Skeletal system – The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Skeletal system
SKELETAL SYSTEM
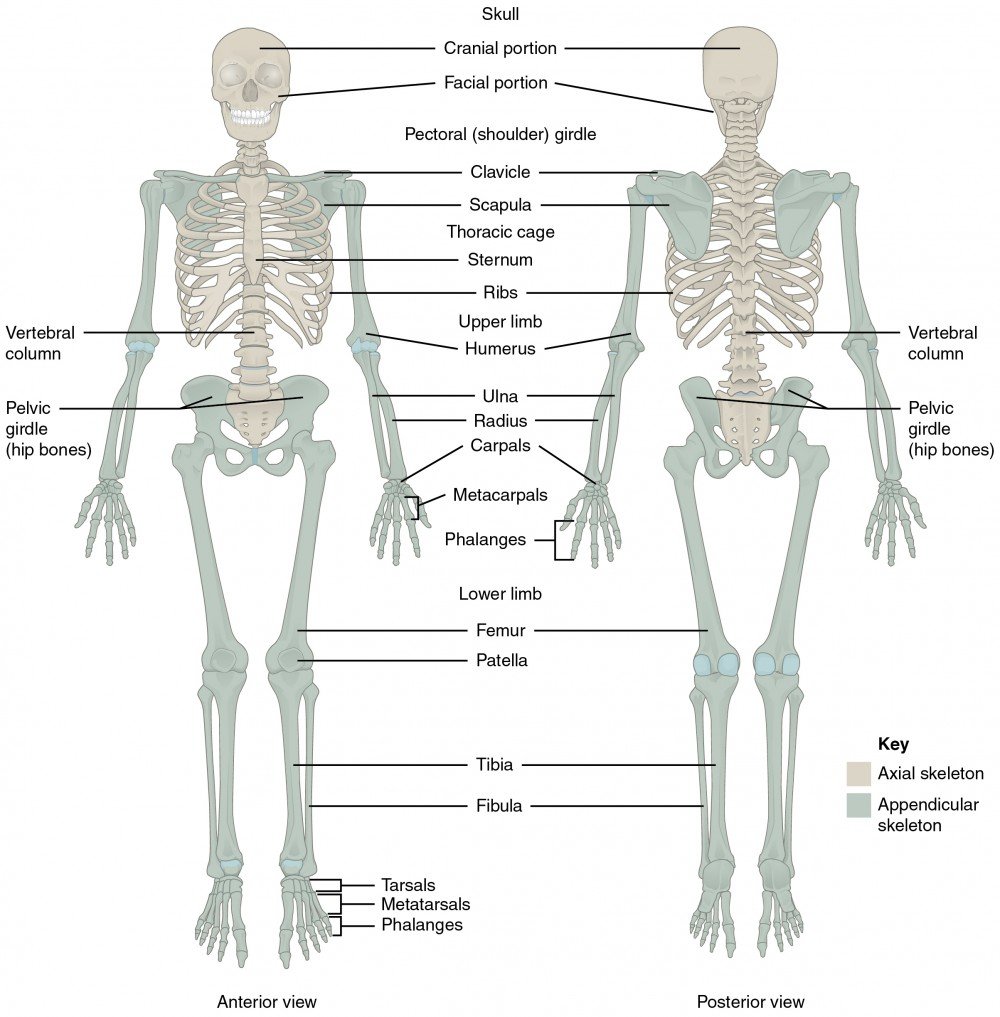
The skeletal system consisting of bones and other connective tissues, that provides the framework and support for our bodies muscles, tissues, nerves and skin. It also protects vital organs, allows movement, stores minerals and, through marrow, produces blood cells. The human body has 206 bones. These bones serve as a framework on which organs, muscles and tissue attach
Parts of the skeletal system are as
- Bones (skeleton)
- Joints
- Cartilages
- Ligaments (bone to bone)
- Tendon = (bone to muscle)
Functions of skeletal system
Bone tissue and the skeletal system perform several basic functions:
1. Support: The skeleton provides a structural framework for the body by supporting soft tissues and providing points of attachment for the tendons of most skeletal muscles.
2. Protection:The skeleton protects many internal organs from injury For example, cranial bones protect the brain, vertebrae (backbones) protect the spinal cord, and the ribcage protects the heart and lungs.
3. Assistance in movement: Because most skeletal muscles attach to bones, when muscles contract, they pull on bones. Together bones and muscles produce movement.
4. Mineral homeostasis: Bone tissue stores several minerals, especially calcium and phosphorus. On demand, bone releases minerals into the blood to maintain critical mineral balances (homeostasis) and to distribute the minerals to other parts of the body
5. Blood cell production: Within certain bones a connective tissue called red bone marrow produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, a process called hemopoiesis. Red bone marrow consists of developing blood cells, adipocytes, fibroblasts, and macrophages.
It is present in developing bones of the fetus and in some adult bones, such as the pelvis, ribs, sternum (breastbone), vertebrae (backbones), skull, and ends of the arm bones and thigh bones.
6. Triglyceride storage: Yellow bone marrow consists mainly of adipose cells, which store triglycerides. The stored triglycerides are a potential chemical energy reserve. Yellow bone marrow also contains a few blood cells. In the newborn, all bone marrow is red and is involved in hemopoiesis. With increasing age, much of the bone marrow changes from red to yellow
(Ref-J. TORTORA, The essentials of anatomy and physiology. 8th edition, P-119)
