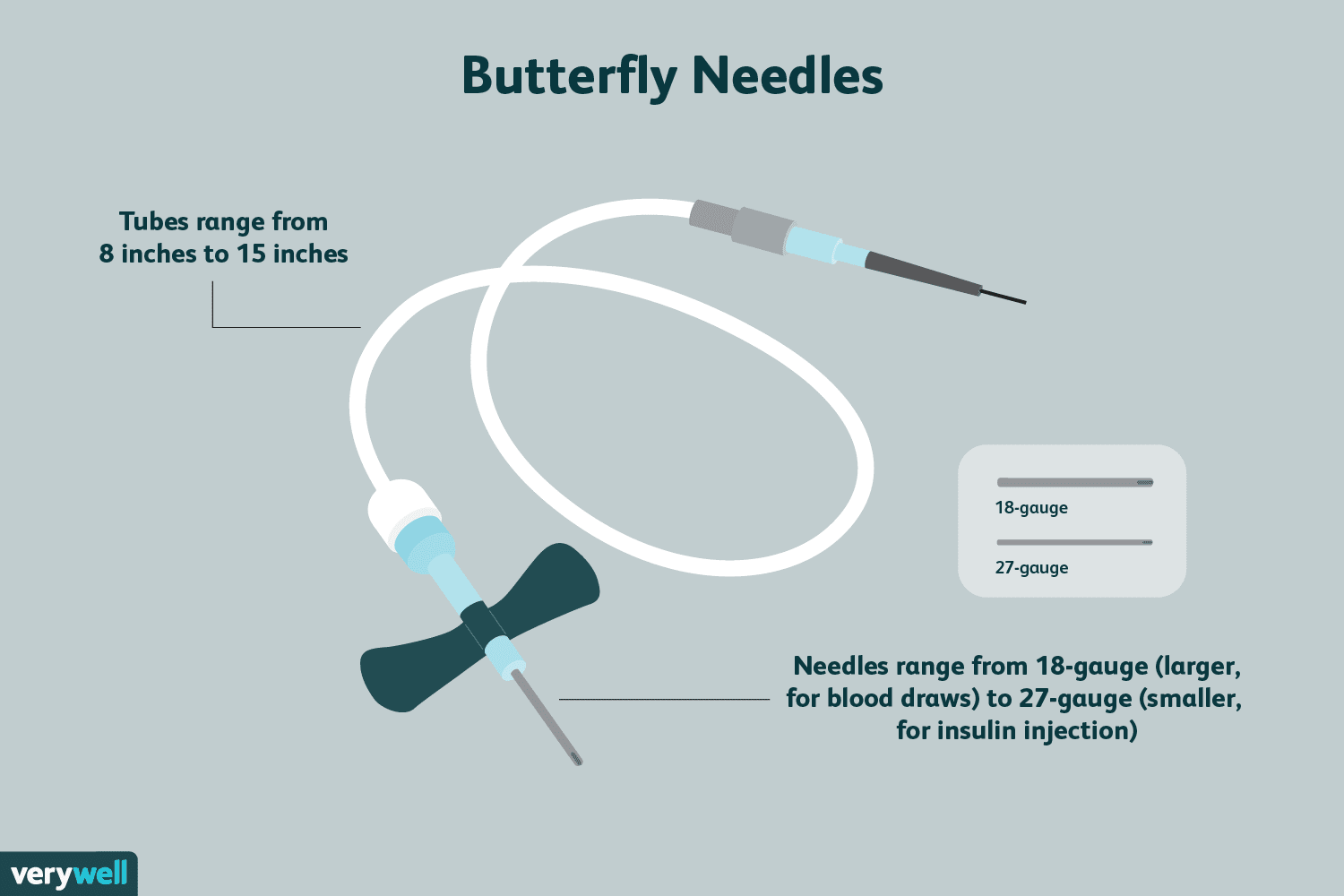
BUTTERFLY NEEDLE
Identification:
The following supplied item is a butterfly Needle.
Parts of Butterfly Needle:
A. Connector
B. Connective tube
C. Fly
D. Needle with cover
Function/Uses/Importance of Butterfly Needle:
1. To open an intravenous channel
2. To introduce infusion
3. To introduce blood transfusion
4. To provide medication
5. To provide parenteral nutrition
6. To collect blood for diagnosis purposes.
INTRAVENOUS CANNULA
Identification:
The following supplied item is an intravenous (I/V) cannula
Made:
It is made by plastic
Parts of (I/V) Cannula:
1. Flashback chamber
2. Luer lock plug
3. Luer connector.
4. Needle grip
5. Injection port cap
6. Wings/ Catheter hub/ Fly
7. Catheter
8. Valve
9. Bushing
10. Needle
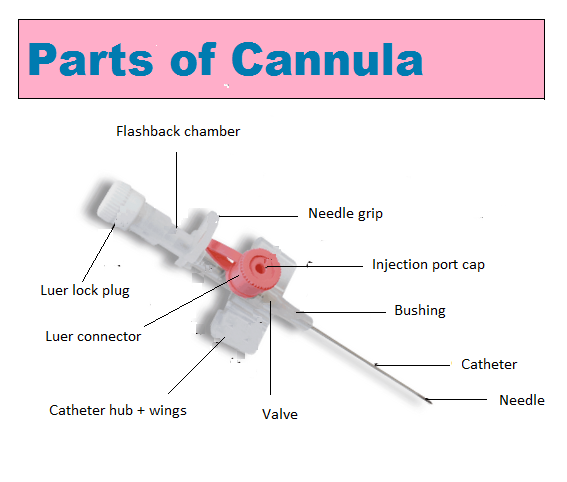
Figure: Parts of I/V Cannula
Function/Uses/Importance of I/V Cannula:
1. To open an intravenous channel
2. To introduce infusion
3. To introduce blood transfusion
4. To provide medication
5. To provide parenteral nutrition
6. To collect blood for diagnosis purposes.
OXYGEN CYLINDER
Identification:
The following supplied item is an oxygen cylinder.
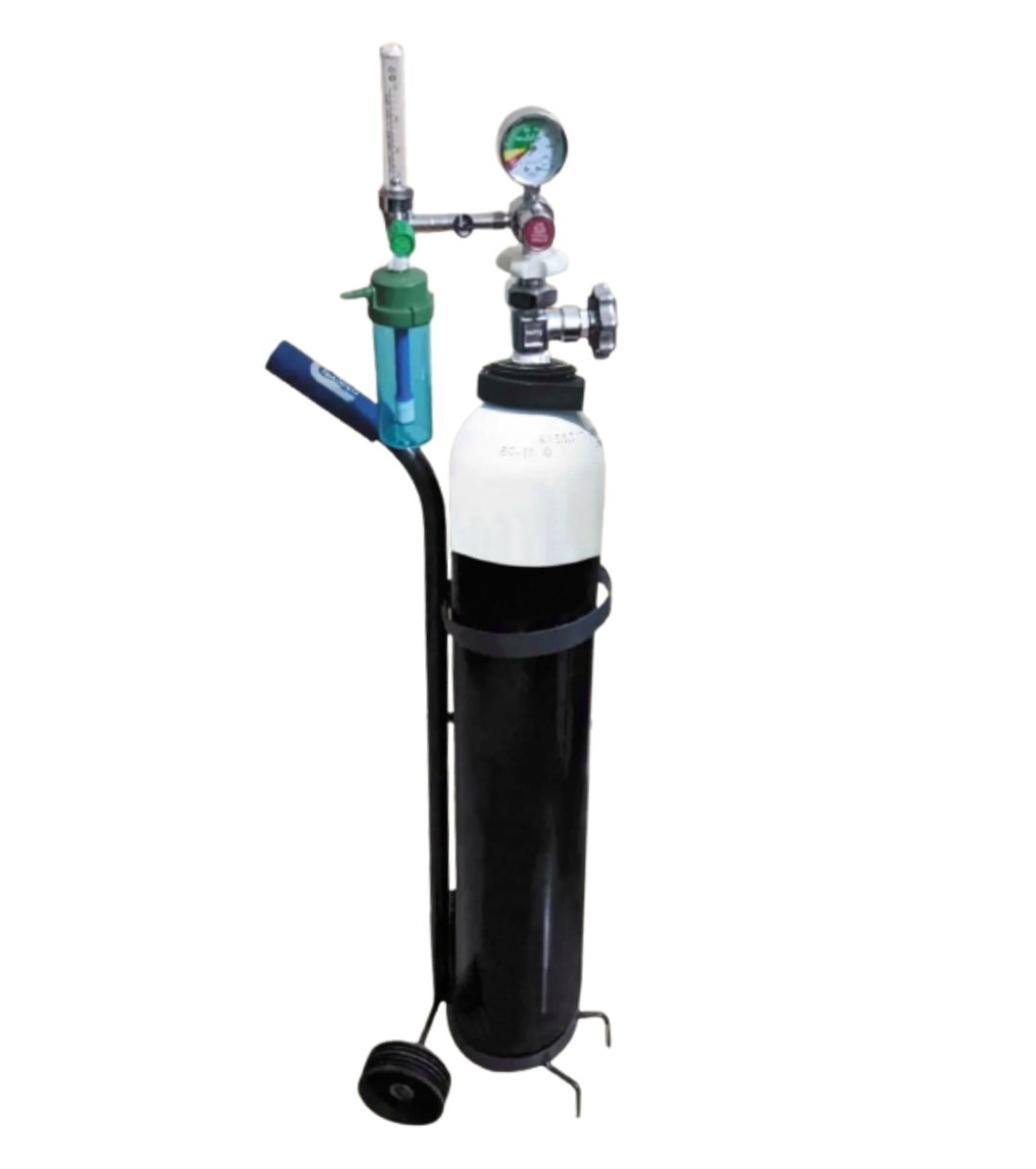

Parts of oxygen cylinder:
- Body.
- Shoulder.
- Nut.
- Stem.
- Spindle.
- Pressure gauge.
- Flow meter.
- Hand wheel valve.
- Outlet.
- Flow meter humidifier
STERILE GLOVES
Identification:
The following supplied item is sterile gloves.
Made:
It is made by rubber
Function /Uses/Importance:
1. It is used during general surgery
2. It is used during wound dressing
3. It is used during inserting catheter
4. It is used during inserting nasogastric tube.
5. It is used at the time of medicine.
6. It is used during operation.
Sterilization:
1. Ethylene oxide gas.
2. Ionizing radiation.
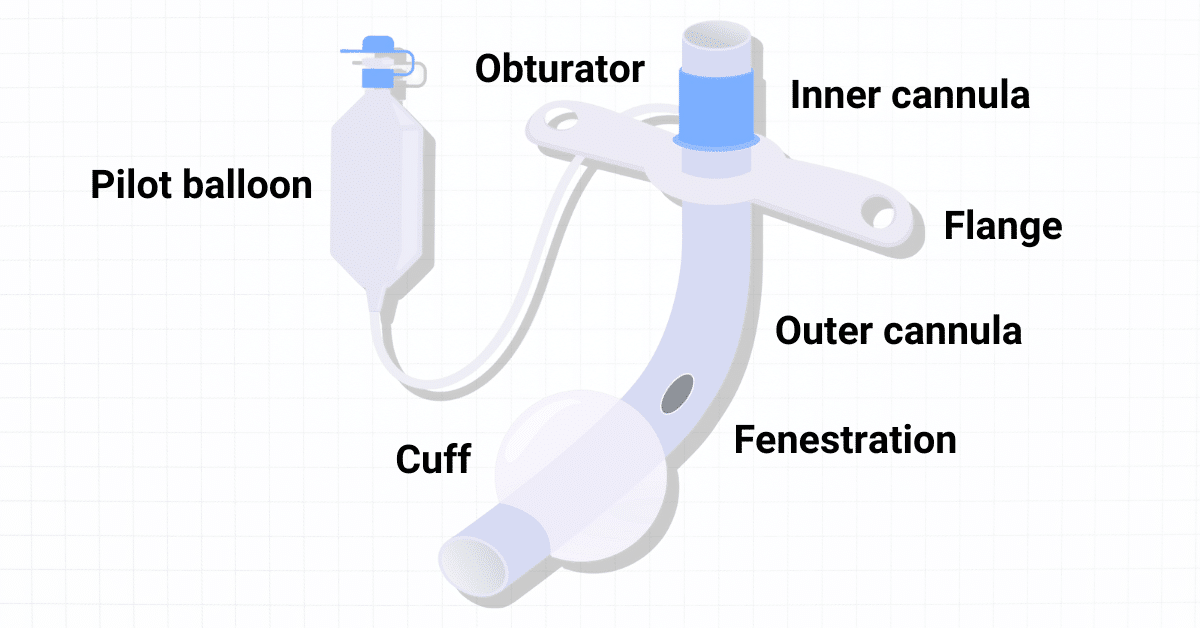
TRACHEOSTOMY TUBE
Identification:
The following supplied item is a tracheostomy tube.
Parts:
- Consists of an outer tube and inner tube.
- Inner tube is slightly longer than the outer tube.
- There is a flange (rounded end) in the outer tube.
- In the flange there are two holes for typing tapes around the neck after tracheostomy.
Uses:
- To bypass upper respiratory tract obstruction.
- Tracheo-broncheal toileting.
- To reduce dead air space.
- Instant intermittent positive pressure ventilation.
INFUSION SET/ SALINE SET
Identification:
The following supplied item is an Infusion set/ saline set.
Parts of Infusion Set:
1. Drip chamber
2. Connecting tube with nozzle
3. Air Vented
4. Regulator/ roller clamp
5. Solution filter
6. Spike
7. Injection port.
8. Needle adaptor/connector.
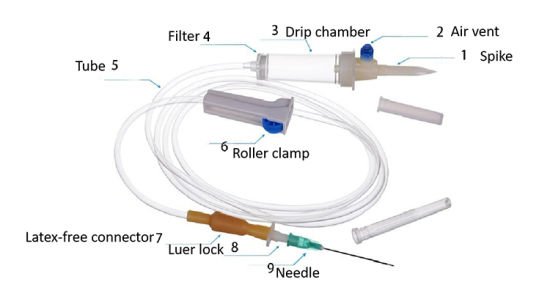
Function /Uses/Importance of Infusion set/Saline Set:
1. To open an intravenous channel
2. To introduce infusion
3. To introduce blood transfusion
4. To provide large volume of injection.
5. Use as tourniquet
6. To provide parenteral nutrition
7. To give enema
BLOOD TRANSFUSION SET
Identification:
The following supplied item is a blood transfusion set.
Parts of Blood Transfusion Set:
1. Insertion spike with cap.
2. Drip chamber with filter
3. Connecting tube
4. Filter
5. Regulator/ Roller clamp.
6. Injection port/connection
7. Needle adaptor.
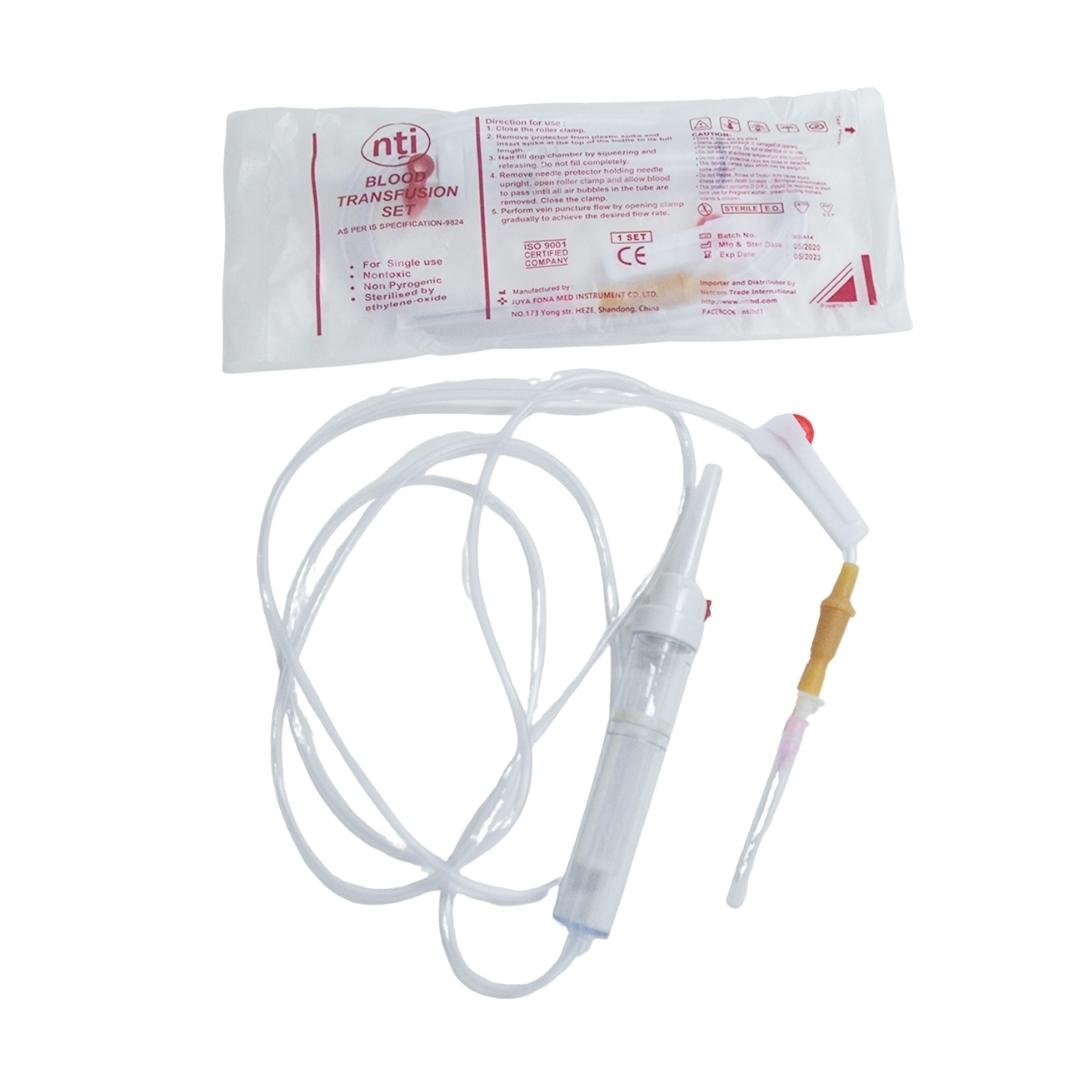
Function /Uses/Importance:
1. To introduce transfusion of blood
2. To introduce infusion
3. Use as tourniquet.
RUBBER AIRWAY TUBE
Identification:
The following supplied item is rubber airway tube.
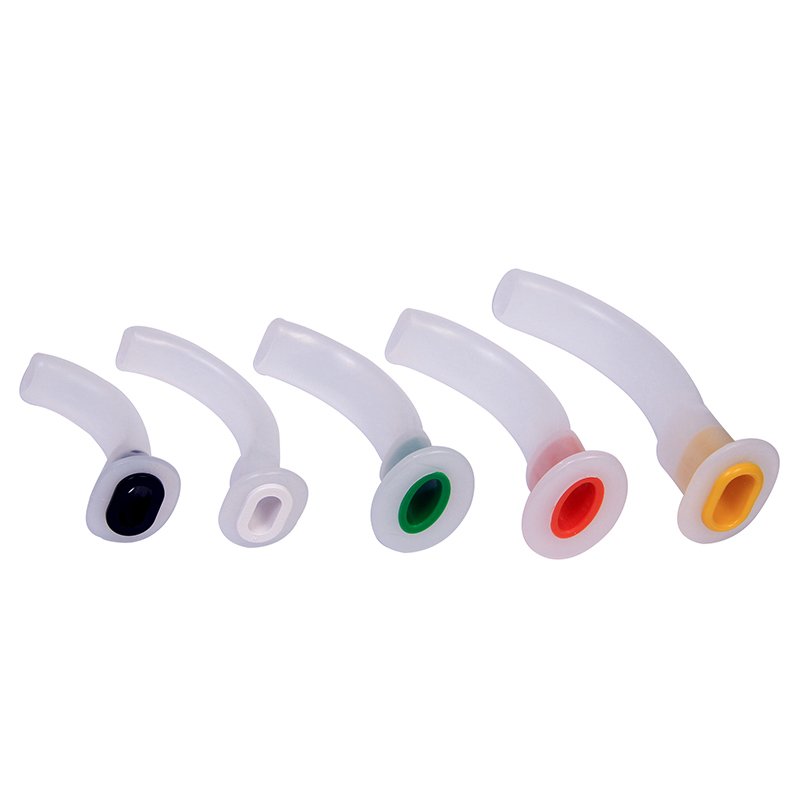

Uses:
- Preventive of tongue falls back & tongue bite unconscious patient.
- Maintenance of airway.
- Used for suction.
GULLY POT
Identification:
The following supplied item is a Gully pot.
Uses/Importance/Function:
1. It is used to carry antiseptic solution.
2. To keep gauge piece.
3. To keep shampoo for hair care.
4. To keep mouth solution for mouth care.

Made:
It is made by stainless steel.
Cleanliness method:
Wash with running soap & water by brush/ gauze piece.
Sterilization:
Boiling and autoclaving.
KIDNEY TRAY
Identification:
The following supplies item is a kidney tray.
Made:
It is made by stainless steel.

Function/Uses/ Importance of Kidney Tray:
1. To carry gauze piece for dressing.
2. To carry surgical instruments for surgical procedure.
3. To carry stich cutting.
4. To carry antiseptic solution.
5. To carry sterile bandage.
Cleanliness method:
Wash with running soap & water by brush/ gauze piece.
Sterilization:
Autoclaving and Boiling.
LARYNGOSCOPE
Identification:
The following supplied item is a laryngoscope.
Parts:
- Observation tube.
- Holding part.
- Light source.
- Part of elevation.
- Separable half.

Uses:
- Helps in intubation during the administration of general anaesthesia or for mechanical ventilation.
- Detects causes of voice problems, such as breathing voice, hoarse voice, weak voice or no voice.
- Detects causes of throat and ear pain.
- Evaluates difficulty in swallowing a persistent sensation of lump in the throat or mucus with blood
THERMOMETER
Identification:
The following supplied item is an oral/ rectal clinical thermometer
Parts of thermometer:
A. Bulb:
a. Mercury or color alcohol
b. Thin glass
B. Glass rod:
a. Fahrenheit or centigrade scale.
b. Thick glass
c. Bore:
- Constriction bore
- Straight bore
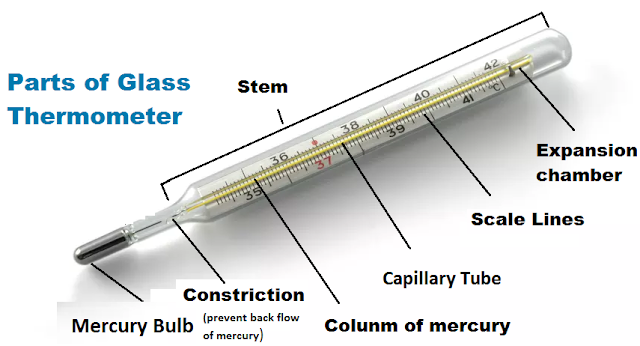
Uses/Importance/Function of Thermometer:
1. To measurement of body temperature.
2. It helps the nurse to prepare the nursing care plan.
3. By measurement of body temperature, we can prognosis of disease
4. It helps the doctor to diagnosis and correct treatment of disease
5. It helps to identify the types of fever by filling completing temperature chart. E.g. Stepladder pattern in case of typhoid fever.
Cleanliness method:
a. Thermometer is to be washed with soap and plain water
b. Dry it by cotton ball / gauze piece
c. Preserved in antiseptic solution
Sterilization:
By antiseptic solution such as:
- Savlon
- Lysol
NASOGASTRIC (NG) TUBE
Identification:
It is a nasogastric (NG) tube/ Ryle’s tube.
Uses
A. Therapeutic purposes:
a) To evacuate gastric contents (nasogastric suction):
- Acute intestinal obstruction.
- Perforation of any hollow viscus.
- Sucking out of gastric contents in gastric outlet obstruction.
b) For introducing vasopressin or sclerosin agents in gastric haemorrhage.
c) For feeding through the tube (nasogastric feeding):
- Unconscious patient.
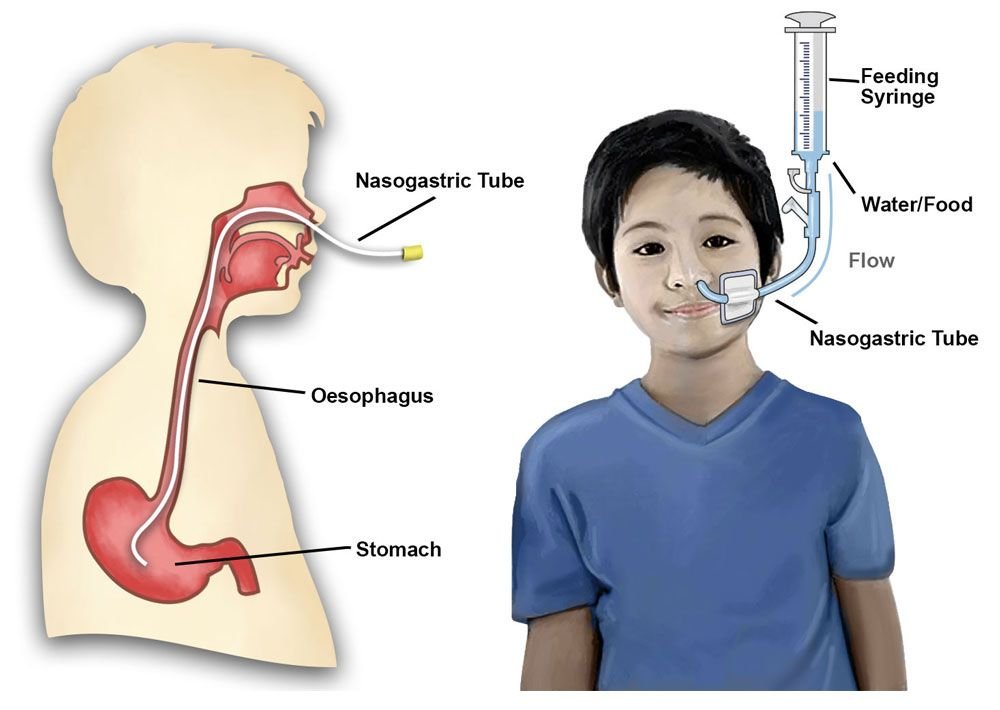
B. Diagnostic Purposes:
a) To collect gastric juice for analysis: To diagnosis:
- Diagnosis of peptic ulcer.
- Postoperative assessment of vagotomy operation.
- To detect achlorohydria (in carcinoma stomach, pernicious anaemia)
b) To collect gastric lavage for Acid fast bacillus.
c) To diagnosis gastric outlet obstruction (gastric aspiration will exceed 200 cc after 12 hr fasting)
URINAL (MALE)
Identification:
The following supplied item is a male urinal.

Made:
It is made by stainless steel/ plastic
Uses/Importance/ Function of Urinal:
a) To collect of urine.
Cleanliness method:
a) Wash with running water and soap by brush/ gauze piece.
Sterilization:
a) For stainless steel: Boiling and autoclaving
b) For plastic: Ethylene oxide gas and Ionizing radiation
BED PAN
Identification:
This is a bed pan
Made:
It is made by stainless steel/ plastic

Uses/ Function:
a) To collection of stool.
Cleanliness method:
Wash with running water & soap by brush/ gauze piece.
Sterilization:
a) For stainless steel: Boiling and autoclaving
b) For plastic: Ethylene oxide gas and Ionizing radiation.
UROBAG
Identification:
This is an urobeg.
Made:
It is made by polythene
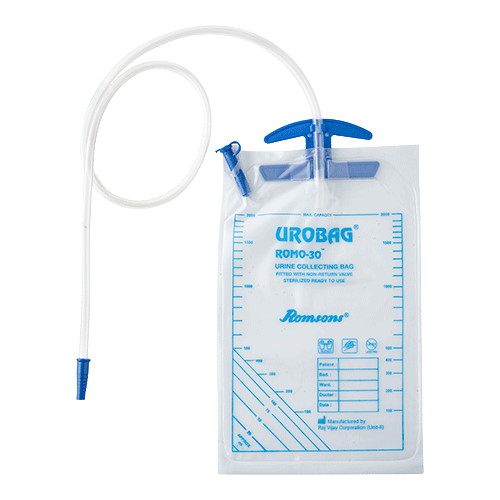

Parts:
1. Connector
2. Hollow tube
3. Measuring beg with scale
4. Holding cap
Uses/Function:
1. It is used to contain urine or store of urine
2. It is used to maintain intake and output chart by measuring urine
3. Method of securing catheter
TONGUE DEPRESSOR
Identification:
The following supplied item is a tongue depressor
Made:
It is made by stainless steel.
Uses/Importance/ Function:
1. It is used in different oral examination. Such as- tongue, buccal mucosa, Tonsil, etc.
2. It is used in mouth care.
3. It helps to prevent tongue falling back towards the throats

Cleanliness method:
Wash with running water by brush/ gauze piece.
Sterilization:
Boiling and autoclaving
MICROPORE
Identification:
The following supplied item is a micropore/ adhesive tape

Uses/Importance/Function:
1. It is used after different surgical procedure.
2. It is used in fixing the IV cannula
3. It is used in Ryles tube, catheterization, drain tube
4. It is used for identification of drug is being used. Such as – Infusion, Hartsol + Inj. KT.
FEEDING CUP
Identification:
The following supplied item is a feeding cup

Use/Function:
1. It is used in mouth care
2. It is used in feeding in semi-conscious, paralyze & bed ridden patient
3. It is used in ryles tube or NG (naso gastric) feeding
4. It is used in feeding in children
Cleanliness method:
Wash with running water & soap by brush/ gauze piece.
Sterilization:
a) For stainless steel: Boiling and autoclaving
b) For plastic: Ethylene oxide gas and Ionizing radiation.
c) For glass/ceramic: Hot air oven
TEST TUBE
Identification:
The following supplied item is a test tube

Uses/Function:
1. It is used for different diagnostic test. E.g. – Blood, Urine, Throat swab
2. It is used for different chemical reaction.
Cleanliness method:
Wash with running water & soap by brush/ gauze piece.
Sterilization: Hot air oven
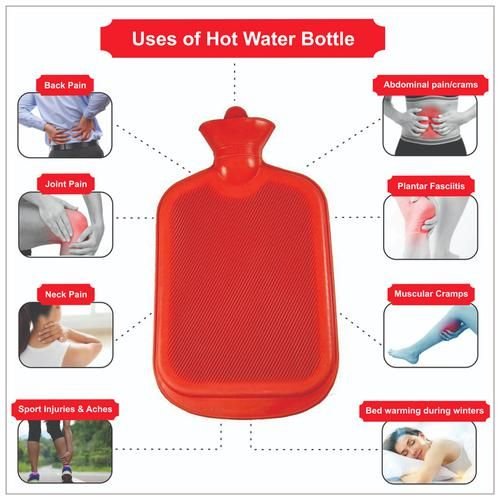
HOT WATER BAG
Identification:
The following supplied item is a Hot water bag
Uses/Importance/ Function:
1. It is used for warm up for the patient.
2. It is used for hair care
3. It is used for bed bath
4. It is used as hot compresses different diseases.
Cleanliness method:
Wash with running water & soap by brush/ gauze piece.
Sterilization: Boiling
ICE BAG/COLD WATER BAG
Identifications:
The following supplied item is an ice bag/ cold water bag

Uses/Importance/Function:
1. It is used for stop the bleeding. E.g.- Any type of haemorrhage
2. It reduce swelling
3. It used as short term pain reliever
Cleanliness method:
Wash with running water & soap by brush/ gauze piece.
Sterilization: Boiling
ANTISEPTIC SOLUTION
Identification:
The following supplied item is an antiseptic solution
Uses/Function:
1. It is used for dressing
2. It used for painting different operative site
3. It is used in sterilization of sharp instrument
ROLLER BANDAGE
Identification:
The following supplied item is a roller bandage
Parts of Roller bandage:
When roller bandage is ready for application,
- The roll is termed the ‘head’
- The loose end is termed as ‘Free end’ or tail

Uses/Importance/Function of Roller bandage:
1. It supports the wound
2. It is used for immobilize a fracture or dislocation
3. It is used for immobilize an injured part so as to relieve pain
4. It prevents contamination of wound
5. It is used for maintain splints is position
6. It prevents or reduce swelling
7. It prevents hemorrhage be means of pressure.
8. It corrects deformity
9. It absorbs discharge
10. It prevents infection and avoid further injury.
TRIANGULAR BANDAGE
Identification:
The following supplied item is a triangular bandage
Parts of Triangular bandage:
1. The apex point
2. The base or lower side, which is the longest
3. The two sides
4. The two ends
5. Inner and outer surface the inner being that next to the body

Uses/Importance/Function of Triangular bandage
1. It is used for slings
2. It is used for immobilized fracture or dislocation
3. It is used for immobilize an injured part so as to relieve pain
4. It is used for maintain splints in position
5. It correct deformity.
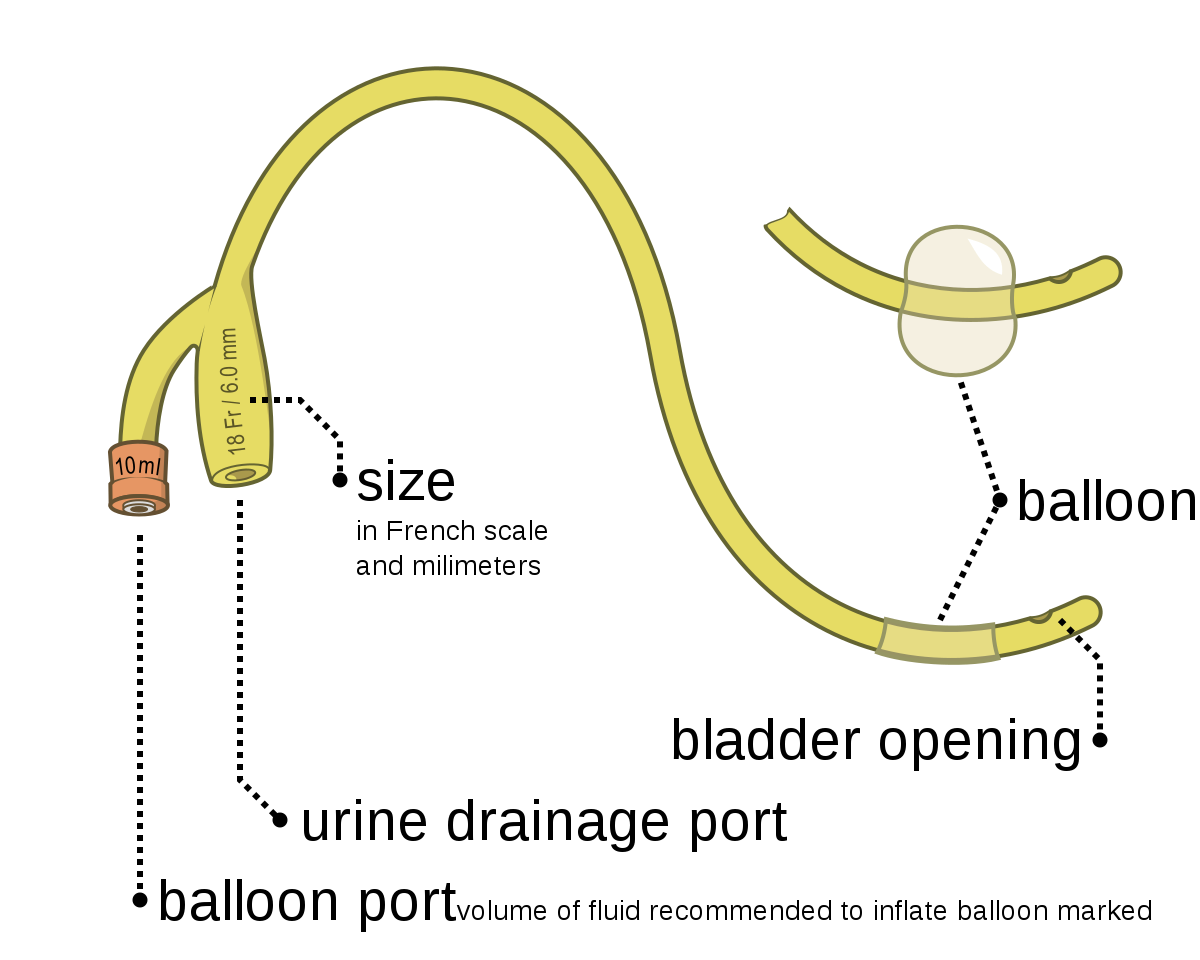
BI-CHANNEL SELF-RETAINING FOLEY’S CATHETER
Identification:
The following supplied item is a bi-channel self-retaining Foley’s catheter
Made:
Made by rubber
Parts:
A. Two channels:
a) Straight channel: For drainage of urine.
b) Oblique channel: For introducing distilled water to inflate the balloon.
B. Balloon: Situated near the tip
Uses/Importance/Function:
1. For continuous drainage of urinary bladder in the conditions like-
- Unconscious patient
- Prostatic operation
- Renal failure. etc
2. For irrigation of urinary bladder after prostatectomy.
3. For drainage of different abscess: e.g
- Appendicular abscess,
- Empyema thoraces,
- Empyema of gall bladder.
4. Can be used as a tourniquet.
Sterilization:
It is sterilized by gamma ray.
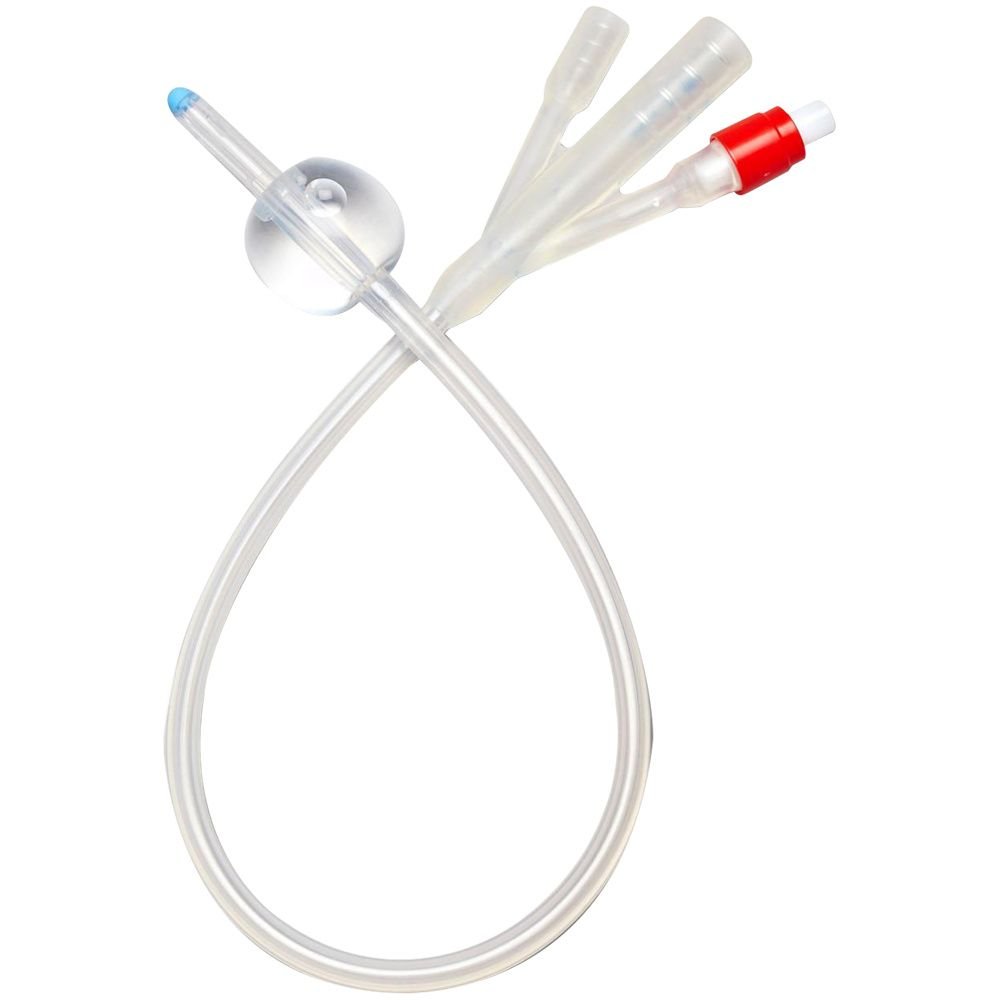
TRI-CHANNEL SELF-RETAINING FOLEYS CATHETER
Identification:
The following supplied item is a tri-channel self-retaining Foyel’s catheter.
Made:
Made by rubber.
Parts:
A. Three channels:
a) Oblique channel: For introducing distilled water to inflate the balloon.
b) Middle channel: For drainage of urine which latter connects with an urobag
c) Third channel: For continuous irrigation of urinary bladder by normal saline.
B. Balloon: Situated near the tip
Uses/Importance/Function:
1. After prostatectomy operation.
2. Any haemorrhagic condition of urinary bladderent
3. To introduce fluid or normal saline into the bladder to prevent blood clotrigor
4. For continuous irrigation
5. For drainage of urine
6. In vesicoveginal fistula operation.
Sterilization:
It is sterilized by gamma ray
PLAIN RUBBER CATHETER
Identification:
The following supplied item is plain rubber catheter
Made:
Made by rubber

Uses/Importance/Function:
1. In case of retention of urine to evacuate the bladder
2. In case of children used as Ryles tube for nasogastric suctions60
3. As a tourniquet for haemostasis
4. For oxygen inhalation (when oxygen musk is not available used as airway tube)
5. For suction clearance of oropharyngeal cavity
Sterilization:
It is sterilized by gamma ray
MALECOT’S RUBBER CATHETER
Identification:
The following supplied item is a Malecot’s rubber catheter.

Uses/Importance/ Function:
1. Supra pubic cystectomy: Rupture of the urethr
2. To give water seal drainage
a) Haemothorax
b) Haemo-pneumothorax
c) Pneumothorax
d) Empyema thoracis
3. Used as a drain for appendicular abscess
4. In gastrectomy for feeding
SPONGE HOLDING FORCEPS
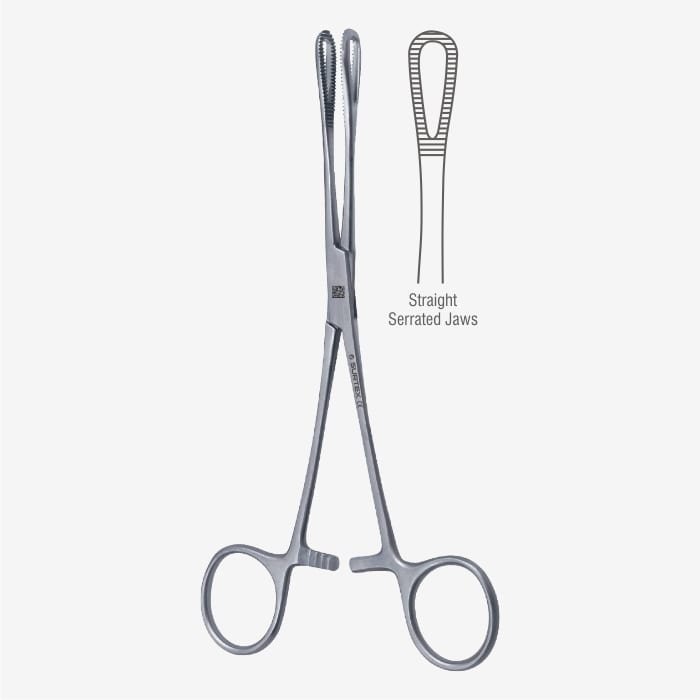

Specifications
- A heavy metal instrument 23 to 75 cm in length.
- Shafts are thin and blades are fenestrated.
- Has a catch-lock, which gives firmness while holding any material.
- Has ring shaped tips, which may be serrated or smooth
Uses
- Used for cleaning the operative field.
- Used for swabbing or packing body cavities like vagina.
- Can be used to catch hold of soft organs like ovary and cervix in pregnancy.
- Can be substituted in the place of an ovum forceps.
- Used for deep moping to clear the area during surgery.
KOCHER’S HAEMOSTATIC FORCEPS
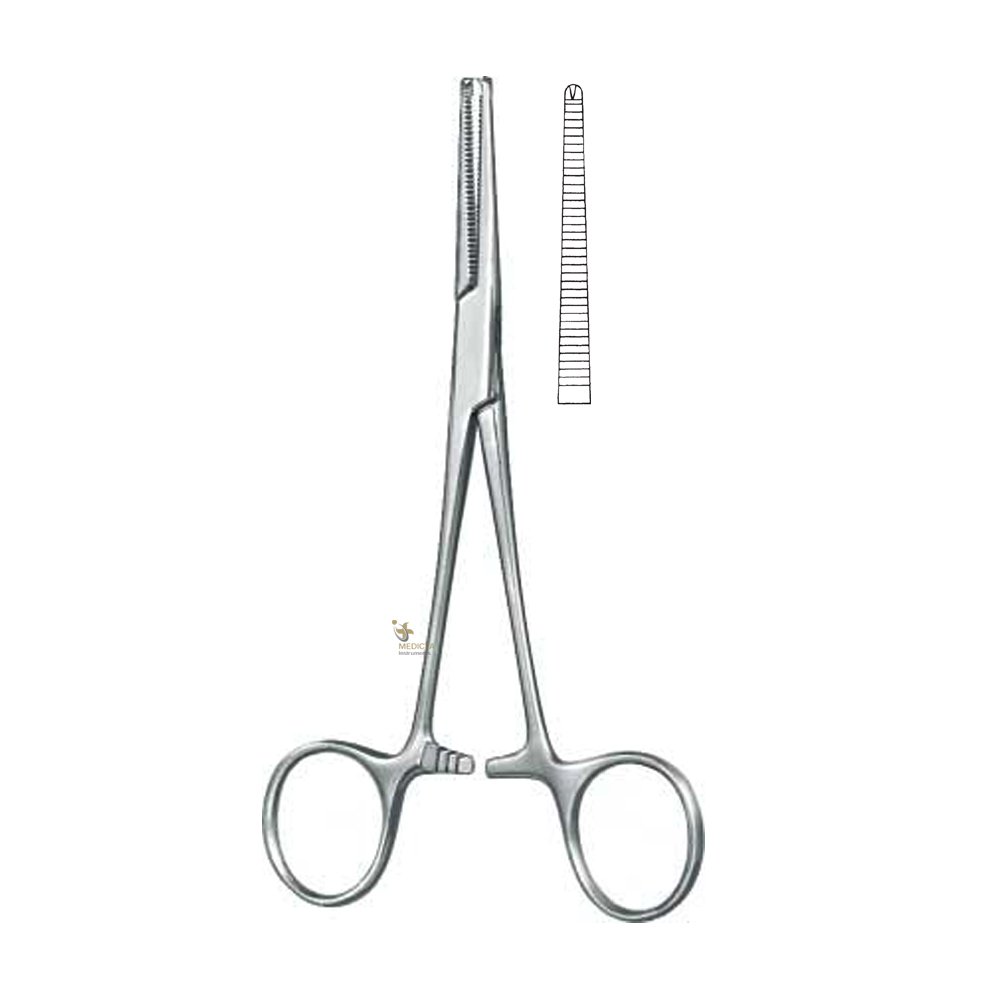
Specifications
- A strong, straight metal instrument.
- Has a catch-lock to bring the blades together for locking.
- Inner surface of both blades are transversely serrated.
- It may be straight or curved.
- Single toothed at distal end.
Uses
- Used to catch the edges of the incision while suturing skin,
- Used for artificial rupture membranes.
- Used to clamp the umbilical cord.
HAEMOSTAT (ARTERY FORCEPS)
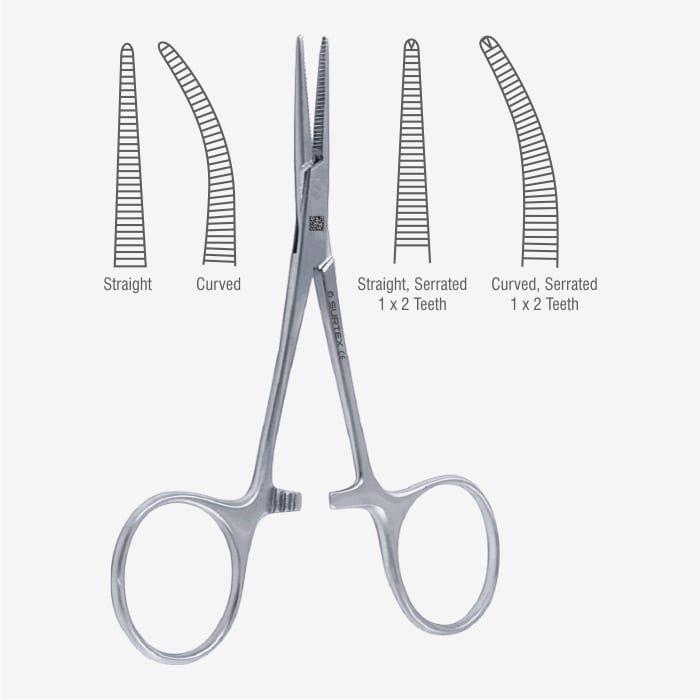
Specifications
- Artery forceps may be small or mosquito, straight or curved, strong metal instrument.
- Medium or large in size.
- Blades are tapering to the distal end but blunt.
- Has a catch-lock to bring the blades together and to lock it.
- Inner surface of the blades are transversely serrated and when locked, the blades are well in apposition.
- Blades are roughly half the size of the handle.
Uses
- Used to stop bleeding by catching the blood vessel.
- Used as a clamp for pedicles of internal organs like kidney, spleen, ligaments of uterus, etc.
- Used to enlarge the opening of an abscess in the absence of a sinus forceps.
- Can be used to substitute a needle holder.
- Used to hold the incised edges of skin and fascia.
- Used to hold the free ends of sutures at the beginning of suturing and to hold the cut ends of tension sutures before tying.
- Used to hold the tape of abdominal pads or sponges during surgeries to prevent them missing in the cavity.
- Mosquito forceps are used to hold the small bleeding points.
- Used for blunt dissection by holding swabs.
OVUM FORCEPS

Specifications
- A moderately heavy metal instrument having cupped blades with linear fenestrations.
- The size and type of blades can hold a reasonable amount of tissues in between with good grip.
- The length is about 30 cm.
Uses
- Used for removing products of conception from the uterus in incomplete abortion
- Used to remove any foreign body from the uterine cavity, e.g. intrauterine device when threads are broken.
- Used to remove any retained placental bits or membrane pieces from the uterus after delivery.
VULSELLUM FORCEPS
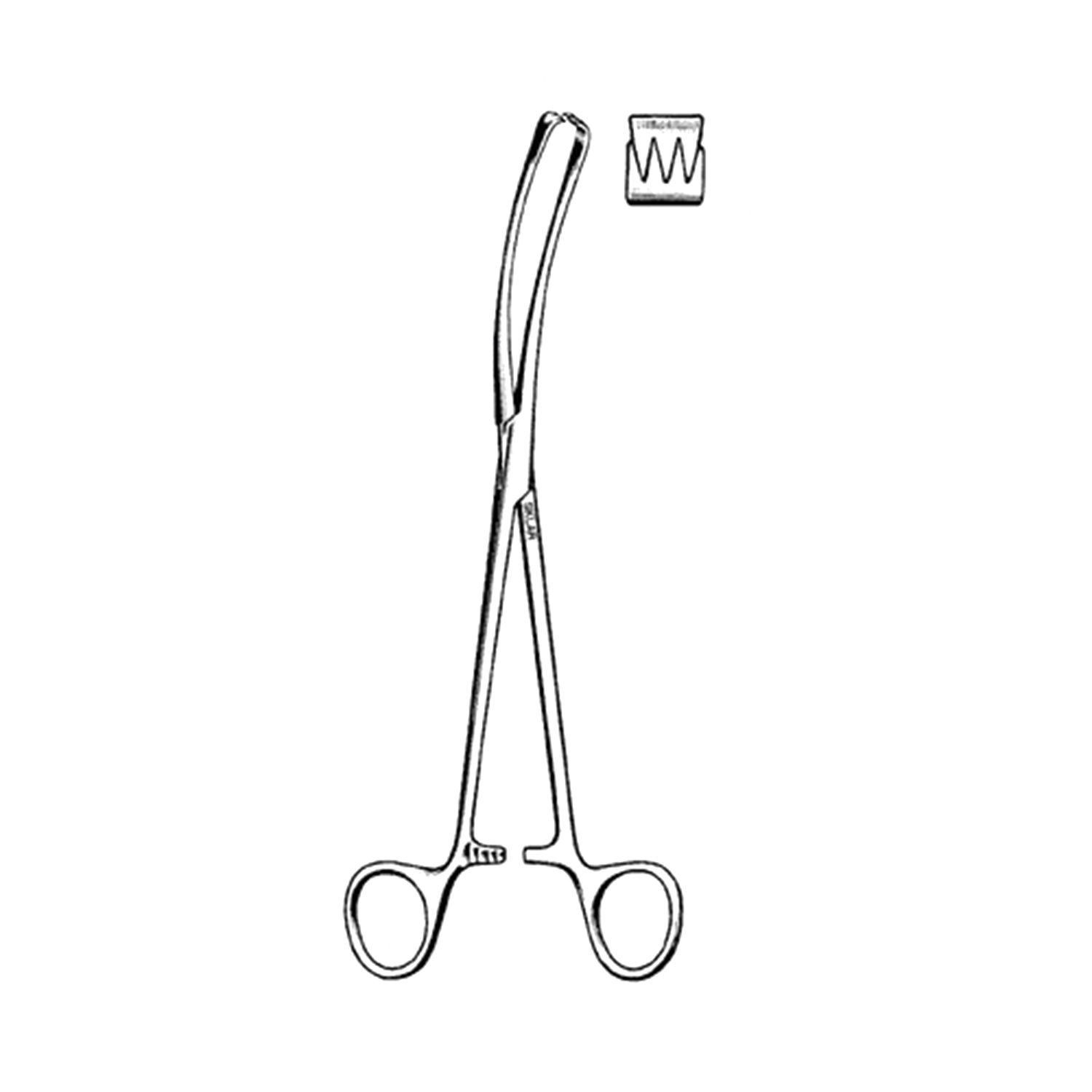
Specifications
- An average sized metal instrument resembling forceps at the distal end.
- The proximal end has a lock for fixing and distal end has multiple sharp teeth for firm grip.
- The curvature of blades helps to retract the anterior vaginal wall when the instrument is pulled up after holding the cervical lip for better visualisation.
Uses
- Used for holding the anterior or posterior lip of cervix in operations like dilatation and curettage (D & C) and cauterisation of cervix.
- Used to test the mobility of cervix and laxity of ligaments in prolapse of uterus.
- Used to bring down the fundus of uterus in vaginal hysterectomy.
- Used to hold the cervical lip for procedures like tubal insufflation or introduction of laminaria tent.
UTERINE PACKING FORCEPS/UTERINE DRESSING FORCEPS.
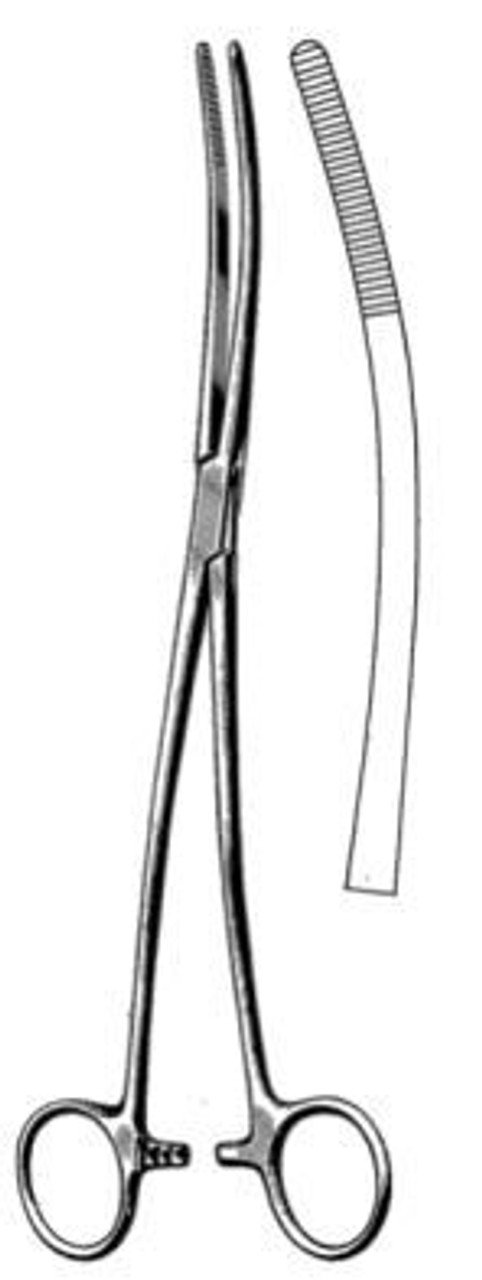
Specifications
- A curved forceps about 35 cm in length, the curvature corresponding to axis of birth canal for easy packing.
- Has blades, handles and finger bows.
- The blades are provided with slight groves on inner surfaces.
Uses
- Used for vaginal packing to control bleeding from lacerations in birth canal due to trauma.
- Used to swab uterine cavity following dilatation and evacuation with small gauze pieces.
- Used to pack the uterine cavity following D and C or delivery to control bleeding.
Used for application of drug into the uterine cavity.
ANTERIOR VAGINAL WALL RETRACTOR
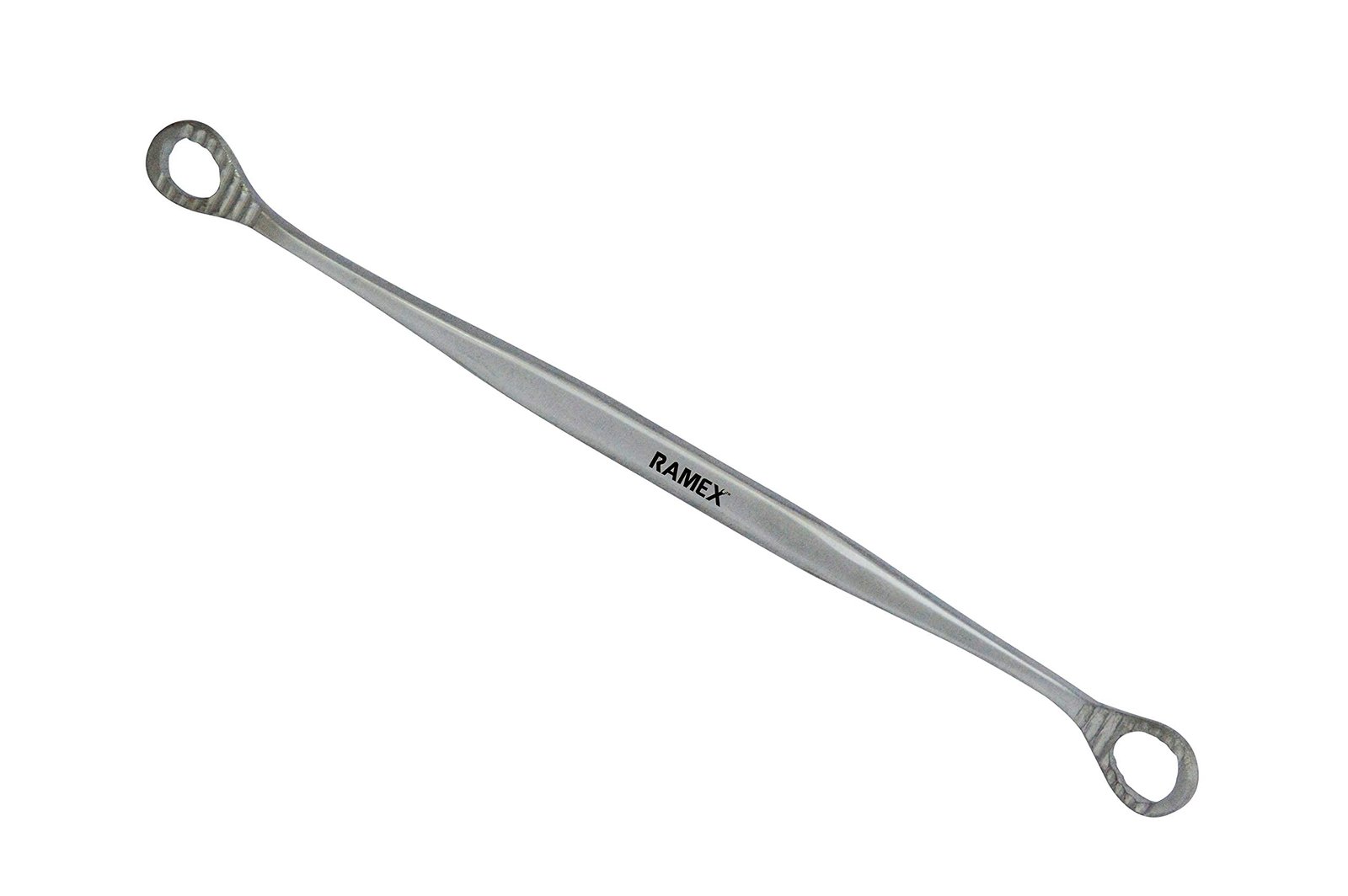

Specifications
- A metal instrument with two oval shaped and fenestrated ends.
- The fenestrated end has transverse serrations.
- The oval shaped ends are connected at an angle of 45° to both ends of the shaft.
Uses
- It is used with Sim’s speculum to retract the anterior vaginal wall for exposing the cervix and anterior fornix.
SIMS’ DOUBLE BLADED VAGINAL SPECULUM
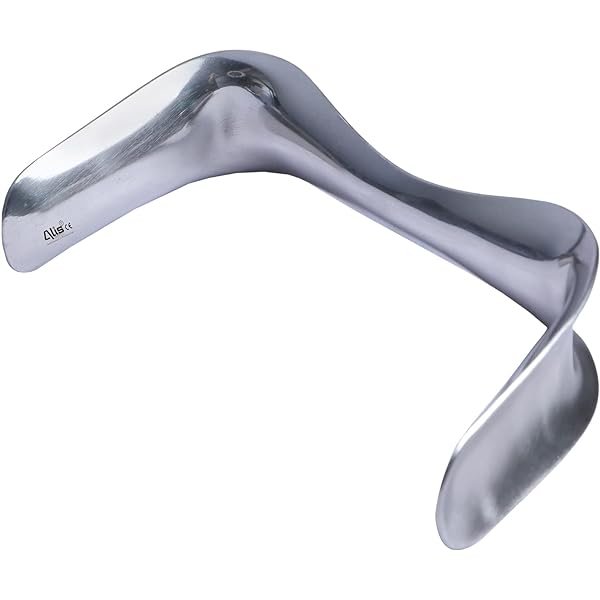

Specifications
- A moderately heavy metal instruments.
- It has two thick blades of unequal breadths to facilitate introduction according to the size of vagina.
Uses
- Sims Speculum is used for inspection of vagina and cervix in the OPD. It retracts posterior vaginal wall
- Use in Gynae OPD for following procedures:
✓ Taking Pap Smear,
✓ Insertion and removal of Copper T,
✓ Colposcopy,
✓ Taking swabs,
✓ Hyseterosalpingography (HSG)
- Use in Gynae Operations:
✓ D&C,
✓ Cervix Biopsy,
✓ Vaginal Hysterectomy,
✓ Fothergills Operation,
✓ Repair of Vesico vaginal fistula,
✓ Hysteroscopy.
- Use in Obstetrics:
✓ For inspection (Bluish discoloration in early pregnancy, local cause for threatened abortion, local cause in APH),
✓ First trimester MTP by suction curettage.
✓ In second trimester MTP by Ethacredyl Lactate.
✓ Os thightening or cervical encircalage,
✓ Removal of os thightening stitch at the onset of labor or at 38 wks.
✓ Inspection for suspected rupture of membranes.
CUSCO’S BIVALVED SPECULUM.
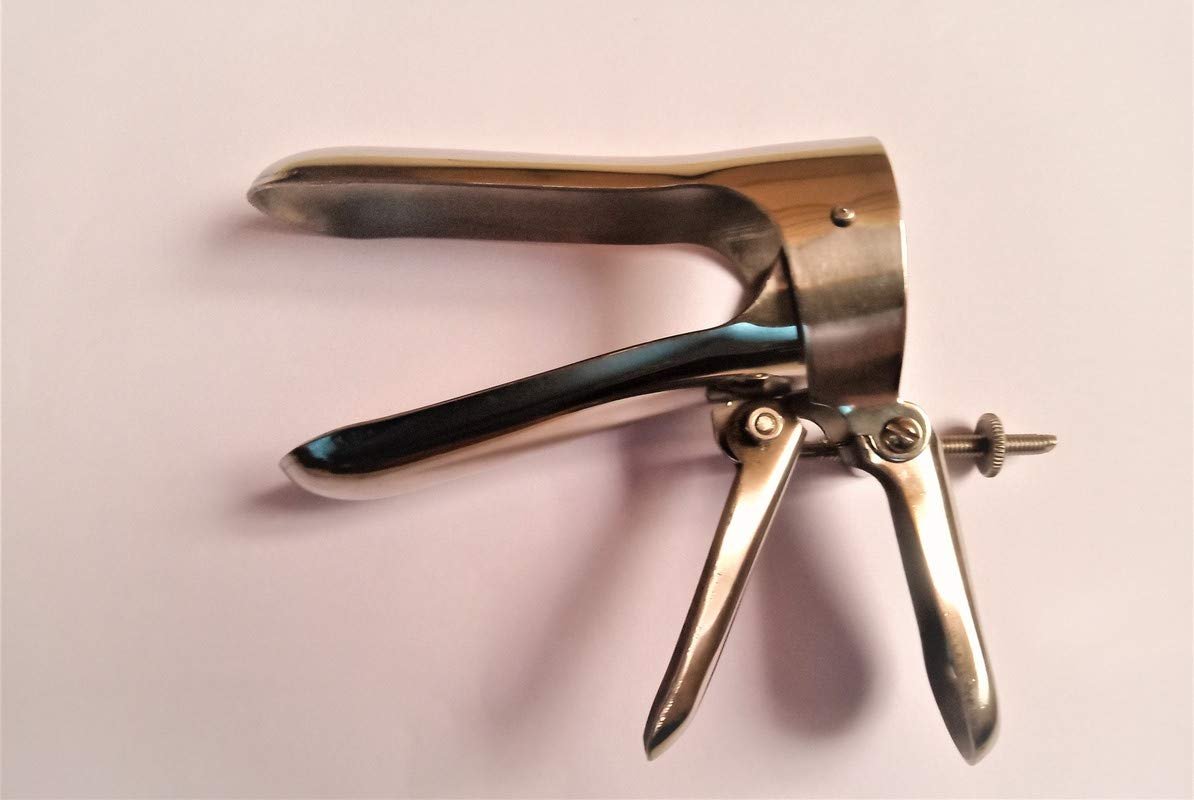

Specifications
- A self-retaining speculum with a special screw arrangement.
- It has two blades, which can be opened laterally and adjusted, at various angles by adjusting the screw after introducing in the vagina.
- It is introduced into the vagina with its blades closed in vertical position and then made horizontal, opened and locked in position. It can be closed and rotated further and opened again to see other sides of vagina after locking in required position.
Uses
- Can be used without any assistance.
- Used to visualise or inspect vagina and cervix.
- Can be used without bringing the patient to the edge of bed.
- Used in insertion of intrauterine contraceptive device.
- Used to reach into the cervix to apply medications, to take swabs for culture and sensitivity, to get biopsy specimens and to do electrocautery in the cervix.
DREW SMYTHE CATHETER (MEMBRANE PERFORATOR
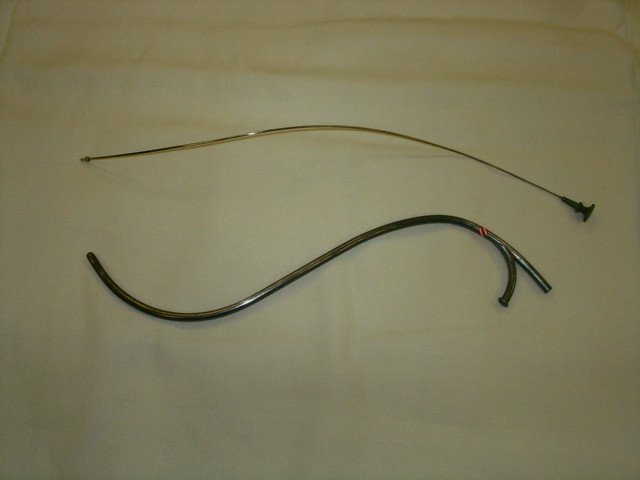

Specifications
- It is an S-shaped, double curved metal catheter with a blunt stilet.
- It has two openings-one inlet and one outlet, and double tube-one inner tube and one outer
tube.
Uses
- It is used for high rupture of membranes in hydramnios.
- It allows controlled escape of liquor amni through it..
- It can be passed between the membranes and uterus some length before puncturing.
- The high rupture of membranes accomplished preserves the dilating effect of bag of waters and reduces the chances of infection and prolapse of the cord.
SCISSORS
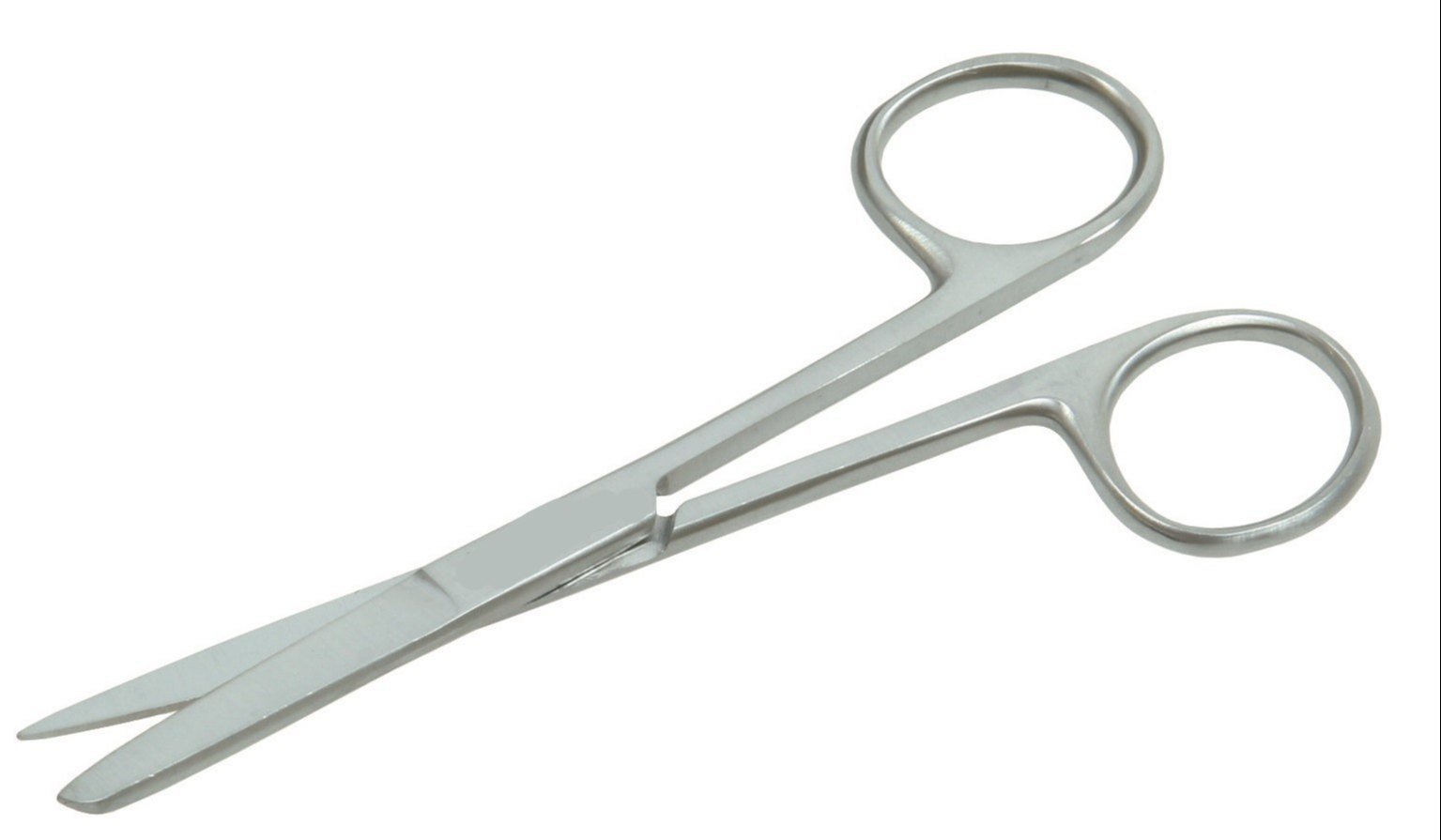

Specifications & USES
- Scissors are used for blunt or sharp dissection.
- Straight or curved Mayo scissors, which are very smooth at the ends, are sued to cut the tissues and internal organs so that adjacent tissues are protected while using.
- Episiotomy scissors are used for cutting the perineum to enlarge the vaginal opening to deliver the foetal head.
- Umbilical cord cutting scissors with broad rounded end are used for cutting umbilical cord.
