Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) – This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
Definition of Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs):
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), or sexually transmitted infections (STIs), are generally acquired by sexual contact. The organisms that cause sexually transmitted diseases may pass from person to person in blood, semen, or vaginal and other bodily fluids. Sometimes these infections can be transmitted nonsexually, such as from mother to infant during pregnancy or childbirth, or through blood transfusions or shared needles.
Or
Sexually transmitted diseases may be defined as infections acquired daring heterosexual or homosexual intercourse with an infected partner.
Or
STDs are the diseases which are predominantly transmitted by through sexual (or intimate) contact from an infected partner.
Common STDs:
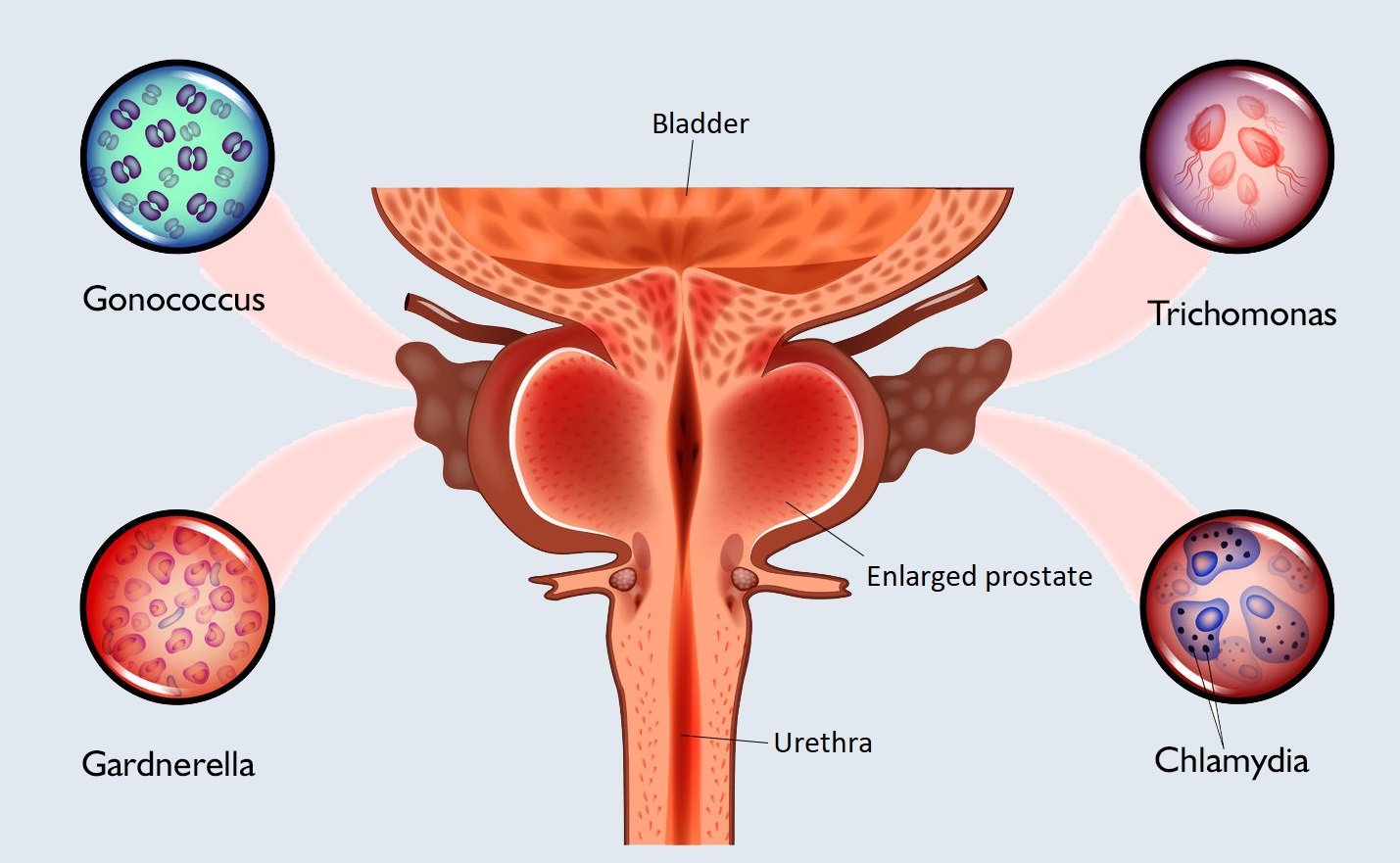
1. Syphilis
2. Gonorrhoea
3. Chancroid (Soft sore)
Other STD:
1. HIV infection & AIDS.
2. Genital human papillomavirus. 3. Chlamydia trachomatis infection.
4. Lymphogramaloma venereum.
5. Genital mycoplasma.
6. Granuloma inguinale.
7. Genital herpes.
8. Trichomoniasis
9. Vulvovaginal pubis.
10. Pediculosis pubis.
11. Genital molluscum contagiosum.
12. Genital scabies.
STD become a common glebat problem. Because-
a.Migration of people from one country to another.
b. Sexual promiscuity.
c. Homosex
d. Increased number of sexual partners due to increased divourzes unstable relationships.
e. Alcohol & drugs
f. Sexual experience at younger age
g.Lack of co-ordination among the government, international agencies and world leaders to
solve the problem at early stage
h. Poverty
i. Lack of awareness about sade se
J. Lack of sex education.
k. Superstition.
Important STDs with causative agent:
1. Gonorrhea: Neisseriagonorrhoeae.
2. Syphilis: Treponema pallidum.
3. Genital warts: Human papilloma virus.
4. Hepatitis: Hepatitis B & C viruses
5. Monilial vaginitis: Candida albicans
Prevention of STD
Primary prevention:
1. Encouraging safer sexual behavior like:
- Correct and consistent use of condom.
- Non preventive sex and abstinence.
- Safe sex with trusted partner.
2. Creating health awareness by mobilizing all education channels.
3. Prevent early sexual life.
Secondary prevention
a. Education, investigation and treatment of targeted population ie those who have placed themselves at risk of infection e.g, sex workers, migrant people and frequent travelers.
b.By promoting STI care seeking behavior
c. Ensuring a continuous supply of highly effective drugs and condom
d. Providing skilled health care providers for comprehensive management of KTI/STI syndrome.
e. Ensuring all women amending ANC and family planning clinic though asymptomatic
f. Contact tracing and treating contacts of infected persons.
Long term effect of STDs on fallopian tubes:
4. Salpingitis
3. Ectopic pregnancy
6. Tubal block
7. Sterility