Post Term Labor – This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
Post Term Labor
Post-term pregnancy:
Post-term pregnancy is defined as a pregnancy that lasts longer than 42 weeks; two weeks past the normal 40-week gestation period. Post-mature births can carry risks for both the mother and the infant, including fetal malnutrition.
Or
A pregnancy that lasts more than 42 weeks is called post-term. A pregnancy that is between 41 and 42 weeks is called late-term. Most women deliver between 37 and 42 weeks of pregnancy.
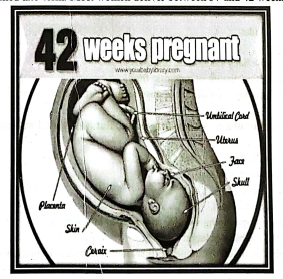
Causative factors of post term labor:
➤ Maternal obesity.
➤ Had past pregnancies that went past 42 weeks.
➤ First baby.
➤ Overweight.
➤ Asphyxia
➤Meconium aspiration.
➤ Respiratory distress.
➤ Abnormalities in the mother’s central nervous system.
➤ Previous pregnancies that went post-term.
➤ Deficiency in the placenta of sulfatase enzyme.
➤ Anencephaly (a malformation of the skull of the baby).
➤ Placental insufficiency.
To calculate due date, healthcare provider will:
➤ Measure the size of uterus at certain points in early pregnancy.
➤ Note the date he or she first hears developing baby’s heartbeat.
➤ Note whe first feel baby moving in the uterus.
➤ Use ultrasound.
➤ Tests may include:
➤ Ultrasound
✓ Seeing how baby’s heart rate responds to activity.
✓ Checking the amount of amniotic fluid.
There are no symptoms of a post-term pregnancy. But it is related with some conditions.
These include:
➤ Pregnancy that lasts longer than 42 weeks.
➤ Stillbirth and newborn death.
➤ Placenta problems.
➤ Decreased amniotic fluid.
➤ The fetus may stop gaining weight, or may even lose weight.
➤ Birth injury if the baby is large.
➤ Baby breathes in fluid containing the first stool (meconium aspiration).
The goal is to prevent problems and deliver a healthy baby. The healthcare provider will base
specific treatment on:
➤ Taking overall health history.
➤ Fetal movement counting: This keeps track of baby’s kicks and movements. A change in the number or frequency may mean the developing baby is under stress.
➤ Non-stress testing: This test watches how baby’s heart rate for increases with baby’s movements. This is a sign of baby’s well-being.
➤ Biophysical profile: This test combines the non-stress test with an ultrasound to look at baby’s well-being.
➤ Ultrasound: This test uses high-frequency sound waves and a computer to make images of blood vessels, tissues, and organs. Ultrasounds are also used to follow the growth of developing baby.
➤ Doppler flow studies: This is a type of ultrasound that uses sound waves to measure blood flow. The test is commonly used if a developing baby is not growing properly.
➤ Amnioinfusion is sometimes used during labor if there is very little amniotic fluid or if the baby is pressing on the umbilical cord. A sterile fluid is put into the uterus with a hollow tube (catheter). The fluid helps replace the amniotic fluid and cushions the baby and cord.
Complications of a post-term pregnancy:
Women with post-term pregnancy, especially with a large baby, are more likely to have:
➤ Longer labor.
➤ Forceps or vacuum-assisted birth.
➤ Vaginal tearing or injury.
➤ Cesarean delivery.
➤ Infection, wound complications, and bleeding after birth.
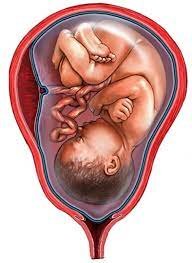
There are also risks for the fetus and newborn in a post-term pregnancy. These include:
➤ Stillbirth and newborn death.
➤ Placenta problems.
➤ Decreased amniotic fluid.
➤ The fetus may stop gaining weight, or may even lose weight.
➤ Birth injury if the baby is large.
➤ Baby breathes in fluid containing the first stool (meconium aspiration).
➤ Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) because the baby has too little glucose stored.
