Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) – Health of the children has been considered as the vital importance to all societies because children are the basic resource for the future of humankind. Nursing care of children is concerned for both the health of the children and for the illnesses that affect their growth and development. The increasing complexity of medical and nursing science has created a need for special area of child care, i.e. pediatric nursing.
Pediatric nursing is the specialized area of nursing practice concerning the care of children during wellness and illness. It includes preventive, promotive, curative and rehabilitative care of children. It emphasizes on all round development of body, mind and spirit of the growing individual. Thus, pediatric nursing involves in giving assistance, care and support to the growing and developing children to achieve their individual potential for functioning with fullest capacity.
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
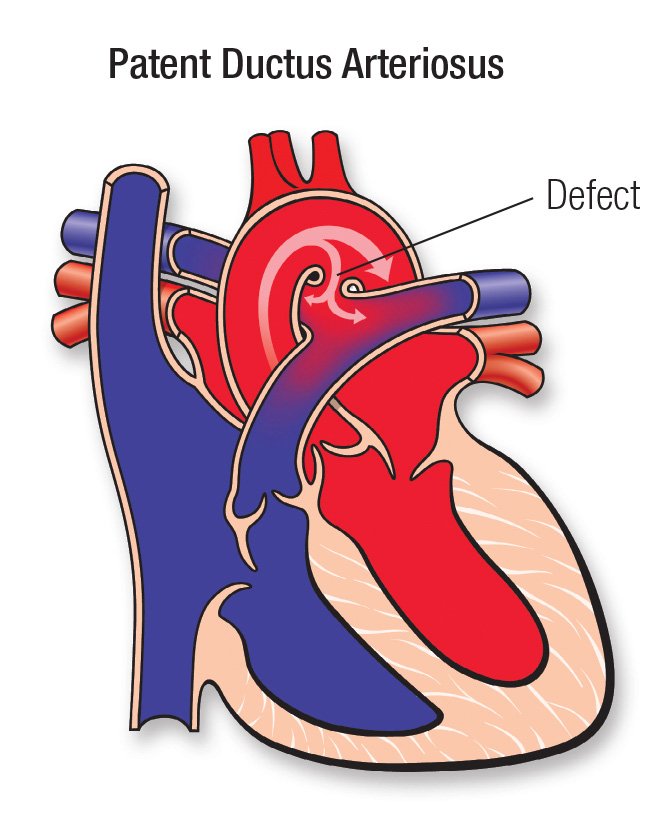
Definition of Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA):
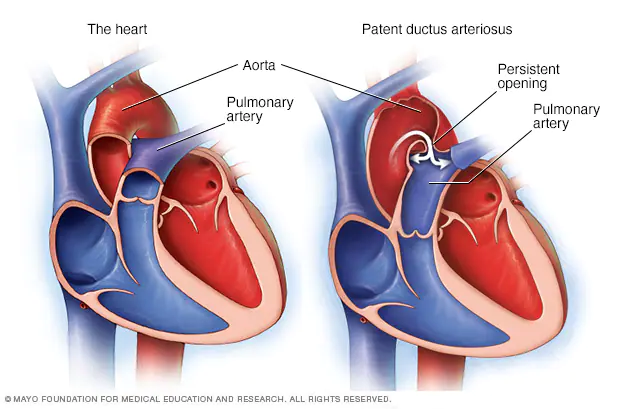
Jenior table du Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a persistent opening between the two major blood vessels leading from the heart. The opening (ductus arteriosus) is a normal part of a baby’s circulatory system in the womb that usually closes shortly after birth. If it remains open, it’s called a patent ductus arteriosus.
Clinical Features:
Symptoms:
- With small shunts there may be no symptoms for years.
- When the ductus is large, growth and development may be retarded.
- Dyspnoea on exertion being the first symptom.
- Fatigue.
Signs:
- Visible cardiac impulse
- Heaving apical impulse.
- A continuous ‘machinery’ murmur is heard with late systolic accentuation, maximal in the 2nd left intercostals space below the space below the clavicle.
- It is frequently accompanied by a thrill
- Pulses are increased in volume.
Investigations
ECG
✓ Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH).
✓ If pulmonary hypertension – RVH.
Chest X-ray P/A view:
✓ Increased pulmonary vascular markings, enlarged main pulmonary artery artery & left ventricle.
Echocardiography:
✓ Hyperdynamic, enlarged left ventricle.
✓ Doppler echo demonstrates abnormal flow through it.
Treatment:
Pharmacological treatment in neonatal period:
- A prostaglandin synthetase inhibitor (indometacin or ibuprofen) may be used in the first week of life to induce closure.
- Closure of PDA by cardiac catheterisation with an implantable occlusive device.
- Closure should be undertaken in infancy if the shunt is significant and pulmonary resistance not elevated. .
- Can be surgically ligated or divided.
(Ref-M.R. Khan-290/3rd+Davidson’s-631/22