Anterior shoulder dislocation – An orthopedic nurse is a nurse who specializes in treating patients with bone, limb, or musculoskeletal disorders. Nonetheless, because orthopedics and trauma typically follow one another, head injuries and infected wounds are frequently treated by orthopedic nurses.
Ensuring that patients receive the proper pre-and post-operative care following surgery is the responsibility of an orthopedic nurse. They play a critical role in the effort to return patients to baseline before admission. Early detection of complications following surgery, including sepsis, compartment syndrome, and site infections, falls under the purview of orthopedic nurses.
shoulder dislocation
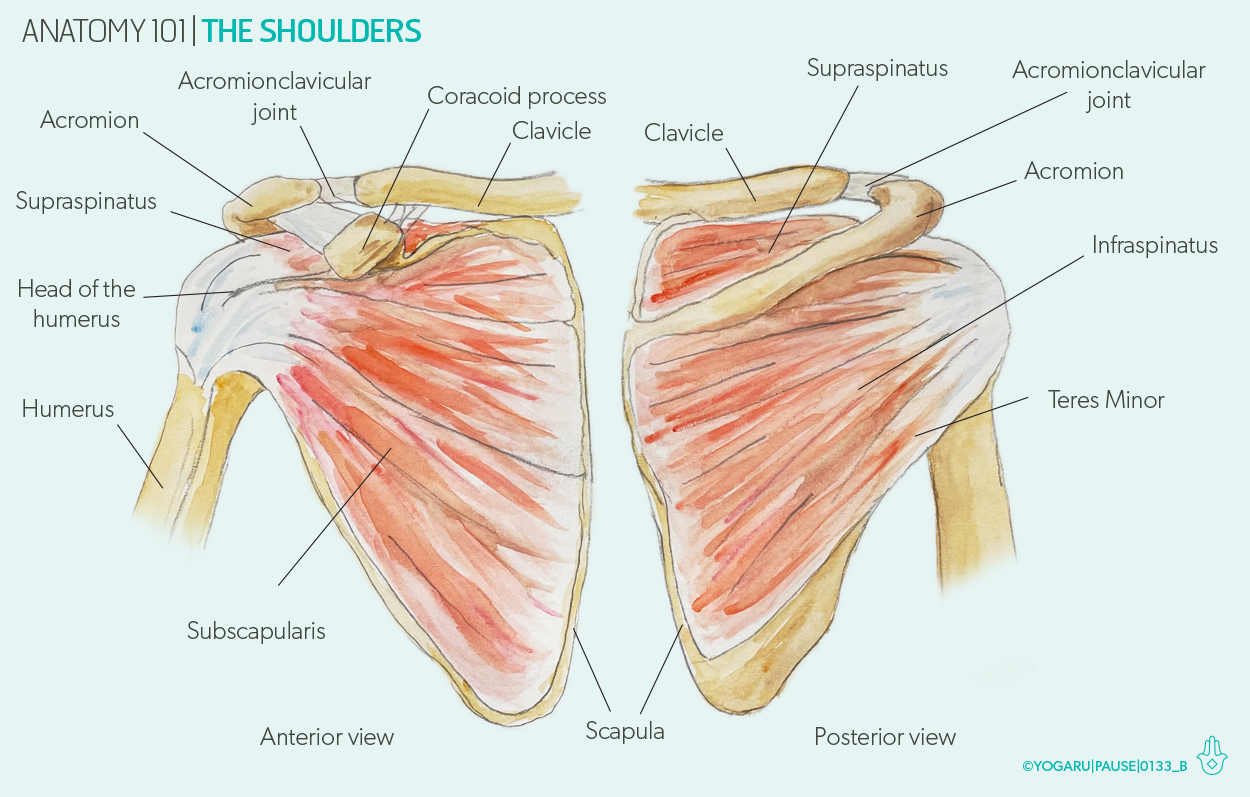
Shoulder dislocation:
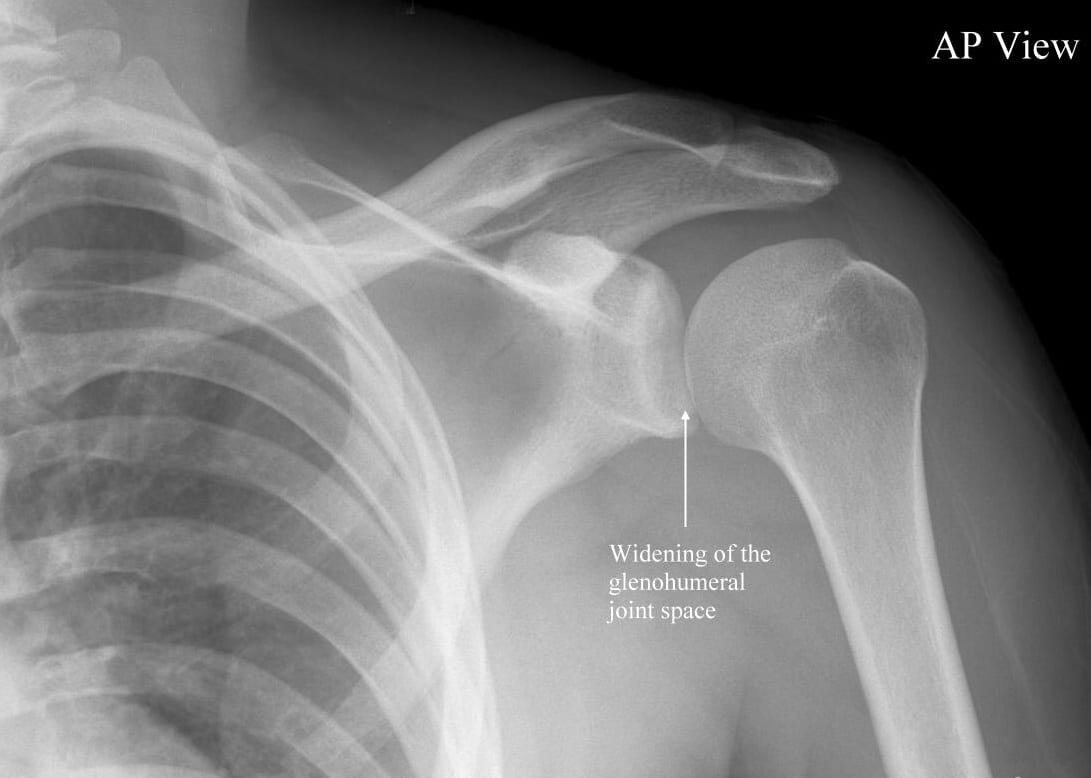
Displacement of the humerus from the glenoid cavity due to high velocity trauma on shoulder is known as shoulder dislocation.
[Ref-Apleys, System of Orthopedics and Fractures, 9th edition, Page-739]
Factors responsible for shoulder dislocation:
1) Shallowness of the glenoid socket.
2) Extraordinary range of movement.
3) Ligamentous laxity.
4) GLenoid dysplasia.
5) Sheer vulnerability of the joint during stressful activity of the upper limb.
[Ref-Apleys, System of Orthopedics and Fractures, 9th edition, Page-739,740]
Classifications of shoulder dislocation:
1) Anterior dislocationof shoulder (95%).
a) Sub- glenoid. a
b) Sub-coracoid.
c) Sub-clavicular.
2) Posterior dislocation of shoulder (5%).
3) Inferior shoulder dislocation (rare).
[Ref-Dr. Jahir’s “Surgery 1st Paper”, 4″ edition, Page-537]
Clinical features of shoulder dislocation:
A. History of patients:
1. H/O trauma, fall from tree, physical assault,
2. Plying-Cricket bowler, badminton.
B. Symptoms:
1) Severe pain on the affected shoulder.
2) Inability to move the limb.
3) Patient s supports his limb with other hand in slight abduction.
C. Signs:
1. Pain increase on movement.
2. Flattening of affected shoulder.
3. Restricted movement.
4. Dugas test: (positive) The patient is unable to touch the opposite shoulder with the affected shoulder.
5. Hamilton ruler test: Positive.
6. Callaways test: positive.
Definitions Hamilton ruler test:
It is a physical examination technique in which straight ruler applied on the upper arm to see, ruler touches the acromion process and lateral epicondyle for
Physical examination: Sit the patients on chair or stands the patients straightly. A physician applied a ruler on the shoulder to lateral epicondyle diagnosis of shoulder dislocation.
Normally straight ruler could not touch the acromion process to lateral epicondyle of the humerus. This is because of presence of greater tuberosity of humerus which pushes the ruler away from the acromion process.
But it is possible in shoulder dislocation patients. This test known as Hamilton ruler test.
[Ref-S.Das,clinical Surgery, 5th edition, Page-134]
Callaways test:
In case of shoulder dislocation, Axillary of the affected side are lowered and so the girth of the axilla is increased.
Management of shoulder dislocation:
A. General management:
1) Complete bed rest.
2) Immobilization of the affected limb for 3-4 weeks.
3) Immobilization with collar and cuff sling with triangular bandage.
B. Specific management:
1) In Hippocrate methods: Gently increasing the traction is applied to the arm with the shoulder in slight abduction, while in assistant applies firm counter traction to the body.
2) In Kochers methods: Closed reduction under G/A
3) If unsuccessful open reduction under G/A.
[Ref-Apleys, System of Orthopedics and Fractures, 9th edition, Page-739,740]
Complications of shoulder dislocation:
A) Early complications:
1) Rotator cuffs tear.
2) Nerve injury.
3) Vascular injury.
4) Fracture-dislocation.
B) Late complications:
1) Shoulder stiffness.
2) Unreduced dislocation.
3) Recurrent dislocation
[Ref-Apley’s “System of Orthopaedics and Fractures” 9th edition, page-741]
Nursing care management for shoulder dislocation:
A. Preoperative nursing care:
1) Keep the patients in comfortable positions.
2) Give analgesics to reduce the pain
3) Carry out an x ray to confirm the diagnosis.
4) Take the decision of operation.
5) Take the written consent from patients or attendants.
6) Give mental supports to reduce fear.
7) Explain the benefits of operation.
8) Carry out all investigation as well as confirm for G/A fitness.
9) Clean the operative area specially hair removing if present.
10) Keep the patients in NPO status from night,6-8 hours prior to operation.
11) Start an i/v line on opposite limb and give the premedication injection like Inj. Rantac, Inj.perinorm, Inj TT, Inj. xylocaine as per the instruction of the surgeon or anaesthesist.
B. Post operative nursing care:
1) After the patients regains consciousness and is shifted to ICU ,shoulder is immobilized by application of a body bandage using 4 or 6″ bandage rolls after sufficient padding of the axilla or by using commercially available shoulder harness.
2) A colar and cuff sling is used to support the limb.
C. Fllow up care:
1) Ensure the body bandage is in position. If it has loosened,tighten it up.
2) Adjust and tighten the sling.
3) Check for any skin allergy, excoriation etc.
4) If the bandage is solid, change it.
5) Instruct the patient to carry out the day to day functional activities with the unaffected arm.
6) Active finger exercise for the affected limb and active exercise for all joints of the unaffected extremity.
7) After 3-4 weeks, gradual mobilization and strengthening exercise of the shoulder has to be done under the guidance of a physiotherapist.
[Ref-BT. Basavanthappa, Orthopedics for nurses, 1″ edition,page-181]