Physiological jaundice – Health of the children has been considered as the vital importance to all societies because children are the basic resource for the future of humankind. Nursing care of children is concerned for both the health of the children and for the illnesses that affect their growth and development. The increasing complexity of medical and nursing science has created a need for special area of child care, i.e. pediatric nursing.
Pediatric nursing is the specialized area of nursing practice concerning the care of children during wellness and illness. It includes preventive, promotive, curative and rehabilitative care of children. It emphasizes on all round development of body, mind and spirit of the growing individual. Thus, pediatric nursing involves in giving assistance, care and support to the growing and developing children to achieve their individual potential for functioning with fullest capacity.
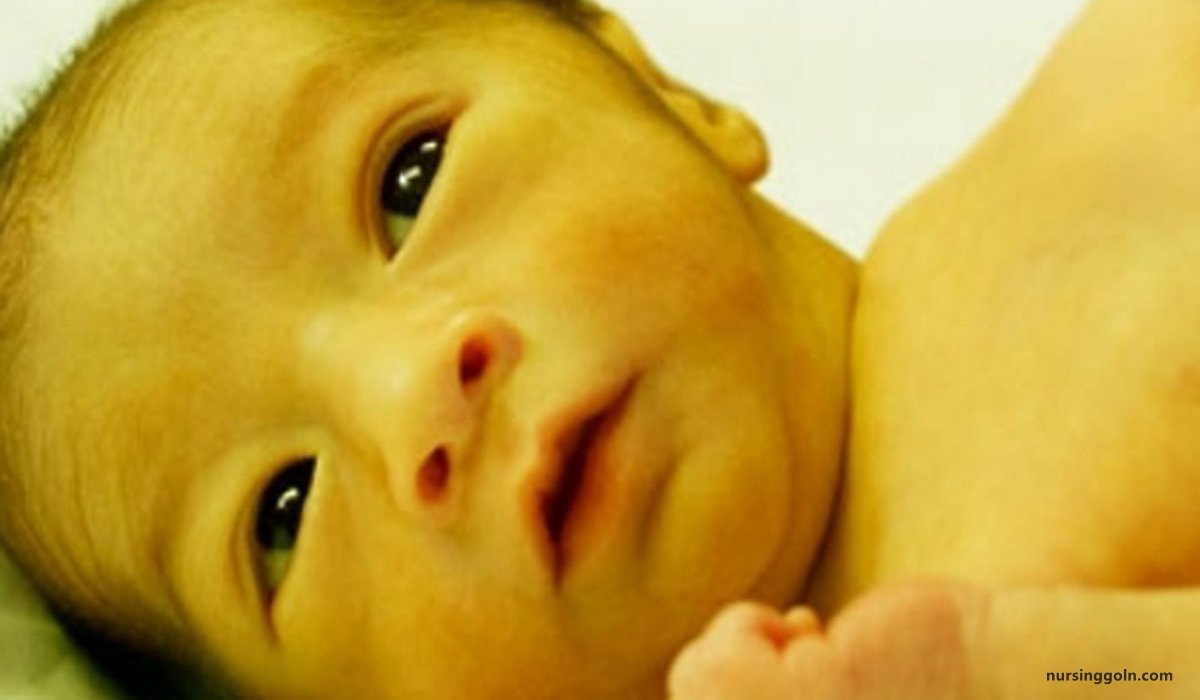

Physiological jaundice
Physiological Jaundice:
Physiological jaundice represents physiological immaturity of the neonates to handle increased bilirubin production. Visible jaundice usually appears between 24-72 hours of age. It does not require any treatment.
[Ref-Vinod Paul/8h/172]
Or,
Physiologic jaundice of the newborn: Yellowish staining of the skin and whites of the newborn’s eyes (sclerae) by pigment of bile (bilirubin). In newborn babies a degree of jaundice is normal. It is due to the breakdown of red blood cells (which release bilirubin into the blood) and to the immaturity of the newborn’s liver (which cannot effectively metabolize the bilirubin and prepare it for excretion into the urine).
Or,
It is defined as jaundice in healthy babies during the first few days of life due to physiological reasons. It appears on second or third day of life, rises at a rate less than 5 mg/dl/day; peaks at 4 to 5 days of age; and spontaneously disappears by day 10-14 days of life.
[Ref-Piyush Gupta/1″/246]

Causes Of Physiological Jaundice:
Diseases or conditions that can cause jaundice include:
◆ Internal bleeding (hemorrhage)
◆ An infection in your baby’s blood (sepsis)
◆ Other viral or bacterial infections.
◆ An incompatibility between the mother’s blood and the baby’s blood.
◆ A liver malfunction.
◆ An enzyme deficiency.
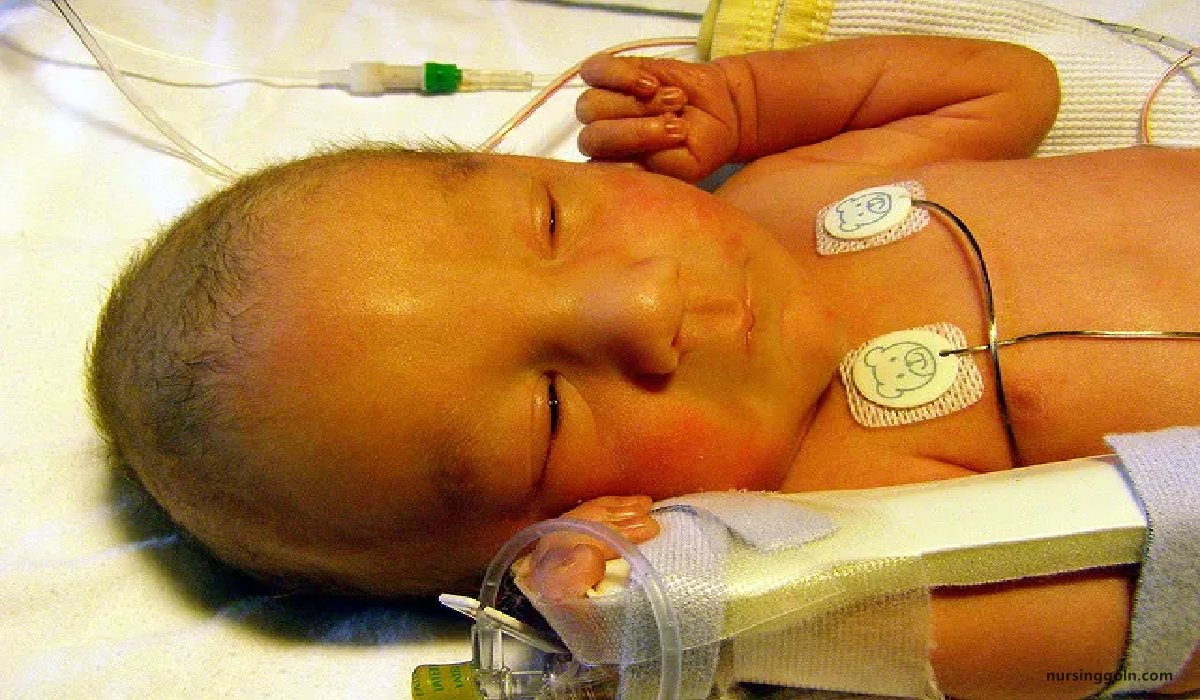
Management of Physiological Jaundice With High Bilirubin Level:
1. Physiological jaundice in the newborn results from accumulation of unconjugated bilirubin in the fetal circulation.
2. It is aggravated by immaturity, hypoxia, acidosis, hypoglycemia, infection, enzyme deficiency in the erythrocyte, cephalhematoma, and drugs administered to the mother during labour and the newborn after.
3. Management is essentially symptomatic.
4. No specific therapy is required.
5. The infant is watched for signs of illness/deepening jaundice.
6. It is important to take care of nutrition, maintain temperature, prevent infection, monitor bilirubin levels, and
7. Maintain the same within safe limits.
[Ref-Amarnath G Bhide/1″/228]
Read more:
