Roles of the pediatric nurse – Health of the children has been considered as the vital importance to all societies because children are the basic resource for the future of humankind. Nursing care of children is concerned for both the health of the children and for the illnesses that affect their growth and development. The increasing complexity of medical and nursing science has created a need for special area of child care, i.e. pediatric nursing.
Pediatric nursing is the specialized area of nursing practice concerning the care of children during wellness and illness. It includes preventive, promotive, curative and rehabilitative care of children. It emphasizes on all round development of body, mind and spirit of the growing individual. Thus, pediatric nursing involves in giving assistance, care and support to the growing and developing children to achieve their individual potential for functioning with fullest capacity.
Roles of the pediatric nurse

Role of the Pediatric Nurse:
The ever expanding demands of medical and nursing practice, emerging challenges in different aspects of child care, consumer demands and improved technology have necessitated the highly specialized roles of pediatric nurse.
The role of the pediatric nurse is both caring and curing. Caring is a continuous process in both wellness and illness. It refers as helping, guiding and counseling. Curing refers to the act of diagnosis and management, usually during illness. Pediatric nurse have the responsibilities of
providing nursing care in hospital, home, clinic, school and community where children and their
parents have health and counseling needs.
The role of the pediatric nurse may vary from one health institution to others, but the basic responsibilities remain the same. It may vary depending upon the educational preparation of the pediatric nurse and exposure to the specialized training. The characteristics social behavior of the pediatric nurse as role model for the child care can be summarized as follows:
Primary caregiver: Pediatric nurse should provide preventive, promotive, curative and rehabilitative care in all levels of health services, as therapeutic agent. She/he acts as case finder and compassionate skilled caregiver as needed by the today’s society. In hospital, care of the sick children, i.e. comfort, feeding, bathing, safety, etc. are the basic responsibilities of the pediatric nurse. Health assessment, immunization, primary health care and referral are basic responsibilities at the community level as quality care provider.
Health educator: Important role of the pediatric nurse is to deliver planned and incidental health teaching and information to the parents, significant others and children to create awareness about healthy lifestyle and maintenance of health. Change in health behavior and attitude and to develop healthful practice regarding child care should be initiated by the pediatric nurse as change agent, teacher and health educator.
Nurse-counselor: Problem-solving approach and necessary guidance in health hazards of children to minimize or to solve the problem and to help the parents and family members for independent decision-making in different situations are essential role of the pediatric nurse in the present health care delivery system.
Social worker: Pediatric nurse can do case work especially for children and try to alleviate social problems related to child health. She/he can participate in available social services or refer the child and family for necessary social support from the child welfare agencies.
Team coordinator and collaborator: Pediatric nurse should work together and in combination with other health team members towards better child health care. She/he should act as liaison among the members and maintain good interpersonal relationship. The nurse interprets the objectives of health care to the family and coordinates nursing services with other services necessary for the child. Co-operations and good communication among team members should be promoted by the nurse.
Manager: The pediatric nurse is the manager of pediatric care units in hospital, clinics and community. She/he should organize the care orderly for successful outcome with better prognosis and good health.
Child care advocate; Child or family advocacy is basic aspect to comprehensive family- centered care. As an advocate, the pediatric nurse can assist the child to obtain best care possible from the particular units. Advocacy can range from consulting dietary department for special foods to arrange team meeting to discuss plan of care.
Recreationist: This supportive role of pediatric nurse is important for the child to adjust to the crisis imposed by illness or hospitalization. She/he can organize play facilities for recreation and diversion for child’s emotional outlet.
Nurse consultant: The pediatric nurse can act as consultant to guide the parents and family members for maintenance and promotion of health and prevention of childhood illness. The nurse can promote self-care within the family and prepare self-care agent for the children who are unable to take care of their own health. The nurse can help the older children to become responsible for their own lives. The nurse assesses the children’s ability to do self-care activities and assist them in developing the ways of self-care and self-responsibility.
Researcher; Nursing research is an integral part of professional nursing. Pediatric nurse should participate or perform research projects related to child health. Clinical and applied research provides the basis for changes in nursing practice and improvements in the health care of children.
Beside the above roles, pediatric nurses have to respond to the social need with expanded roles. The independent role of pediatric nurse reflects the expansion of the role as pediatric nurse practitioner, pediatric clinical nurse specialist, etc. New roles and responsibility can be added to the pediatric nurse in changing situations of child care in future.
(Ref by: Parul Datta/4/12-13)
Qualities of a Pediatric Nurse;
- A pediatric nurse should have all desirable and preferable qualities of a professional nurse. More than those a professional nurse should possess the following qualities to be a pediatric nurse:
- She should be a loving person and have liking for the children.
- She should have patience, pleasant appearance and ability to understand the child’s behavior.
- She should be able to maintain good interpersonal relationship and to provide safety and security to the children.
- She should be friendly, honest, gentle, diligent and humorous.
- She should have good observation, judgment and communication ability-based on scientific knowledge and experience.
- She should be well-informed, skillful, responsible, truthful and trustworthy.

(Ref by: Parul Datta/4/12)
Definition of Pediatric Nurse:
Pediatric nurse may be defined as the nurses who specialize in pediatrics devote their knowledge and skills to caring for children from infancy through the late teen years and their families.
Goals of Pediatric Nursing:
- To provide skillful, intelligent, need based comprehensive care to the children in health and sickness.
- To interpret the basic need of the children to their parents and family members and to guide them in child care.
- To promote growth and development, of children towards optimum state of health for functioning at the peak of their capacity in future.
- To prevent disease and alleviate suffering in children.
(Ref by: Parul Datta/4/12)
Functions of Pediatric Nurse:
- Identify changes in a child’s signs and symptoms and intervene in emergent situations
- Maintain privacy and confidentiality in nurse/child relationships
- Differentiate between normal and abnormal physical findings
- Serve as a child advocate
- Participate in activities to manage a child’s pain
- Analyze situations to anticipate pathophysiological problems and detect changes in status
- Administer medication using age-appropriate guidelines
- Determine a child’s needs related to pain management
- Evaluate a child for signs and symptoms of abuse
- Provide supportive care to dying children
Functions of Pediatric Nurse
The dynamic nature of nursing profession has had an impact on trends in pediatric nursing care and functions of pediatric nurse. Nursing care of children is directed towards understanding of nature and nurture of children and environmental influence on their development. The core activity of pediatric nursing practice is developing a therapeutic relationship with parents and children and then applying the nursing process.
The use of nursing process for both independent and dependent nursing functions provides significant assistant in planning and implementing care.
Based on assessment, the nurse determines the nursing diagnosis and makes planning for necessary care on priority basis. Interventions and evaluation of care help to implement nursing action with necessary modification. Nursing process can be used both in hospital and community during illness or in maintenance of health.
Implementation of physical care to the children through provision of rest, comfort, hygienic measures, dietary arrangement, administration of medications and other therapies, maintenance of safe and supportive environment, performance of diagnostic procedures and caring in special management schedule are essential functions of pediatric nurse for hospitalized children.
An important function of pediatric nurse is the psychological care that helps children and parent to adapt in illness and hospitalization.
Emotional support to child and family, encouragement of children and parental participation in child care, preparation of children and parents for procedures and surgery, allowing child to express feelings about illness and hospitalization, promotion of therapeutic relationship, strengthening coping mechanism and monitoring emotional reactions of child, parents and family members during illness and hospitalization are the delicate functions of pediatric nurse.
The vital function of pediatric nurse is to contribute to increase knowledge and understanding of parents and family members about child health. Information should be provided about illness, hospital procedures, treatment plan, discharge plan and possible outcome of the illness.
Health counseling about different aspects like prevention of diseases, promotion of healthful practices, child rearing and family welfare is also important. Information about community resources, health care facilities, referral services, available social and economical support should be provided by the pediatric nurse for necessary child care.
Pediatric nurse should function as a member of the health team and acts in cooperation and coordination towards better child care. Clinical rounds, case study, case discussion, etc. are essential aspects of team approach to the solution of child’s problems.
Thus, the functions of pediatric nurse are directed towards the welfare of children and their family, promotion of growth and development towards highest possible state of health of children, prevention of diseases and injuries, meeting health needs and rehabilitating children in the family and community.

(Ref by: Parul Datta/4/13-14)
Principles of Pediatric Nursing:
- The nurse should begin to build a working relationship with the parents and their children from the time of first contact with them.
- The nurse should be aware that all behaviors of child are meaningful.
- The nurse should accept the parents and their children exactly as they are.
- The nurse should have empathy for parents and children.
- The nurse should let the parents and children know that their problems are important and the nurse is there to aid in solution of those problems.
- The nurse must be willing to acknowledge the parents’ rights to decision concerning their children.
- The nurse allows the parents and children to express their emotions and even negative emotions.
- The nurse should ask questions limited to a single idea or reference so that it is easy for the parents and child to understand what is being asked.
- The nurse should speak in language which the parents and child can understand
- The members of health team must make the parents feel that they are working in a collaborative manner for the treatment of their child.
Trends in Pediatric Nursing
Remarkable changes have occurred in the field of pediatric nursing in recent years due to changing needs of society, medical and technological advances, political interests and changing trends within the nursing profession. Other influencing factors are consumers’ demands, increased public awareness and greater understanding of child health problems along with psychological aspects of illness and hospitalization.
Modern approach of child health care emphasizes on preventive care rather than curative care. Most childhood diseases are preventable and nurses play pivotal role in preventive health services, e.g. immunization, nutrition demonstration, health education, etc. So nurses are considered as key person in child care.
Growth of specialization within the field of pediatric medicine has had an impact on nursing care of children. There is need for specialized well-trained pediatric nurses with continuous reorientation about the advancement of technical aspect of child care.
Nurses are assuming an increasing share of the services to children in health and illness and working significantly towards the promotion of child health. Pediatric nurses are performing specialized care in neonatal intensive care unit, pediatric intensive care unit and in any special care system of child care.
Because of growth and maturation of the nursing profession, nurse may become an independent practitioner who can fulfill an autonomous position as a member of an interdisciplinary health team. Pediatric nursing is the area where independent practices are mostly accepted, especially in the community services for improvement in the child care.
The large number of child population with various health problems required more numbers of health care providers along with specially trained nurses. So, special importance must be given in basic nursing curriculum to prepare the nurses with specialized knowledge and skill on child health.
Acceptance of family-centered care of children impart more responsibility on pediatric nursing and pediatric nurse. The nurses are working in liaison with the health team and family to prepare mutually developed plan of care and to minimize psychological trauma in relation to holistic approach of child care.
Pediatric nursing practices are influenced by the research findings of nursing sciences and other health disciplines. Psychological approach of child care, acceptance of beneficial traditional practices, newer diagnostic and treatment modalities are the different aspects which have impact on pediatric nursing towards modernization.
Consideration of ethical, moral and legal dilemmas in child care creates problems and nurses may need to decide to perform nursing activities based on professional and personal judgment. Ethical decision-making, legal safeguards and quality assurance are the recent trends in nursing practice in all fields including pediatric nursing.

(Ref by: Parul Datta/4/14)
Emerging Challenges in Pediatric Nursing
In the changing trends and changing attitude towards care of children, the pediatric nurse has to face various challenges on the following aspects.
Emergence of medical specialty and super-specialty of pediatric care need specialized education and training of pediatric nurse. Nurses required to be up-to-date in the field of specialized care to be at per with their coworker and team members especially medical counterpart in intensive care, neonatology and in any special care system.
Increasing numbers of HIV infected innocent children create problems in pediatric care and nursing practices which need for specialized approach.
Increasing numbers of psychological problems among children due to unhealthy competition, comparison, single parent and family disruption call for special attention of pediatric nurse in child care.
Ethical decision-making in ethical dilemmas about issues like refusal of treatment (discontinuing life support system, withholding or withdrawing nutrition and fluids), euthanasia, prolongation of life, prenatal genetic screening, abortion, in vitro fertilization, allocation of scarce medical resources and rights of children in health care research, etc. are the new challenges in nursing. pediatric
Moral dilemmas for pediatric nurses arise from power conflicts about treatments in which the nurse may need to decide whether to continue to cooperate with the health team and follow the physician’s directions or not to follow them.
Legal issues related to Consumer Protection Act, malpractice and negligence are great challenges in all areas of nursing practice and also in child care.
Poverty and illiteracy are two big obstacles need to overcome to improve child health. Nurse must be confident and engaged to advocate for the child’s protection in these situations in hospital and community.
Childhood illness leads to frustrating and stressful situations, nurses also need to adjust and cope with those situations and develop tolerance of own feelings.
Emphasis on ‘quality care’ and increased complexity of medical and nursing practices, required for highly specialized, expert and competent practitioners, with special preparation for super- specialty areas. It calls for better education in pediatric nursing for specialized knowledge and skill of motivated pediatric nurse for better contribution as health team members towards improvement of child health.
(Ref by: Parul Datta/4/14)
Nursing Process
Definition of Nursing Process
Nursing process may be defined as a systematic problem solving approach used to identify, prevent and treat actual or potential health problems and promote wellness.
Or
The nursing process is a method of planning, organizing and delivering nursing care.ดร
Or
The nursing process has traditionally been defined as a systematic method for assessing health status, diagnosing health care needs, formulating a plan of care, initiating plan and evaluating the effectiveness of plan.
(Ref by- Capt. (Retd.) Alphonsa Jacob/Fundamentals of Nursing/Vol-11/6/158)
Or
The nursing process is an orderly, systematic manner of determining the clients’ (patients’) problems, making plans to solve them, initiating the plans or assigning others to implement it and evaluating the extent to which the plan was effective in resolving problems identified. It should be planned, client-centered, problem-oriented, goal-directed, dynamic and continuous phenomenon.
(Ref by: Parul Datta/4/15)
Purpose of Nursing Process;
- The purposes of use of nursing process in child health are the followings:
- It assists to deliver optimum, need-based nursing care to the children effectively and intelligently.
- It guides nurses to take deliberate steps to identify client’s problems to set realistic goals and to intervene individualized care.
- It encourages for identification and utilization of client’s strength.
- It enhances communication and interpersonal relationship with clients and team members
- It provides continuity of care by reducing omissions and duplications of actions.
(Ref by: Parul Datta/4/15)
Nursing Process in Child Health Care:
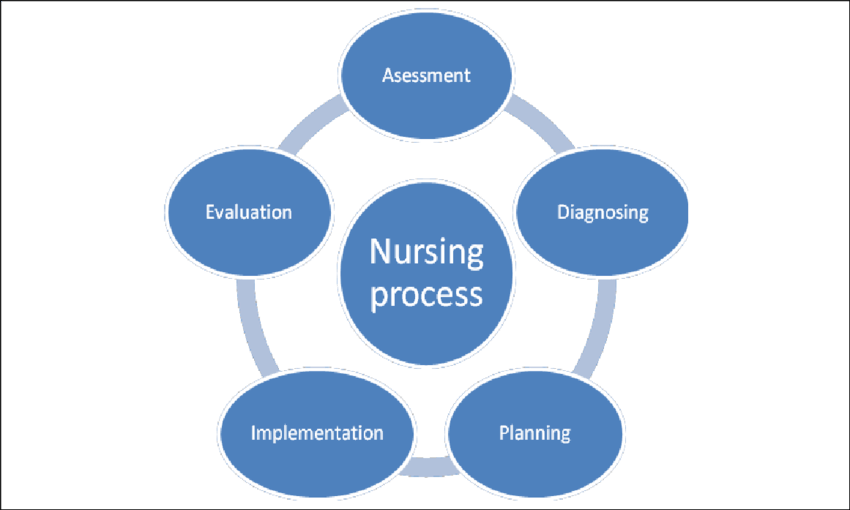
The nursing process has been described by many authors as having five basic steps:
1. Assessment
2. Diagnosis (nursing diagnosis),
3. Planning
4. Implementation (intervention) and
5. Evaluation.
Assessment
Assessment includes gathering of subjective and objective data. It is done by collection of data through-
- History taking.
- Physical assessment,
- Review of investigations reports and Record analysis.
- It comprises comparison of data with the normal value and analysis of the data gathered to ascertain the client’s condition and identify problems.
Nursing Diagnosis
Nursing diagnosis are judgments and conclusions made by the nurse after analyzing the data base. It indicates actual or potential problem or unmet need of the client/patient. It differs from medical diagnosis. Medical diagnosis refers to disease, whereas nursing diagnosis refers to difficulty experienced by the patient due to disease process.
Planning
Planning includes establishing goals, setting priorities, determining Resources, stating nursing strategies and assigning care. It is a written document with intervention strategies and outcome of nursing actions as nursing care plan, which should be available for all members of the nursing team. Client’s participation in planning of care is an important aspect in terms of effectiveness.
Implementation
It is putting the plan into action to achieve the goals. It includes performance, assistance or assignment of nursing actions and completion of plan of care. This phase involves decision- making, observation and communication among client, nurse and other team members. It requires up-to-date and correct knowledge with skill and competency to perform the activities.
Evaluation
Evaluation helps to measure the extent of achievement of goals and effectiveness of interventions. Attention should be given to the client’s response in the planned nursing action. During this step, the nurse also will be able to identify omissions from the assessment, planning and implementation phases of the process. A decision can be made to continue, modify or terminate all or part of the nursing care plan.
The nursing process provides an organized nursing assistance to the child and the family towards better outcome.
(Ref by: Parul Datta/4/15-16)
Characteristic of Nursing Process:
1. The system is open, flexible, and dynamic.
2. It individualized the approach to each client’s particular needs.
3. It is planned.
4. It is goal directed.
5. It is flexible to meet the unique needs of client, family or community.
6. It permits creativity for the nurse and client in devising ways to solve the stated health problem.
7. It is interpersonal. It requires the nurse to communicate directly and consistently with clients to meet their needs.
8. It is cyclical. Since all steps interrelated, there is no absolute beginning or end.
9. It emphasizes feedback, which leads either to reassessment of the problem or to revision of the care plan.
10. It is universally applicable. The nursing process is used as a framework for nursing are in all types of health care settings, with clients of all age groups.
Or,
1. Dynamic.
2. Client centered.
3. Planned.
4. Purposeful
5. Interactive
6. Goal directed
7. Systematic
8. Interpersonal and collaborative.
9. Universally applicable.
10. Can focus on problems.
11. Theoretically based
12. Flexible
Advantages/Importance of Nursing Process:
The use of the nursing process has many advantages:
1. The nursing process provides a framework for meeting the individual needs of the client. the client’s family/significant other (s), and the community.
2. The steps of the nursing process focus the nurses attention on the individual human responses of a client / group to a given health situation, resulting in a holistic plan of care addressing their specific needs.
3. The nursing process provides an organized, systematic method of problem solving, which may minimize dangerous errors or omissions in care giving and avoid time-consuming repetition in care and documentation.
4. The use of nursing process promotes the active involvement of the client in his or her own health care, enhancing consumer satisfaction.
5. The use of the nursing process enables nurses to have more control over their own practice.
6. The use of the nursing process provides a common language for practice, unifying the nursing profession.
7. The use of the nursing provides a means of assessing nursing economic contribution to client care. The nursing process supplies a vehicle for the quantitative and qualitative measurements of nursing care than meets the goal I of cost effectiveness and still promotes holistic care.
(Ref by- BT Basavanthappa/2/244)
Nurses’ Roles in Nursing Process:
1. Scope of nursing practice.
- Principles for determining scope of practice.
2. Roles in different areas.
3. Level of critical thinking in nursing.
- Basic.
- Complex and
- Commitment.
4. Continuing professional development.
5. Autonomy and accountability.
6. Caregiver.
7. Professional role.
8. Advocate.
9. Educator.
10. Communicator.
11. Manager.
12. Medication administrator.
13. Nurse researcher.
List of Approved Nursing Diagnosis
North American Nursing Diagnosis Association (NANDA) approved a list of nursing diagnosis through the 12th conference, 1996. Some of them are given below in alphabetical order.
1. Activity intolerance
2. Activity intolerance, risk for
3. Adjustment, impaired
4. Airway clearance, ineffective
5. Anxiety
6. Aspiration, risk for
7. Body temperature, altered, risk for
8. Bowel incontinence
9. Breastfeeding, ineffective
10. Breathing pattern, ineffective
11. Cardiac output decreased
12. Comfort, altered, pain
13. Communication, impaired, verbal
14. Confusion
15. Constipation
16. Coping, ineffective, family
17. Coping, ineffective, individual
18. Diarrhea
19. Diversional activity, deficit
20. Family process, altered
21. Fatigue
22. Fear
23. Fluid volume deficit
24. Fluid volume, deficit, risk for
25. Fluid volume, excess, risk for
26. Gas exchange, impaired
27. Growth and development, altered
28. Hopelessness
29. Hyperthermia
30. Hypothermia
31. Infant feeding pattern, ineffective
32. Infection, risk for
33. Injury, risk for
34. Knowledge deficit
35. Memory, impaired
36. Mobility, impaired, physical
37. Noncompliance
38. Nutrition, altered, less than body requirements
39. Nutrition, altered, risk for, more than body requirements
40. Oral mucous membrane, altered
41. Pain, acute
42. Pain, chronic
43. Parental role conflict
44. Parenting, altered
45. Poisoning, risk for
46. Post-trauma response
47. Protection, altered
48. Self-care deficit: Feeding, bathing/hygiene, dressing, toileting
49. Sensory alteration: Visual, auditory, tactile, etc.
50. Skin integrity, impaired
51. Skin integrity, impaired, risk for
52. Sleep pattern disturbance
53. Social interaction, impaired
54. Suffocation, risk for
55. Swallowing, impaired.
56. Thermoregulation, ineffective
57. Thought processes, altered
58. Tissue integrity, impaired
59. Tissue perfusion, altered, cerebral, renal, cardiopulmonary, gastrointestinal, peripheral
60. Urinary elimination, altered patterns of
Rights of the Child:
The ten basic rights of the child are:
1. Right to develop in an atmosphere of affection and security and protection against all
forms of neglect, cruelty, exploitation and traffic.
2. Right to enjoy the benefits of social security, including nutrition, housing and medical care.
3. Right to a name and nationality.
4. Right to free education.
5. Right to full opportunity for play and recreation.
6. Right to special treatment, education and appropriate care, if handicapped.
7. Right to be among the first to receive protection and relief in times of disaster.
8. Right to learn to be a useful member of society and to develop in a healthy and normal manner and in conditions of freedom and dignity.
9. Right to be brought up in a spirit of understanding, tolerance, friendship among people, peace and universal brotherhood;
10. Right to enjoy these rights, regardless of race, color, sex, religion, national or social origin
(Ref by: Parul Datta/4/9)
Childhood Health Problem
Common Childhood Health Problems:
Acute Health Problem
- A. Nutritional Problem
- B. Eye Problem. (Conjunctivitis)
- C. Dental Problem.
- D. Ear and throat infections (Otitis, sore throat, tonsillitis, bronchitis).
- E. Skin disease, e.g.- scabies, ring worm.
- F. Parasitic infections, e.g.- Hookworm infection, measles, diarrhea, tuberculosis etc.
- G. Communicable diseases, c.g.-measles, mumps, whooping cough, diphtheria, chicken pox, diarrhea, tuberculosis etc.
- H. Mental problemi. Feeble minded idiots, ii. Mental retardation.
- I. Psychological problems: Phobia, maternal deprivation, emotional deprivation, maladjusted children etc.
Chronic Health Problem:
- A. Asthma
- B. Cerebral Palsy
- C. Diabetes.
- D. Sickle Cell Anemia
- E. Cystic fibrosis.
- F. Cancer.
- G. AIDS.
- H. Epilepsy.
Major nutritional health problems in Bangladesh:
a) Low birth weight
b) Protein-energy malnutrition (PEM)
- Kwashiorkor
- Marasmus
c) Vit-A deficiency disorder (VADD):
- Night blindness
- Xerophthalmia
- Total blindness
d) Nutritional anaemia:
- Iron deficiency anaemia
- Folate & vit-B12 deficiency anaemia.
e) Iodine deficiency disorder (IDD):
- Goitre
f) Neurolathyrism
- Khesari dhal intoxication
g) Endemic Fluorosis: Lack of fluoride
- Dental fluorosis.
- Skeletal fluorosis.
- Genu valgum.
Preventive Measures to Decrease Childhood Health Problems:
- A. Prenatal nutrition: Supplementation of mother’s diet helps in improving the birth weight
of babies thereby helping in reducing neonatal mortality. - B. Prevention of infection: Immunization is the best way of preventing infectious diseases which take a heavy toll of life in children. The vaccine preventable diseases are – TB, Diphtheria, Pertussis, Tetanus, Polio, measles. Hepatitis, Meningitis ete.
- C. Breastfeeding: The most effective measure of lowering infant mortality is breastfeeding which provides passive immunity to infants.
- D. Family planning: Infant mortality increases as birth order increases. Limiting the family size and spacing of children is effective in lowering infant mortality rate.
- E. Sanitation: Adequate sanitation and safe drinking water facilities have significant positive impact on health of society including mothers and children. It helps in lowering mortality due to diarrhea, vomiting, respiratory infections, hepatitis, dengue etc.
- F. Primary health care: Provision of primary health care for high risk pregnant females and babies will help in lowering mortality and morbidity rate.
- G. Socio economic development: IMR and PMR can be effectively lowered by uplifting the socio economic condition of the country that includes increasing female literacy.
- H. National health program: Proper planning and implementation health related activities and immunization program.
Child Health in Bangladesh
The last few decades have brought significant improvements in child health in Bangladesh. The mortality rate in children under-five declined from 152 deaths per 1.000 live births to 94 deaths per 1,000 live births, but these rates are still high, and have remained constant for several years. Pneumonia, diarrhoea, measles, malaria, malnutrition, injuries and the high number of neonatal deaths, and poor care-seeking behaviour, all contribute to the high levels of child mortality.

The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has, for the last decade, implemented several vertical programmes centrally organized services focused on single issues such as the control of diarrhoeal diseases (CDD) and the control of acute respiratory infections (ARI). From 1998, though, the Government started to adopt a more holistic, sector-wide approach to implementing the programmes.
The Child Health Programme, promotes the rights of children to survival and well-being through interventions under four categories:
- Expanded Programme on Immunization (EPI)
- Control of Diarrhoeal Diseases (CDD)
- Control of Acute Respiratory Infections (ARI)
- Integrated Management of Childhood Illnesses (IMCI).
Objectives
The project aims to meet the following targets by the year 2005:
- 80 per cent of children under one year are fully immunized
- 80 per cent of caregivers know the three golden nules:
Increase fluid consumption
Continue feeding, including breastfeeding
Recognize when to seek care from trained health workers.
- 60 per cent of caregivers are knowledgeable in the use of Oral Rehydration Therapy (ORT)
- All public health providers are trained in the management of ARI
- All health providers in all upazilas sub-district are knowledgeable and skilled in IMCL
Strategies
The project is designed to be implemented by bringing together essential services: immunization; ORT; detection, treatment and referral of ARI, diarrhoea and other common illnesses through community outreach and local health facilities. A central aspect of this strategic planning is the adaptation and implementation of IMCI so that the interventions through individual programmes like ARI and CDD can be gradually merged into IMCI programmes.
To reduce levels of vaccine-preventable diseases, specific strategies include routine vaccination through a nationwide network of 120,000 community outreach sites and health facilities, Supplementary Immunization Activities (SIAs) such as National Immunization Days (NIDs) for polio eradication, and area-based multi-antigen campaigns to eliminate neonatal tetanus and control of measles.
Regular reviews of performance and progress reflect approaches to issues that span several areas and issues. These:
- Promote accountability, and strengthen communication, enabling people to articulate their demands, and change behaviour to improve participation of all stakeholders,
- Involve NGOs in mobilizing communities and providing services based on need
- Collaborate with partners working on other programmes.
