Second Stage Of Labor – This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
Second Stage Of Labor
2nd stage of labour:
The second stage begins with the complete dilation of the cervix and ends with the expulsion of the fetus. This stage is concerned with the descent and delivery of the fetus through the birth canal. Second stage has two phase:
a. Propulsive: from full dilation until head touches the pelvic floor.
b. Expulsive: Since the time mother has irresistible desire to hear down and push until the baby is desired.
Clinical features of 2nd stage of labour:
1. Pain: The intensity of pain increases.
2. Membranes status: Membrane may rupture with a gush of liquor per vaginam.
3. Descent of the fetus.
4. Abdominal examinations:
- progressive descent of the head, assessed in relation to the brim,
- Rotation of the anterior shoulder to the midline and change in position of the fetus.
- Shifted of the fetus sound downward and medially.
5. P/V findings:
a. Descent of the head in relation to ischial spies.
b. Gradual rotation of the head evidenced by position of the sagittal suture and the occiput in relation to the quadrants of the pelvis.
c. Perineum progressively bulges during pain.
d. Vaginal introits open up and hairy head shows.
e. Cervix not palpate.
6. During the second stage, the cervix is fully dilated.
7. Some women may feel the urge to push right away or soon after they’re fully dilated.
8. The baby may still be high up in the pelvis for other women. It may take some time for the baby to descend with the contractions so that it’s low enough for the mother to start pushing.
9. Women who don’t have an epidural typically have an overwhelming urge to push, or they have significant rectal pressure when the baby is low enough in the pelvis.
10. Women with an epidural may still have an urge to push and they may feel rectal pressure, although typically not as intensely. Burning or stinging in the vagina as the baby’s head crowns is also common.
11. Vaginal signs: As the head descends down, it distends the perineum, the vulval opening looks like a slit through which the scalp hair is visible.
12. Maternal signs:
a. There are features of exhaustion.
b. Respiration is however, slowed down with increased perspiration.
c. During the bearing down efforts, the face becomes congested with neck veins prominent.
13. Fetal effects: Slowing of FHR during contractions is observed, which comes back to normal before the next contraction.
Management of 2nd Stage of Labour:
1. Confirmation of 2nd stage of labour by –
a) Character of pain
– Intensity
– Interval between pains
– Duration of contraction
– Bearing down pain.
– Cervix fully dilated
b) Rupture of membranes with gush out liquor
c) After rupture of membranes P/V exam done to confirm 2nd stage
– Further confirmation presenting part
– Character of liquor
– To exclude cord prolapsed
2. After confirmation, the patient is shifted to the labour room
3. Psychological support is given
4. All diet by mouth withheld if necessary nutrition maintained by IV fluid
5. Monitoring of maternal and fetal condition: Pulse, BP, Temperature, Dehydration
a) Per abdominal examination:
– Fetal heart rate
– No uterine contraction/10 minutes
– Duration of uterine contraction
– Head fully engaged or not
b) Per vaginal examination to see
– Station of presenting part
– Degree of rotation of presenting part
– Dilatation and effacement of cervix
– Membranes ruptures-condition of liquor
6. If bladder is full catheterize modified dorsal position of the patient knee hip flexed buttock at the edge of labour table
7. When crowing occurs the patient is asked to bear down at the time of contraction
8. With crowing of the head episiotomy is given either after local infiltration with 1% xylocaine or after pudendal block
9. Head of the fetus/baby is to be maintained in a flexed position
10. Delivery of head is done by extension in between contractions of uterus with guard over the perineum
11. Following delivery of the head, mouth and nose are cleaned
12. After delivery of anterior shoulder posterior shoulder is delivered by drawing the baby’s head in upward direction towards the mother’s abdomen
13. Then trunk is delivered by lateral flexion
14. Then the baby is put on a tray with head slightly tilled downwards
15. The cord is to be clamped at 2 places and cord is divided in between the clamps after cessation of cord pulsation
16. Immediate care of the new born –
– Wrapped well with dry cloths
– Mouth and nose cleaned with sucker
– Mild stimulated to make it cry
– Identification
Nursing considerations:
Care of the Woman During the Second Stage:
Nursing Interventions:
– Provide client support
– Assess and record v/s, FHR, uterine contractions
– Prepare place of birth in advance
– Convert the labor room to birth room
– Make the client select positioning for birth
– Promote second stage pushing
– Clean perineum with warm antiseptic before birth
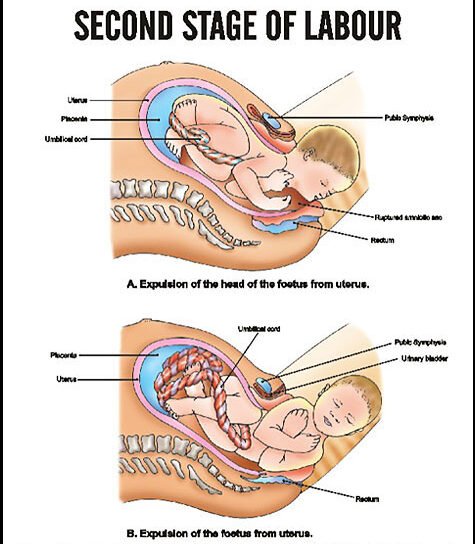
As soon as head is about 8cm across:
– Perform the Ritgen’s maneuver
– Encourage the woman to continue pushing until the occiput of fetal head is firmly a the pubic arch
– Once head is delivered
– Note time of birth, announce sex of infant
– Cut and clamp the cord
– Introduce infant to initiate parent child relationship.
Complication of Second Stage of Labour:
1. Delayed second stage due to mal-position
2. Fetal distress
3. Cord prolapsed
4. Shoulder dystocia
5. Arrest of the after coming head of the breech
6. Air embolism
7. Maternal distress
