Qualitative Research & Quantitative Research – In its most common sense, methodology is the study of research methods. However, the term can also refer to the methods themselves or to the philosophical discussion of associated background assumptions. A method is a structured procedure for bringing about a certain goal, like acquiring knowledge or verifying knowledge claims. This normally involves various steps, like choosing a sample, collecting data from this sample, and interpreting the data. The study of methods concerns a detailed description and analysis of these processes. It includes evaluative aspects by comparing different methods.
In this way, their benefits and drawbacks are evaluated, as well as the research goals for which they may be used. These descriptions and evaluations are predicated on philosophical background assumptions; examples include how to conceptualize the phenomena under study and what constitutes evidence in favor of or against them. In its broadest sense, methodology encompasses the discussion of these more abstract issues.
Qualitative Research & Quantitative Research
Qualitative Research:
Qualitative research is a method of inquiry that develops understanding on human and social sciences, to find the way people think and feel.
Or
By qualitative research we can identify and explore a number of often related variables that give insight into the nature and causes of certain problems and into the consequences of the problems of those affected.

Uses/Purposes:
- To explore a topic about which little is known in order to provide insights for interventions.
- To develop appropriate questionnaire at the early stage of study.
- To validate quantitative data.
- To complement the quantitative component of a study by providing concrete examples or explaining observed practices.
- To develop appropriate materials for educational interventions.
- To identify problems in ongoing interventions.
- To assess the impact of ongoing or completed interventions.
(Ref by-Selim reza/The essentials of community medicine/15/699)
Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is a research method that is used to generate numerical data and hard facts, by employing statistical, logical and mathematical technique. By quantitative research we can quantify the size, distribution and association of certain variables in a study population.
Quantitative research asks-
- How many?
- What is the relationships between the variables?
Positive methods of quantitative’ research
- Survey
- Epidemiological studies
- Study of data from records.
(Ref by-Selim reza/The essentials of community medicine/15/699)

Difference between Qualitative Research & Quantitative Research:
| Basis for Comparison | Qualitative Research | Quantitative Research |
| 1. Meaning | Qualitative research is a method of inquiry that develops understanding on human and social sciences, to find the way people think and feel. | Quantitative research is a research method that is used to generate numerical data and hard facts, by employing statistical, logical and mathematical technique. |
| 2. Nature | Holistic | Particularistic |
| 3. Approach | Subjective | Objective |
| 4. Research type | Exploratory | Conclusive |
| 5. Reasoning | Inductive | Deductivg |
| 6. Sampling | Purposive | Random |
| 7. Data | Verbal | Measurable |
| 8. Inquiry | Process-oriented | Result-oriented |
| 9. Hypothesis | Generated | Tested |
| 10. Elements of analysis | Words, pictures and objects | Numerical data |
| 11. Objective | To explore and discover ideas used in the ongoing processes. | To examine cause and effect relationship between variables. |
| 12. Methods | Non-structured techniques like In-depth interviews, group discussions etc. | Structured techniques such as surveys, questionnaires and observations. |
| 13. Result | Develops initial understanding | Recommends final course of action |
Criteria for selecting a research topic
1. Importance
2. Relevance
- How large or widespread is the problem
- Who is affected.
- How severe is the problem
3. Avoidance of duplication
4. Feasibility and answerability
5. Political acceptability.
6. Applicability
7. Urgency of data needed
8. Ethical acceptability
(Ref by- Handout)
Sequence of Steps in a Research Work/Process
The following steps of research process are as follows:
1. Problem identification
2. Knowledge gathering about the problem and finding lacunae in the existing knowledge.
3. Problem statement
4. Precise statement of research questions or hypothesis formulation.
5. Statement of objectives of research.
6. Planning research.
7. Selection of research design and methodology.
8. Planning data collection.
9. Data collection.
10. Data analysis, interpretation of findings and drawing of inferences.
11. Writing research report based on the data.
12. Dissemination of research findings through publication of report or presentation in a seminar
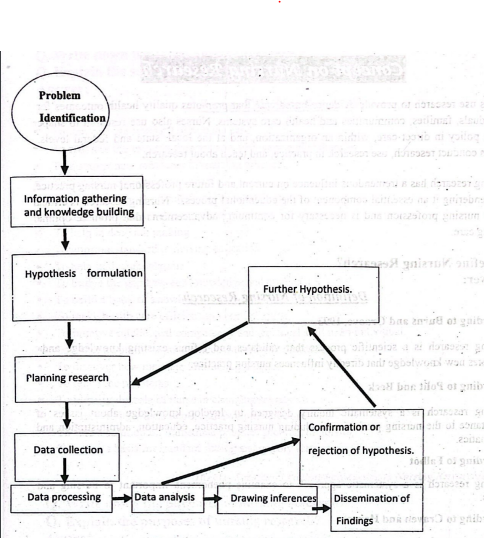
(Ref by-Sadeka Tahera Khanom/Research Methodology/24/15)
