Specimen Collection – Nursing is a profession within the healthcare sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other healthcare providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialisms with differing levels of prescriber authority.
Many nurses provide care within the ordering scope of physicians, and this traditional role has shaped the public image of nurses as care providers. However, nurses are permitted by most jurisdictions to practice independently in a variety of settings depending on training level. In the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced and specialized credentials, and many of the traditional regulations and provider roles are changing.
Nurses develop a plan of care, working collaboratively with physicians, therapists, the patient, the patient’s family, and other team members, that focus on treating illness to improve quality of life. Nurses may help coordinate the patient care performed by other members of an interdisciplinary healthcare team such as therapists, medical practitioners, and dietitians. Nurses provide care both interdependently, for example, with physicians, and independently as nursing professionals.
Specimen Collection
A specimen may be defined as a small quality of a substance or which shows the kind and quality of the sample.
Or
A specimen of anything that is selected for diagnosis examination study or testing.
Or
A specimen is a small quantity of a substance which is collected for investigation purposes and this sample shows the kind and quality of the whole substances
Definition of Specimen Collection:
Specimen collection is the collection of a required amount of tissue or fluid for laboratory examination is called specimen collection.
Or,
The collection of tissue or body fluids for laboratory investigations to aid diagnosis and/or treatment of medical conditions.
Purpose/Importance of Specimen Collection:
1. To collect a specimen of body discharges or excreta for examination.
2. To aid the doctor is diagnosing and treating the disease.
3. To detect any abnormalities.
4. To identify the disease and nature of disease.
5. To determine the cause for treatment.
6. To note the progress of disease.
Indication of Specimen Collection:
1. Microbiological.
2. Blochemical and
3. Other laboratory investigations are indicated. 10012
Specimen collection offers the first crucial step in investigations that define the nature of the disease and determine diagnosis and the mode of treatment.
Principles of Specimen Collection;
1. The patient should be intimated will in advance regarding the procedure and sample of specimen.
2. The specimen container should be clean.
3. Every specimen should be separately labeled clearly with patient’s name, bed number, reg. number, ward number, etc. and nature of specimen with nurse’s signature and date or time of collection etc.
4. All specimens duly labeled should be kept in separate tray for dispatching to lab. 197720
5. Morning specimens should be collected by the night nurse on duty. Other samples should be collected by day -nurse only.
6. Any special instruction for special test should be noted by nurse in nursing lab not book and instructions is followed accordingly.
Types of Specimen:
There are mainly two types of specimen;
1. Routine examination.
2. Special examination.
A. Routine examination
a) Urine for R/M/E.
b) Stool for R/M/E.
c) Blood for TC, DC, ESR, Hb%.
B. Special examination:
a) Excretion/Body secretion:
- Urine.
- Stool,
- Blood
- Sputum.
- Wound discharge.
- Vaginal swab
- Throat swab
- Nasal swab.
b) Aspiration:
- Ceribral spinal fluid,
- Peritoneal fluid.
c) Biopsy:
- Segment of the body tissue.
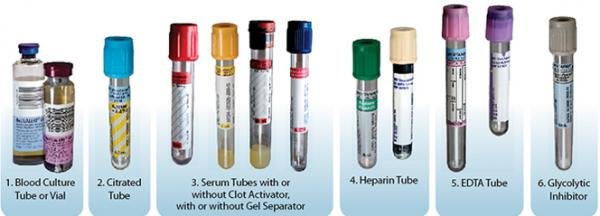
Rules of Specimen Collection:
1. The specimen must be collected from right person.
2. Kinds of specimen should be collected as by doctor’s order.
3. Adequate amount should be collected according to nature of test.
4. The container must be sterile for collection of any specimen and free from outside contaminated,
5. Use special container for some specimen such as fasting blood sugar, random blood sugar, blood for electrolytes etc.
6. Correctly fill a label and attach it to the container.
- Name and age of patient.
- Registration number.
- Bed no.
- Ward no.
- Unit no.
- Date or Time.
- The nature of test.
Time of specimen collection:
- Usually early in the morning. (Stool, Urine)
- Before washing of mouth-Oral swab, throat swab.
- Specific instruction-fasting blood sugar Collects early in the morning during fasting period.
