Properties of Homeostasis – Introduction to fundamental concepts of Biological Science including the organization and common characteristics of living matters, cell structures and functions, food production by photosynthesis, harvesting energy, mechanism of cells reproduction, genetics, evolutions, and Human Biology. Introduction to general chemistry including basic concepts about matter, atomic structure, chemical bonds, gases, liquid, and solids, solutions, chemical reactions, acid, bases, and salt;
organic and biochemistry including hydrocarbons and their derivatives, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, enzymes, vitamins, and minerals, nucleic acids; principles of physics and applications to nursing including gravity and mechanics, pressure, heat and electricity; nuclear chemistry and nuclear physics, effects of radiation on human beings, and protection and disposal. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in general biological science, general chemistry and physics.
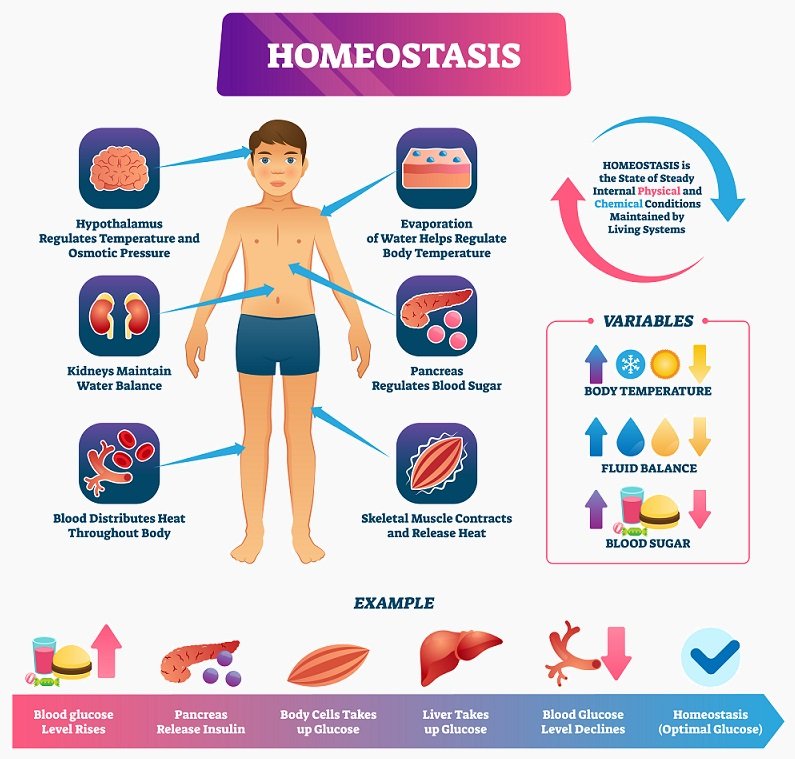
Body Organization & Homeostasis
Definition of Homeostasis:
Homeostasis means maintenance of nearly constant conditions in the internal environment. All the organ & tissues of the body performs specific functions that help to maintain these constant conditions.
For example –
- The lungs provide O2 to the ECF to replenish the O2 that is being used by the cells.
- The kidneys maintain constant ion concentration.
- The GIT system provides nutrients to the body.
In 1929 the American physiologist Walter Cannon (1871-1945) coined the term homeostasis
Properties of Homeostasis
- Homeostasis is highly developed in warm-blooded animals living on land.
- It maintains body temperature, fluid balance, blood pH, and oxygen tension within rather narrow limits, while at the same time obtaining nutrition to provide the energy to maintain homeostasis.
Systems Involved in Homeostasis Mechanism:
The systems that involved in homeostasis mechanism are-
1. Nervous system
2. Endocrine system (Hormonal regulation).
A. Nervous system: It is composed of 3 parts –
- Sensory input portion (sensory receptor)
- The central nervous system.
- Motor output portion.
A large segment of the nervous system is called the autonomic system. It control many functions of the internal organs such as pumping activity of the heart, motility of GIT & secretion of glands.
B. Endocrine system: It is regulated by hormones. Hormones are transported in the ECF to all parts of the body to regulate cellular functions.
e.g
- Insulin: Control glucose metabolism.
- Thyroid hormones: It helps to co-ordinate the rate of the body activity
- Parathyroid hormones: Controls Ca++ & PO4 metabolism
The nervous system regulates mainly muscular and secretory activities of the body, whereas the hormonal system regulates mainly metabolic functions.

