Pharmacology Rectal route – This book covers the entire syllabus of “Pharmacology” prescribed by BNMC- for diploma in nursing science & midwifery students. We tried to accommodate the latest information and topics. This book is an examination set up according to the teachers’ lectures and examination questions.
At the end of the book, previous questions are given. We hope in touch with the book students’ knowledge will be upgraded and flourish. The unique way of presentation may make your reading of the book a pleasurable experience.
Pharmacology Rectal route
Certain irritant and unpleasant drugs can be put into rectum as suppositories or retention enema for systemic effect. This route can also be used when the patient is having recurrent vomiting or is unconscious.
However, it is rather inconvenient and embarrassing; absorption is slower, irregular and often unpredictable, though diazepam solution and paracetamol suppository are rapidly and dependably absorbed from the rectum in children.
Advantages of rectal route
- Drugs that are irritant to the stomach can be given by suppository.
- Suitable route in vomiting, motion sickness, migraine. Non-co-operative patient.
- Avoid first pass metabolism.
Disadvantages of rectal route
- Patient may be embarrassed.
- Rectal inflammation may occur with repeated use.
- Absorption may be unreliable
Intravenous Route
Definition of Intravenous Injection:
Intravenous injection is the injection of liquid substances which is given directly into a vein. It is given through the vein directly, delivers the drugs directly into the bloodstream. Medications administered intravenously have an immediate effect.
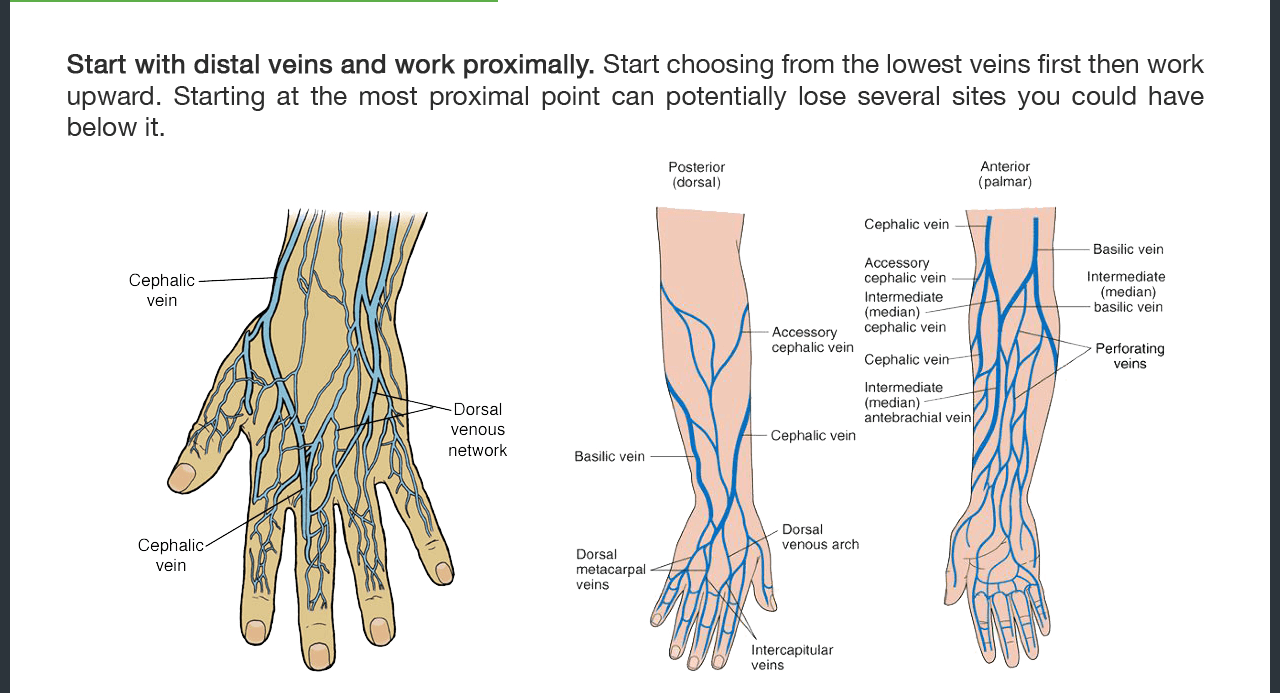
Sites of Intravenous Injection:
| A. Inner Arm: |
|
| B. Dorsal surface of hand: |
|
| C. Dorsal surface of foot |
|
Advantages of Intravenous (IV) Route:
1. Intravenous route is used in emergency cases to obtain immediate effect and highly predictable blood volume.
2. Large volume, unpleasant and irritant solution can be given.
3. Suitable for unconscious and non-co-operative patients.
4. Drugs can be given through I.V. route in case of Diarrhea, vomiting or where the patient is unable to swallow.
5. Rapid action and accuracy of dose are ensured.
Disadvantages of Intravenous (IV) Route:
1. It is invasive painful procedure.
2. Self-medication is is difficult.
3. Strict aseptic measures, special, technique and skill are essential.
4. Risks: like infection, hypersensitivity reaction, pyrogenic reaction, local venous thrombosis, & hemolysis may occur.
5. Leakage of the drug outside the vein can produce severe irritation
6. Overdose may have effects so immediate that it is impossible to reverse them
7. Chance of injury to surrounding nerves and vessels.
8. Drugs must be water-soluble.
9. Short duration of action, as excretion is rapid,
10. Expensive.
(Ref by-Dr. Javed Yousuf’s/7/36)

Purposes of Injection:
1 .To get the rapid and systemic effect of the drug
2. Some medications are cannot be given by mouth. So they should be given by parenteral route. These are:
- Some medications are rendered ineffective in the gastro-intestinal tract by the action of gastric juice. E.g. Insulin
- Some are not retained in the intestine for a sufficient period for its absorption due to diarrhea, vomiting or gastric suction.
- Some medications are poorly absorbed from gastro-intestinal tract
- When the drug is toxic and irritating to the gastro-intestinal mucosa
3. To give required effect when the patient is unconscious or unable to swallow due to surgical or neurological problems or when the patient is not co-operative
4. . To get a local effect at the site of the injection.
- For diagnostic purpose Tuberculine Test
- For local anaesthesia-Inj. Xylocaine
- To test allergic condition of the drug. E.g. serum or penicilline test.
- To treat local conditions. E.g. Hydrocortisone injection into joint cavity.
5. To restore blood volume and electrolyte balance by replacing fluid e.g. in shock conditions.
6. To give nourishment when it cannot be taken by mouth.
(Ref by-Madhuri Inamdar’s/24/166)
An intramuscular injection is a technique used to deliver a medication deep into the muscles. This allows the medication to be absorbed into the bloodstream quickly.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Intramuscular (IM) Route:
1. Absorption of drug is more rapid and uniform than subcutaneous injection due to rich blood supply to the muscle,
2. Lightly irritant drugs can be given that is too irritant for subcutaneous route.
3. Moderately large volume can be given, (but not more than 5ml)
4. Deport preparation can be administered, e.g. penicillin medroxyprogesterone. (Site: deltoid, gluteal region, thigh).
Disadvantages of Intramuscular (IM) Route:
1. It is invasive and painful route.
2. Self-medication is difficult.
3. Large volume of drug cannot be given (max: 7-10ml)
4. Chance of local inflammation, infection, abscess formation, irritation and haematoma formation
5. Chance of nerve injury, which may cause severe pain, paresis and even paralysis of the muscles.
6. Tissue binding or precipitate from solution may delay the appearance of drug in systemic circulation, e.g. Diazepam.
Sites for Giving Intramuscular Injection:
A. Dorsal Gluteal site-
Find out the greater trochanter of the femur and the posterior superior iliac spine. Draw an imaginary line between these two bony prominencer. Site will be upper and outer quadrant or divide the buttocks into four regions by imaginary lines, select the site at the upper and outer quadrant for the intramuscular injection.
B. Vastus Lateralis Site-
It is located on the lateral aspect of the thigh. It is the area between mid anterior thigh and mid lateral thigh one hands breadth from below the greater trochanter to one hand’s breadth above knee. The site avoids injury to the sciatic nerve.

C. Mid Deltoid Site-
Locate the lower edge of the acromion process and form a rectangle. The deltoid area is used to inject very small quantities of non irritating drugs.
D. Ventro-Gluteal Site-
Place the tip of the index finger on the anterior superior iliac spine of the patient, the middle finger just below the iliac creast. The “V shaped area is the area in which the injection can be given easily.
Read more: