Pregnancy induced hypertension – This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
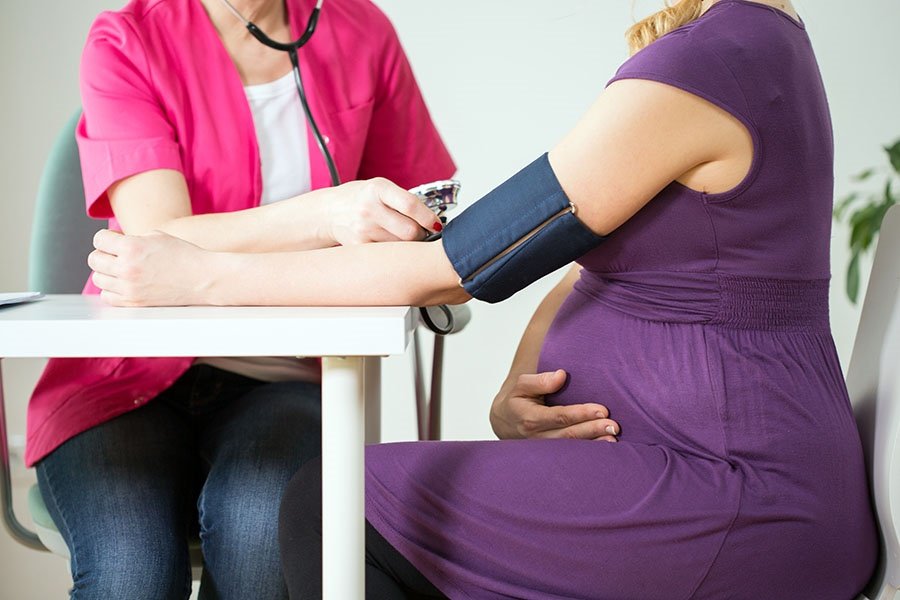

Pregnancy induced hypertension
Definition of Pregnancy Induced Hypertension (PIH):
It is defined as the hypertension that developed as a direct result of the gravid state for the first time in a previously normotensive patient,
Or,
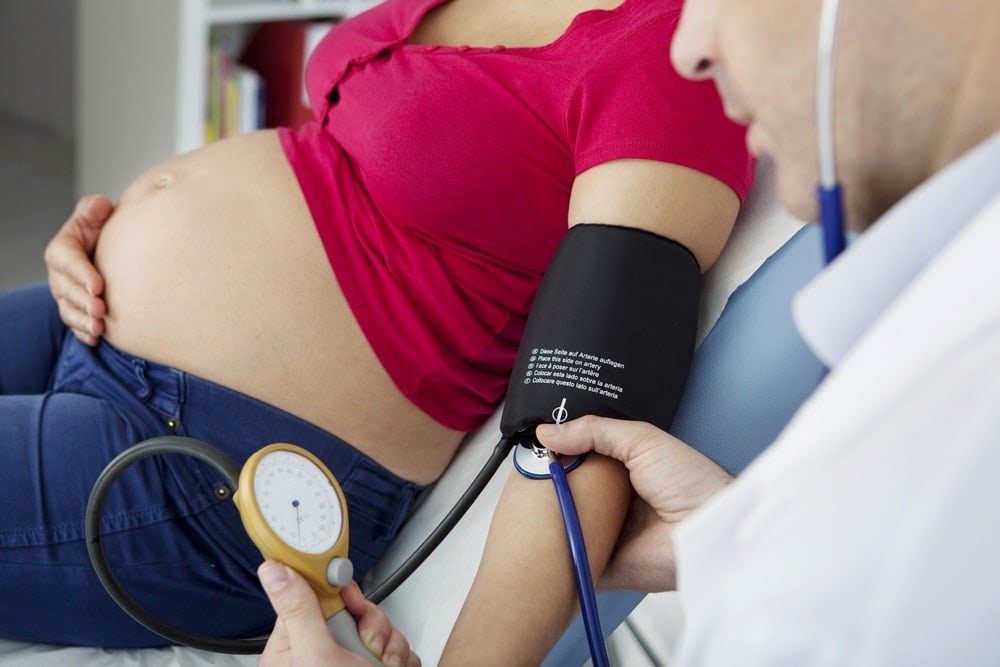
Gestational hypertension or pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) is the development of new hypertension in a pregnant woman after 20 weeks gestation without the presence of protein in the urine or other signs of preeclampsia.
Component of PIH:
- Gestational hypertension
- Preeclampsia
- Eclampsia
Classification of Hypertensive Disorder In Pregnancy:
1. Gestational hypertension: Without proteinuria or pathological edema
2. Preeclampsia (PET): Hypertension and proteinuria with or without pathological edema
3. Eclampisa: Preeclampsia complicated with convulsion and or coma
4. Chronic hypertension:
- Essential hypertension
- Chronic renal disease
- Thyrotoxicosis
- Pheochromocytoma
- Connective tissue disease eg. SLE
5. Preeclampsia or eclampsia superimposed on chronic hypertension
Predisposing Factors of PIH or Eclampsia or Preeclampsia:
1. Primigravidae (young and elderly)
2. Family history of HTN, preeclampsia and eclampsia
3. Genetic
4. Immunologic phenomenon
5. New paternity
6. Polyhydramnios
7. Preexisting vascular or renal disease
8. Placental abnormalities:
- Poor placental circulation: Decreased trophoblast invasion
- Hyperplacentosis: Multiple pregnancies, Rh incompatibility, DM
- Placental ischemia
- Molar pregnancy
9. Thrombophilias (anti-phosphoripid syndrome & protein C & S deficiency)
