Obstetric operations – This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
Obstetric operations
Obstetric operations:
1. Caesarean section.
2. Episiotomy.
3. Ventouse delivery.
4. Forceps delivery.
5. Version.
6. Amniocentesis.
7. Artificial rupture of the membranes
8. Destructive operations:
➤ Craniotomy.
➤ Evisceration.
➤ Decapitation.
➤ Cleidotomy.
9. Repair of the cervical tear.
10. Repair of the perineal tear.
[Ref-D. C. Dutta’s Obs/9h/524]
Prerequisite of obstetric operation:
1. Written informed Consent.
2. Catheterization: Bladder should be emptied before operation.
3. P/V examination is done in most of the cases prior to the operation for position, presentation, station, show, condition of the membranes etc.
4. Per-abdominal examination prior to the operation for FHS or FHR.
5. Position: Lithotomy position/supine position.
6. Anaesthesia:
➤ Local infiltrative anaesthesia.
➤ General anaesthesia.
➤ Spinal anaesthesia.
7. Full surgical asepsis:
➤ Surgeon is to wear sterile mask, gown and gloves.
➤ Aseptic wash of the operative area.
➤ Draping by sterile towel.
[Ref-D. C. Dutta’s Obs/9h/524]
Anaesthetic hazards in obstetrics:
Hazards of epidural anesthesia:
1. Hypotension due to sympathetic blockade.
2. Patient should be well hydrated with crystalloid solution before operation.
3. Pain at the insertion site. Post spinal headache due to leakage of cerebrospinal fluid through the needle hole in the dura.
4. Total spinal due to inadvertent administration of the drug in the subarachnoid space.
5. Injury to nerves.
Hazards of spinal anaesthesia:
1. Hypotension
2. Vasodilatation and low cardiac output.
3. Respiratory depression may occur.
4. Post-spinal headache due to low or high CSF pressure and leakage of CSF.
5. Meningitis due to faulty asepsis.
6. Transient or permanent paralysis.
7. Toxic reaction of local anesthetic drugs.
8. Nausea and vomiting are not uncommon.
9. Urinary retention.
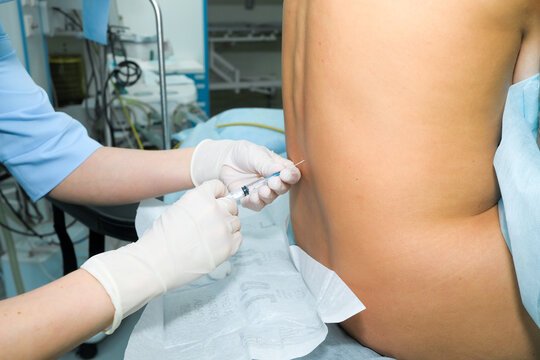
Hazards of general anesthesia:
1. Aspiration of gastric content.
2. Cardiac arrhythmia.
3. Hypotension.
4. Laryngospasm and asphyxia.
5. Persisting sedation.
6. Nerve palsies.
7. Pneumonia.
8. Failure in intubation and ventilation.
9. Nausea, vomiting.
10. Sore throat
