Retinal detachment – This course is designed to understand the concept of community health nursing: nurses’ roles and interventions in family health, school health, occupational health, environmental health, elderly health care, gender issues, disaster management and principles and terminology of epidemiology. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in community health nursing.
Retinal detachment
Definition of Retinal Detachment:
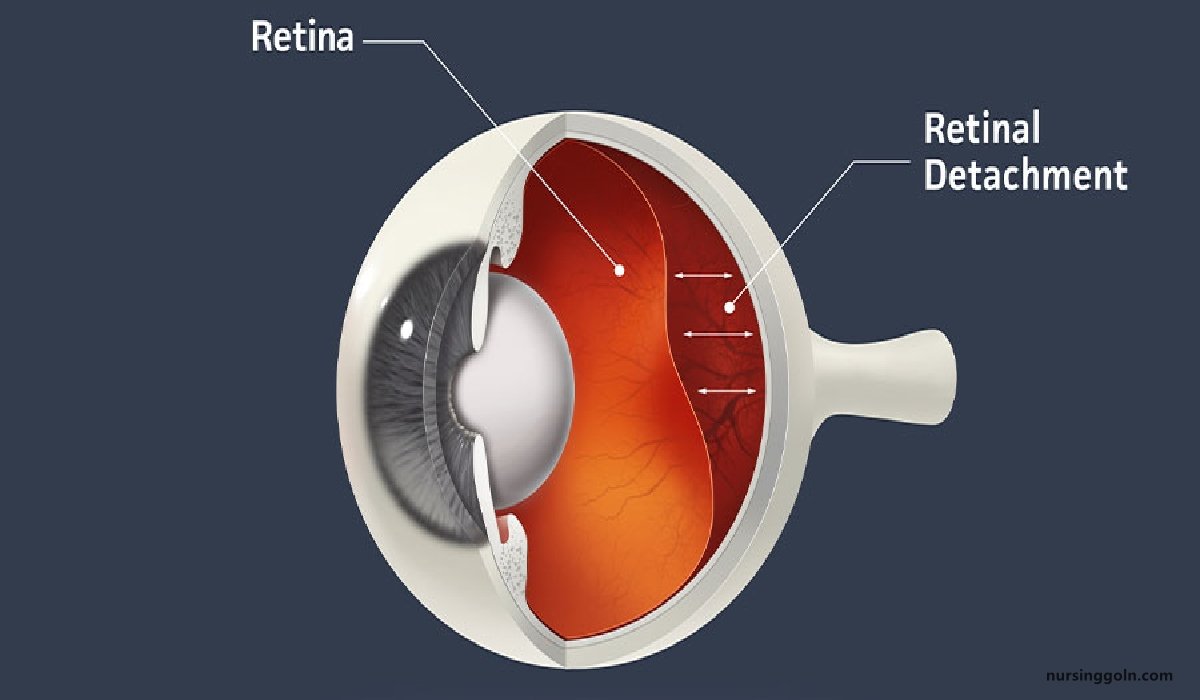
Retinal detachment is a disorder of the eye in which the retina separates from the layer underneath. Symptoms include an increase in the number of floaters, flashes of light, and worsening of the outer part of the visual field.
Signs and symptoms Retinal detachment:
A retinal detachment is commonly preceded by a posterior vitreous detachment which gives rise to these symptoms:
- Flashes of light (photopsia)- very brief in the extreme peripheral (outside of center) part of vision
- A sudden dramatic increase in the number of floaters
- A ring of floaters or hairs just to the temporal (skull) side of the central vision.
Although most posterior vitreous detachments do not progress to retinal detachments, those that do produce the following symptoms:
- A dense shadow that starts in the peripheral vision and slowly progresses towards the central vision
- The impression that a veil or curtain was drawn over the field of vision
- Straight lines (scale, edge of the wall, road, etc.) That suddenly appear curved (positive ambler grid test)
- Central visual loss
Causes of Retinal Detachment:
Retinal-detachment can occur as a result of –
- Shrinkage or contraction of the vitreous (the gel like materials that fills the inside of eye)
- Injury
- Advanced diabetes
- An inflammatory eye disorders
- Aging> 40 years
- In certain inflammatory condition
- Retinal tear
- Previous severe injury or trauma in eye
- Extreme(myopia)
- Previous eye surgery
Risk Factors
The following factors increase your risk of retinal-detachment:
- Aging-retinal-detachment is more common in people over age 50
- Previous retinal-detachment in one eye
- A family history of retinal-detachment
- Extreme nearsightedness (myopia)
- Previous eye surgery, such as cataract removal
- Previous severe eye injury
- Previous other eye disease or inflammation.

Management of Retinal Detachment:
➤ Patient is placed in the position instructed by the surgeon and eye patch is placed over both eye to restrict the movement
➤ Preoperative medications are applied as per instructions
➤ Face is washed with antibacterial solutions
➤ Patient is instructed not to touch the eyes.
➤ Asepsis is followed while using eye medications
➤ Postoperatively the patient is instructed against coughing sneezing, rapid movements of head, bending the head below the waist level, straining.
➤ Patient has to be assisted in his activities
➤ Proper instructions is given to the patients like to avoid driving, avoid rapid eye movements for several weeks,
➤ Patient has to be advised to avoid fall, jerks and bumps.
➤ Patient is advised to resume lighter activities in 3 weeks and heavier in 6-8 weeks.
Specific management:
➤ To provide sedation to the patient
Surgery if necessary
➤ Retinal-detachment can be prevented by timely recognition of retinal breads and sealing it with photocoagulation or cryotherapy.