Regulating the Cell Cycle – Introduction to fundamental concepts of Biological Science including the organization and common characteristics of living matters, cell structures and functions, food production by photosynthesis, harvesting energy, mechanism of cells reproduction, genetics, evolutions, and Human Biology. Introduction to general chemistry including basic concepts about matter, atomic structure, chemical bonds, gases, liquid, and solids, solutions, chemical reactions, acid, bases, and salt;
organic and biochemistry including hydrocarbons and their derivatives, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, enzymes, vitamins, and minerals, nucleic acids; principles of physics and applications to nursing including gravity and mechanics, pressure, heat and electricity; nuclear chemistry and nuclear physics, effects of radiation on human beings, and protection and disposal. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in general biological science, general chemistry and physics.
Regulating the Cell Cycle
Definition of Cell Cycle:
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) to produce two daughter cells.
or
The cell cycle is a cycle of stages that cells pass through to allow them to divide and produce new cells. It is sometimes referred to as the “cell division cycle” for that reason.
Function of Cell Cycle
- Because cells reproduce by dividing, new “daughter” cells are smaller than their parent cells, and may inherit the bare minimum of cellular machinery they need to survive.
- Before these daughter cells can divide to produce still more cells, they need to grow and reproduce their cellular machinery.
- The importance of the cell cycle can be understood by doing simple math about cell division. If cells did not grow in between divisions, each generation of “daughter” cells would be only half the size of the parent generation. This would become unsustainable pretty quickly!
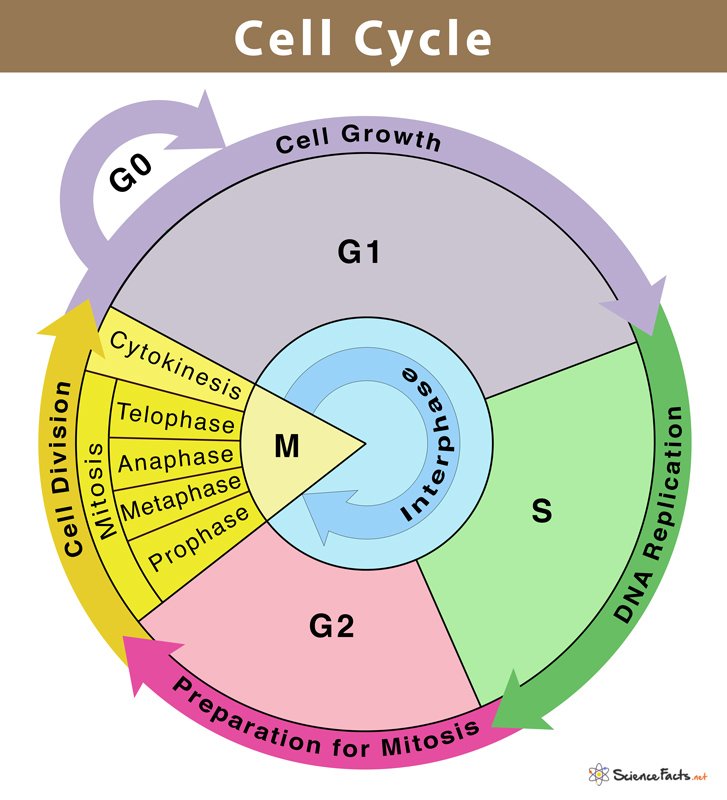
Phases of Cell Cycle
| State | Phase | Abbreviation | Description |
| Resting | Gap 0 | Go | A phase where the cell has left the cycle and has stopped dividing, |
Interphase | Gap 1 | G |
|
| Synthesis | s |
| |
| Gap 2 | Gap 2 |
| |
| Cell division | Mitosis | M |
|