Identifying Client’s Needs / Expectations/Responses to Actual or Potential Health Problems – Nursing is a profession within the healthcare sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other healthcare providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialisms with differing levels of prescriber authority.
Many nurses provide care within the ordering scope of physicians, and this traditional role has shaped the public image of nurses as care providers. However, nurses are permitted by most jurisdictions to practice independently in a variety of settings depending on training level. In the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced and specialized credentials, and many of the traditional regulations and provider roles are changing.
Nurses develop a plan of care, working collaboratively with physicians, therapists, the patient, the patient’s family, and other team members, that focus on treating illness to improve quality of life. Nurses may help coordinate the patient care performed by other members of an interdisciplinary healthcare team such as therapists, medical practitioners, and dietitians. Nurses provide care both interdependently, for example, with physicians, and independently as nursing professionals.
Identifying Client’s Needs / Expectations/Responses to Actual or Potential Health Problems
Nursing Process
Definition of Nursing Process:
Nursing process may be defined as a systematic problem solving approach used to identify, prevent and treat actual or potential health problems and promote wellness.
Or
The nursing process is a method of planning, organizing and delivering nursing care.
Or,
The nursing process has traditionally been defined as a systematic method for assessing health status, diagnosing health care needs, formulating a plan of care, initiating plan and evaluating the effectiveness of plan.
Or,
The nursing process is a treatment management process engaged in by nurse and client as a primary means of achieving specific health goals. Health goals can relate to wellness promotion, disease and illness prevention, health restoration and coping and altered functioning.
Or,
The nursing process is a series of organized steps designed for nurses to provide excellent care.
Or,
Nursing process is often defined as the application of critical thinking to client care activities.
Characteristic of Nursing Process:
1. The system is open, flexible, and dynamic.
2. It individualized the approach to each client’s particular needs.
3. It is planned.
4. It is goal-directed.
5. Tt is flexible to meet the unique needs of the client, family, or community.
6. it permits creativity for the nurse and client in devising ways to solve the stated health problem
7. it is interpersonal. it requires the nurse to communicate directly and consistently with clients to meet their needs
8. it is cyclical. since all steps are interrelated, there is no absolute beginning or end.
or
1. Dynamic.
2. Client centered.
3. Planned.
4. Purposeful
5. Interactive
6. Goal directed
7. Systematic
8. Interpersonal and collaborative. 9. Universally applicable.
10. Can focus on problems.
11. Theoretically based
12. Flexible
13. Interdependent
Advantages/Importance of Nursing Process:
The use of the nursing process has many advantages:
1. The nursing process provides a framework for meeting the individual needs of the client, the client’s family / significant other (s), and the community.
2. The steps of the nursing process focus the nurses attention on the individual human responses of a client / group to a given health situation, resulting in a holistic plan of care addressing their specific needs.
3. The nursing process provides an organized, systematic method of problem solving, which may minimize dangerous errors or omissions in care giving and avoid time-consuming repetition in care and documentation.
4. The use of nursing process promotes the active involvement of the client in his or her own health care, enhancing consumer satisfaction.
5. The use of the nursing process enables nurses to have more control over their own practice.
6. The use of the nursing process provides a common language for practice, unifying the nursing profession.
7. The use of the nursing provides a means of assessing nursing economic contribution to client care. The nursing process supplies a vehicle for the quantitative and qualitative measurements of nursing care than meets the goal of cost effectiveness and still promotes holistic care.
Purposes of Nursing Process:
1. To identify a client’s health status, actual or potential health care problems.
2. It assists to deliver optimum need-based nursing care to the patient effectively and intelligently.
3. To establish plans to meet the identified needs.
4. It helps to ensure continuity of care.
5. It guides nurses to take deliberate steps to identify client’s problems to set realistic goals and to intervene individualized Care.
6. It encourages for identification and utilization of client’s strength.
7. It enhances communication and inter-personal relationship with clients and team members.
8. It provides continuity of care by reducing omissions and duplications of actions.
9. It helps to keep a complete record of nursing care provided to the patient.
Nurses’ Roles in Nursing Process:
1. Scope of nursing practice.
- Principles for determining scope of practice.
2. Roles in different areas.
3. Level of critical thinking in nursing.
- Basic.
- Complex and
- Commitment
4. Continuing professional development.
5. Autonomy and accountability.
6. Caregiver.
7. Professional role.
8. Advocate.
9. Educator.
10. Communicator.
11. Manager.
12. Medication administrator.
13. Nurse researcher.
Benefits of Nursing Process:
A. Benefits for the cllent:
1. Quality clients care: The nursing care is planned to meet the unique needs of the individual, family or community. Continuous evaluation and reassessment of the client’s changing needs ensure an appropriate level of care.
2. Continuity of care: The written care plan is accessible to all the persons involved in the client’s care and it prevents the client from repeating information and preferences to each caretaker.
3. Participation by the client in their health cares: The process can help the clients to develop skills related to their health care and to become more committed to the goals of care.
B. Benefits for the nurse:
1. Consistent and systematic nursing education: The agency which accredits nursing education programs requires all graduates to be competent in using the nursing process.
2. Job satisfaction: Well-written care plans, has given the nurses to be confident about that nursing interventions which are based on correct identification of the clients problems, thus preventing the unco-ordinated, trail-and-error nursing. Plans can also instill a sense of pride when the goals of care are accomplished.
3. For professional growth: By evaluating the effectiveness of the nursing interventions, the nurse learns which interventions are most effective and which ones can be adapted to meet the needs of other clients. This process enhances the skill and expertise the nurse.
4. Meet professional standards: Learning and implementing the nursing process while providing client care is a basic requirement for professional nursing competence
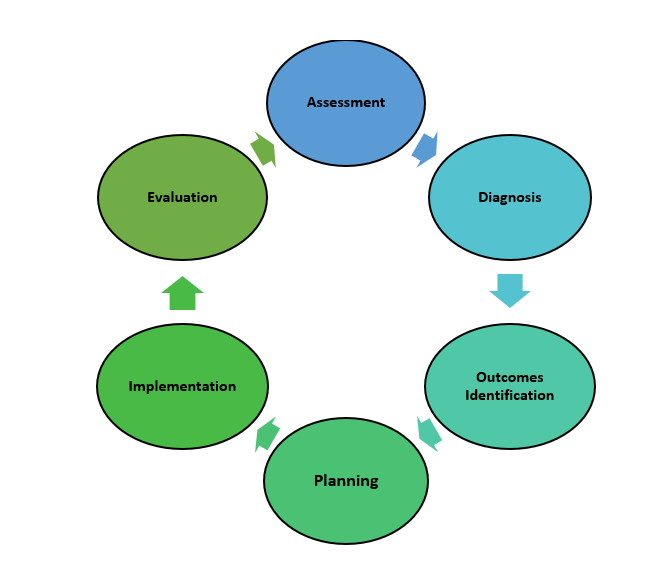
Steps of Nursing Process:
The five steps in nursing process are-
1. Assessment.
2. Nursing diagnosis.
3. Planning.
4. Implementation.
5. Evaluation.
A. Assessment: Assessment is the gather, verify, differentiate and impart data about the patient to establish a data base. It is done by collection of data through-
a) History taking.
b) Physical examination.
c) Review of investigations reports and
d) Record analysis.
It comprises comparison of data with the normal value and analysis of the data gathered to ascertain the client’s condition and identify problems.
B. Nursing diagnosis: The diagnosing phase involves a nurse making an educated judgment about a potential or actual health problem with a patient. Multiple diagnoses are sometimes made for a single patient. These assessments not only include an actual description of the problem (e.g. sleep deprivation) but also whether or not a patient is at risk of developing further problems.
C. Planning: Once a patient and nurse agree on the diagnoses, a plan of action can be developed. If multiple diagnoses need to be addressed, the head nurse will prioritize each
assessment and devote attention to severe symptoms and high risk factors.
Planning includes-
a) Establishing goals.
b) Setting priorities.
c) Determining resources.
d) Stating nursing strategies and
e) Assigning care.
D. Implementation: The implementing phase is where the nurse follows through on the decided plan of action. This plan is specific to each patient and focuses on achievable outcomes.
Actions involved in a nursing care plan include monitoring the patient for signs of change or improvement, directly caring for the patient or performing necessary medical tasks, educating and instructing the patient about further health management, and referring or contacting the patient for follow-up. Implementation can take place over the course of hours, days, weeks, or even months.
E. Evaluation: Once all nursing intervention actions have taken place, the nurse completes an evaluation to determine of the goals for patient wellness have been met. The possible patient outcomes are generally described under three terms: patient’s condition improved, patient’s condition stabilized, and patient’s condition deteriorated, died, or discharged. In the event the condition of the patient has shown no improvement, or if the wellness goals were not met, the nursing process begins again from the first step.
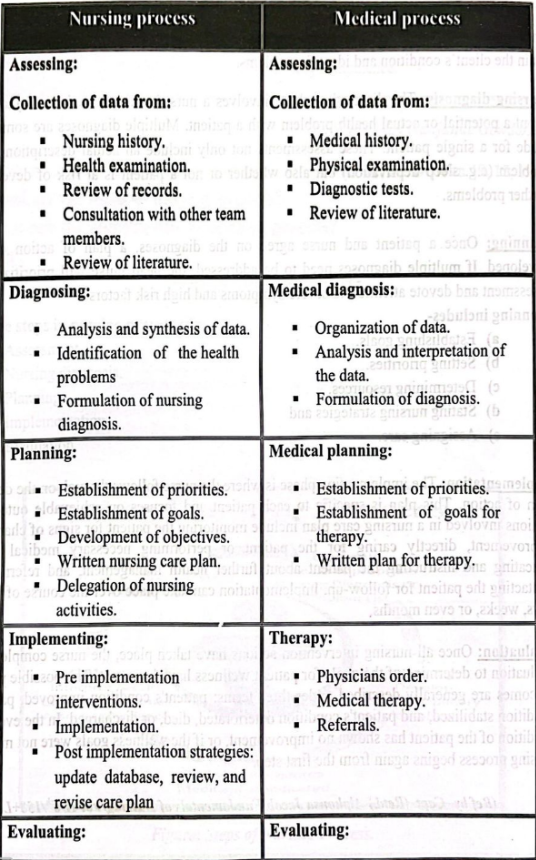
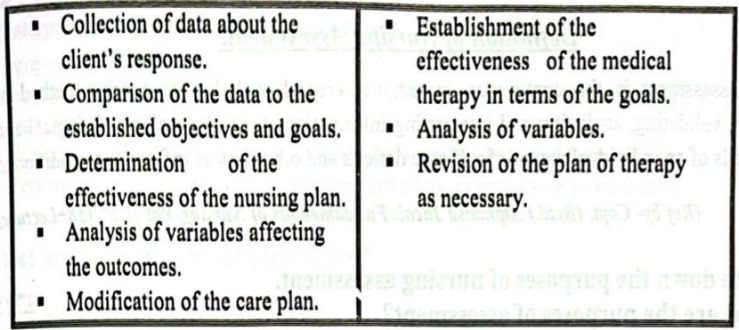
Difference between Nursing Process and Medical process: