Omphalocele or Exomphalos – Health of the children has been considered as the vital importance to all societies because children are the basic resource for the future of humankind. Nursing care of children is concerned for both the health of the children and for the illnesses that affect their growth and development. The increasing complexity of medical and nursing science has created a need for special area of child care, i.e. pediatric nursing.
Pediatric nursing is the specialized area of nursing practice concerning the care of children during wellness and illness. It includes preventive, promotive, curative and rehabilitative care of children. It emphasizes on all round development of body, mind and spirit of the growing individual. Thus, pediatric nursing involves in giving assistance, care and support to the growing and developing children to achieve their individual potential for functioning with fullest capacity.
Omphalocele or Exomphalos
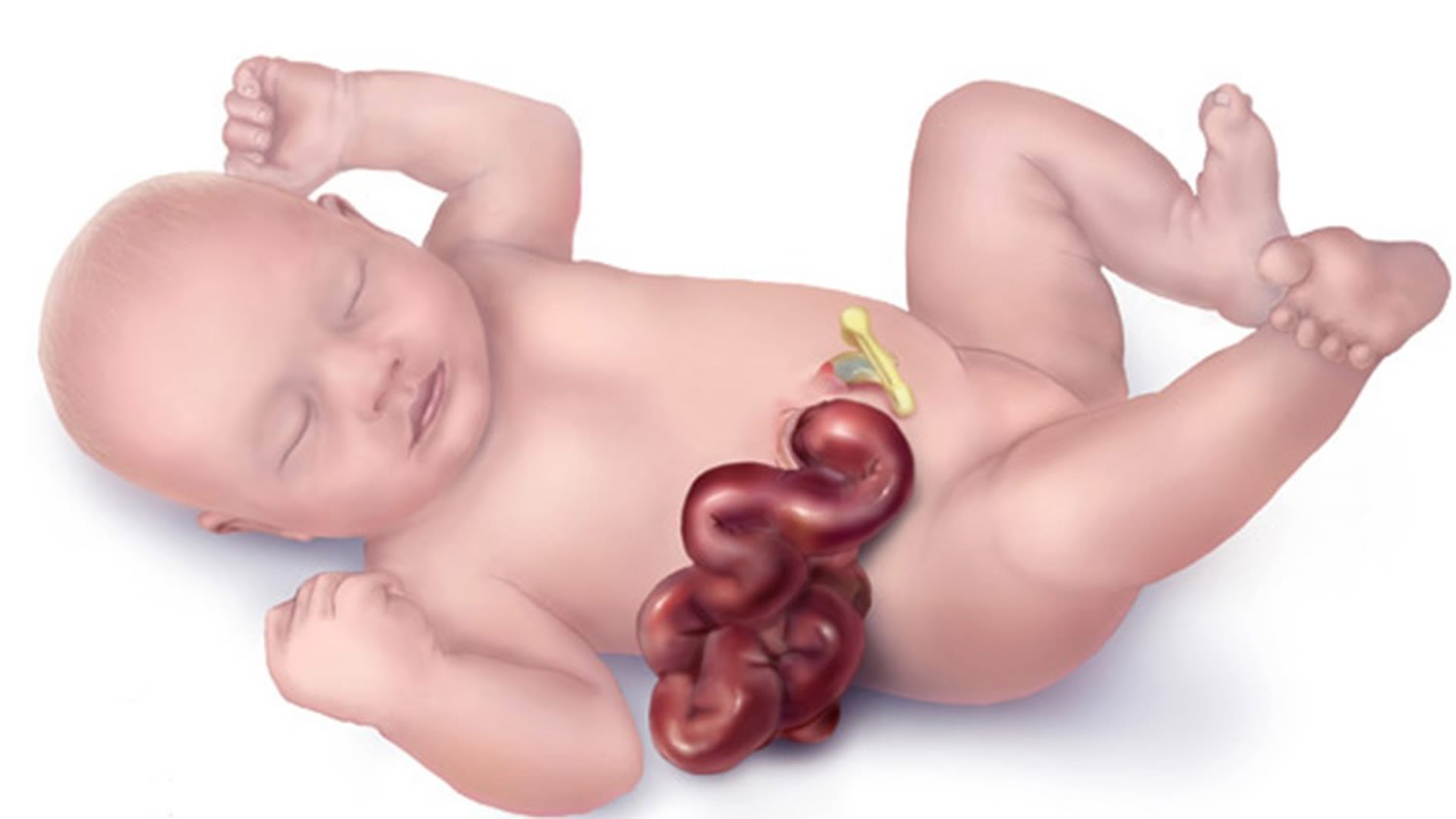
Exomphalos is the herniation of the abdominal organ through a wide open umbilicus.
[Ref-Paediatric Nursing, Parul Datta/3/294]
Or
A birth defect in which part of the intestine, covered only by a thin transparent membrane, protrudes outside the abdomen at the umbilicus.
Or
[Ref-www.medicinenet.com/]
Omphalocele, also spelled omphalocoele, is a rare abdominal wall defect in which the intestines, liver and occasionally other organs remain outside of the abdomen in a sac because of failure of normal return of intestines and other contents back to abdominal cavity during around ninth week of intrauterine development.

Risk For Developing An Omphalocele:
Many babies born with an omphalocele also have other abnormalities.
1. Thirty percent have a genetic abnormality, most commonly Trisomy 13, Trisomy 18, Trisomy 21, Turner syndrome or triploidy.
2. Some infants with omphalocele have a syndrome known as Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome.
3. More than half of babies with omphalocele have abnormalities of other organs or body parts, most commonly the spine, digestive system, heart, urinary system and limbs.
Causes of Omphalocele:
1. The causes of omphaloceles are unknown.
2. Pregnant women who consume alcohol.
3. Heavy smokers.
4. Take antidepressant medications called selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
5. Overweight or obese before pregnancy.
6. Genetic problems such as chromosomal abnormalities.
Management Of Omphalocele:
1. The definitive management of the defect is done by surgical repair of the abdominal wall and reposition of the herniated contents into the peritoneal cavity.
2. Surgery can be done in stages depending upon the size of the defect.
Preoperative management: It should include –
1. Nasogastric tube aspiration to prevent intestinal distention.
2. Covering of sac and its contents by sterile plastic sheet directly to prevent evaporative loss of fluid.
3. Wet saline sponges should not be used to cover the sac.
Supportive measures:
It should include-
1. IV infusion.
2. Warmth.
3. Breast feeding.
4. Oxygen therapy & mechanical ventilation,
5. Basic preoperative and postoperative care nursing care same as abdominal surgery. if required to be provided along with routine
6. Note: Prognosis depends upon severity of associated anomalies.
Therapeutic Management Of Gastroschisis/Omphalocele:
1. I/V and NG tubes are placed immediately.
2. Total parenteral nutrition is provided.
3. Synthetic material (Silastic) is used to cover the gut in a sac (if the sac has ruptured or large)
4. The defect is closed surgically after all contents have been returned to the abdominal cavity.
5. Even if the defect is small, immediate surgical repair may be done in several stages.
6. If the condition is diagnosed prenatally, surgical delivery is recommended
7. Necrotic bowel may need to be removed surgically.
Nursing Care Of Gastroschisis/Omphalocele:
1. Use warmers and monitor the child’s temperature.
2. Use sterile technique in dealing with the defect. Immediately cover with warm most sterile.
3. Minimize movement of the infant and handling of the intestines.
4. Assess circulatory compromise, obstruction, sepsis: monitor temperature, pulses, skin color, changes in respiratory pattern, heart rate.
5. Observe for respiratory distress secondary to secondary to high intra-abdominal pressure as the gut returns to the peritoneal cavity.
6. Monitor intake and output, daily weights, assess fontanels, monitor electrolytes and maintain UV line.
7. Postoperatively, monitor and manage ileus, maintain nasogastric tube decompression,
monitor
8. Provide emotional support for parents as they deal with the loss of the perfect child’s.
9. Encourage patients to provide care as they are able, talk to and touch infant and hold the infant, when appropriate.
[Lecture/B. A. Siddikey NI
Complications of Omphalocele:
Omphalocele may be complicated with-
1. Rupture of sac.
2. Evisceration of bowel loops.
3. Sepsis.
4. Hypothermia.
5. Hypovolemia (due to evaporative water loss).
[Ref-Paediatric Nursing, Parul Datta/34/294)
(Another answer)
1. Poor lung development
2. Intestines that are slow to handle food
3. Heart malformations (20 percent)
4. Beckwith-Wiedeman Syndrome (a condition typified by a large tongue, high insulin and low blood sugar)
5. Chromosomal abnormalities
