Open Fracture- An orthopedic nurse is a nurse who specializes in treating patients with bone, limb, or musculoskeletal disorders. Nonetheless, because orthopedics and trauma typically follow one another, head injuries and infected wounds are frequently treated by orthopedic nurses.
Ensuring that patients receive the proper pre-and post-operative care following surgery is the responsibility of an orthopedic nurse. They play a critical role in the effort to return patients to baseline before admission. Early detection of complications following surgery, including sepsis, compartment syndrome, and site infections, falls under the purview of orthopedic nurses.
Open Fracture | CHAPTER 5 | Orthopedic Nursing
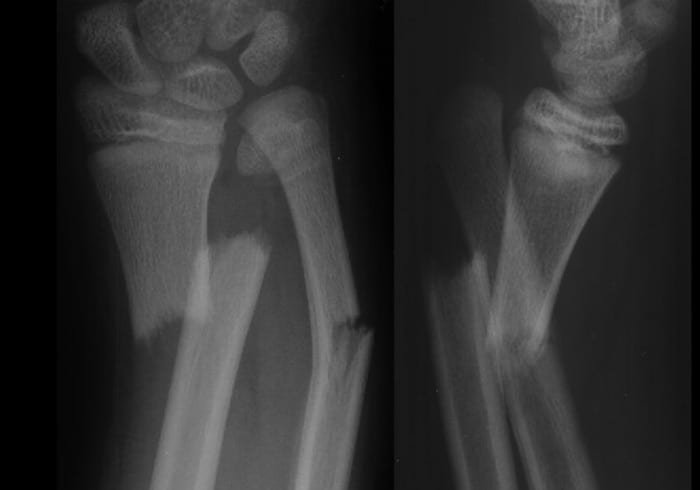
Compound or open fracture:
Fracture which communicates with external air is called compound or open fracture.
[Ref-John Ebnezar, Text Book of Orthopedic, 4th edition, Page-23]
Or
It is a definitive type of fracture which communicates with the external atmosphere due to break in the soft tissue cover.
[Ref-Luckmann and Sorensen, Medical and Surgical nursing, 2nd edition, Page-1685]
Classification of compound fracture:
A) According to GUSTILLO and ANDERSON s classifications:
1) Type-I:
- Caused by low velocity trauma.
- Wound size < 1 cm.
- Less or no contamination.
- Less soft tissue injury.
- Good prognosis.
1) Type II:
- Caused by high velocity trauma.
- Wound size 1-10 cm
- Slightly contaminated.
- Some soft tissue injury.
2) Type III:
- Wound may moderate or severe and size become 10 cm. Soft tissue are devitalized and contaminated.
i) Type III A:
- Extensive soft tissue injury.
- Adequate soft tissue cover the bone.
- No bony exposure.
ii) Type III B :
- Extensive soft tissue injury.
- Bone exposed to atmosphere.
- Periosteal stripping.
iii) Type III C: Any type of open fracture associated with vascular damage.
(Ref-John Ebnezar, Text Book of Orthopedic, 4th edition, Page-23)
B) Another classifications:
1) From within: End of the fracture bone come out by the penetrating the skin.
2) From without: Open injury of skin and soft tissues caused by trauma and the fracture communicates with external air.
Clinical fractures of open fracture:
A) History of patients :
1) Patients give H/O direct or indirect trauma. E.g. fall, RTA, Physical assault.
B) Symptoms:
1) Severe pain at the site of fracture.
- Pain increase on movement of injured part.
- Pain may absent immediately after shock or impaired nerve functions
2) Swelling: Swelling may appear rapidly as a result of localizations of serous fluid.
3) Deformity: Patient may unable to move affected part.
4) Loss of functions: Patient can not use the limbs as before.
C) Signs:
1) Inspection of the injured limb:
a) Compare with healthy side.
mayo Anamagsaam svileng
b) General condition of the patients.
c) Facial expression – on pain scale.
d) Swelling-diffuse.
e) Anaemia of patients- due to blood loss (Open fracture)
f) Tongue-dry in case of blood loss.
g) Mental condition of the patients.
h) Is a patient in shock?
2) Palpation on the injured limb:
a) Tenderness-pain on touch of the injured limb.
b) Swelling- Size,shape consistency, fluctuations.
c) Abnormal mobility- occurs in fracture but mobility only possible in the joint.
d) Bony crepitus-grating sound may be felt or heared due to movement at site of injury.
e) Echymosis-bruising due to subcutaneous bleeding.
f) Palpate the vascular supply of the distal part:
- Palpate radial pulse in upper limb injury.
- Palpate posterior tibial artery in lower limb
Causes of open fracture: Open fracture are usually serious injuries and are due to high velocity trauma,
1) RTA (road traffic accident)
2) Car crash.
3) Falls from height.
4) Sports injuries.
5) Poliyical violence
6) Industrial accident during working in factory.
7) Drop of stone or rods up of the body.
First aid management of open fracture:
Please add from first aid management of fracture.
Aims of management open fracture:
1) To convert a contaminated wound into a clean wound.
2) To prevent the hypovolumic shock.
3) To prevent infection.
4) To establish re-union of the bone.
5) To convert open to closed fracture.
[Ref-John Ebnezar, Text Book of Orthopedic, 4th edition, Page-24]
Social consideration:
1) To stabilize the general condition of the patients. From shock. it consists of, resuscitation, BT, I/V fluid, oxygen administration, antibiotics.
2) To keep the fracture part near the correct position by immobilization technique.
3) To keep the wound covered with proper sterile bandage till patients is ready for surgery.
4) Operative management: open fracture is a surgical emergency.
[Ref-John Ebnezar, Text Book of Orthopedic, 4th edition, Page-24]
Medical management of a open fracture:
A) Initial management:
1) Removal of all dirty clothing from the patients body.
2) Assess vital signs quickly-pulse, BP, respiration, temperature.
3) Check for ABC (airway,breathing,circulation)
4) Assess the GCS (Glasgow coma scale) of patients.
5) Immobilize the wound by plaster/splints.
6) Stop the external bleeding by proper bandaging.
7) Clean the wound aseptically if there is any dirty things clean with normal saline.
9) Assess the signs and symptoms of shock..
8) Opening an intravenous line and give i/v fluid to prevent hypovolaemia.
10) Examining the other vital structure-head, neck chest pelvis etc.
11) Tetanus prophylaxis: TT and TIG is given to in two hands to protect from tetanus.
12) Analgesics -to reduce pain
13) Prepare the patients for operation.
B) Preoperative management:
1) Explain the benefits of operation.
2) Give mental support.
3) Investigations are carried out to detect any other problems of patients.
4) Clean the operative area if hair present.
5) Take written consent from patients or attendants.
C) Operative treatment: After stabilization of the patient, operative treatment should be done.
1) Surgical toileting: After exposing the injured area, wound is thoroughly washed with normal saline
or Hydrogen peroxide.
2) Debridement : All devitalized tissues and dirty materials are should be cleaned.
a) Exploration of the wound: The wound should be sufficiently explored proximally and distally to have a proper assessment of the extent of the damage.
b) Excision of the non viable structure:
i. Skin: here the plan is to excise all dead skin.
ii. Muscle: Non viable muscle should be removed.And viability of muscle depend on color, consistency, capacity to bleed, circulation, contractility.
iii.Nerves and vessels: nerve and vessels repair is done if the wound is clean.
iv. Evacuation of the foreign body: Like dirt, glass, stones and foreign bodies are removed
3) Reduction: Internal fixation when indicated.
4) External immobilization: POP
5) Primary amputation.
[Ref-John Ebnezar, Text Book of Orthopedic, 4th edition, Page-25 +Dr.Jahir, Surgery(P-1),4th edition,538]
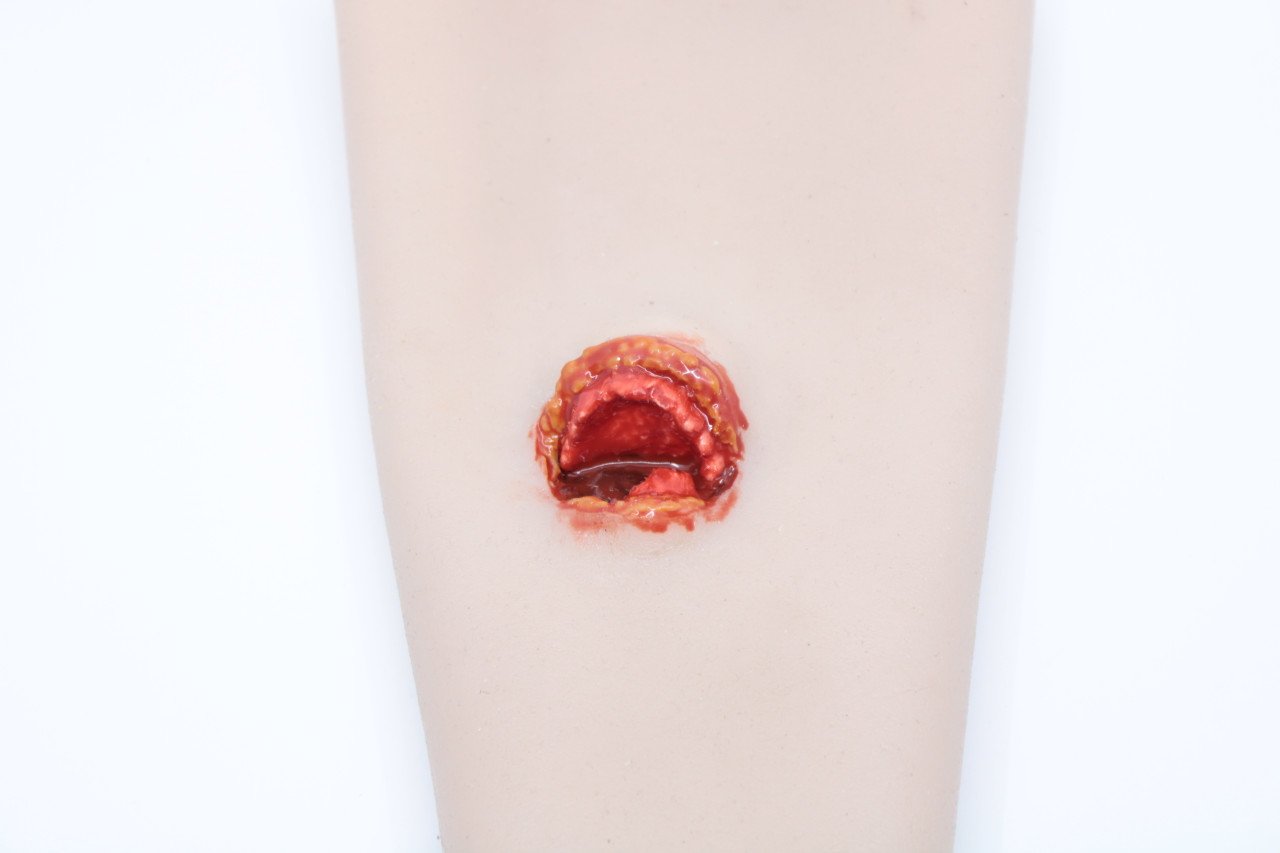
Complications of open fractures:
1) Haemorrhage.
2) Hypovolumic shock.
3) Tetanus.
4) Gas gangrene.
5) Septicaemia.
6) Pyaemia.
7) Chronic osteomyelitis.
8) Non-union, malunion, delayed union.
9) Joint stiffness.
10) Disabilities.
[Ref-John Ebnezar’s “Textbook of Orthopedics” 4th edition page-26+Appleys, Systems of orthopedic and fracture]
Please add from nursing management of a fracture patients (Above given)
a) Immediate care of open fracture patients:
1) Removal of all dirty clothing from the patients body.
2) Assess vital signs quickly-pulse,BP, respiration, temperature.
3) Check for ABC (airway,breathing,circulation)
4) Assess the GCS (Glasgow coma scale) of patients.
5) Immobilize the wound by plaster/splints.
6) Stop the external bleeding by proper bandaging.
7) Clean the wound aseptically if there is any dirty things clean with normal saline.
8) Opening an intravenous line and give i/v fluid to prevent hypovolaemia.
9) Assess the signs and symptoms of shock..
10) Examining the other vital structure-head, neck chest pelvis etc.
11) Tetanus prophylaxis: TT and TIG is given to in two hands to protect from tetanus.
12) Analgesics -to reduce pain
13) Prepare the patient for operation.
b) Complications: please see above.
c) Importance of TT & TIG: Due to open fracture there is a chance of infection. Again if skin is cut by dirty, unsterile, soil contaminated instruments there is a chance of invasion of bacteria, specially clostridium tetani. And this bacteria is the main culprit for causing tetanus.
TT injection giving long time protection and TIG giving immediate protection from tetanus. That’s why TT, TIG is given in open fracture patients to protect the patients from development of Tetanus.
d) Primary amputation: Primary amputation is not indicated in the open fracture but it will be done when –
1)Type III C injury:
a) Wound size >10 cm.
b) Extensive soft tissue injury.
c) If the warm ischaemia more than 6 hours,
2) Vascular and neural injury.
