Spinal cord and spinal nerves-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Spinal cord and spinal nerves
Spinal cord:
The spinal cord is the elongated, almost cylindrical part of the central nervous system, which is suspended in the vertebral canal surrounded by the meninges and cerebrospinal fluid. It is continuous above with the medulla oblongata and extends from the upper border of the atlas to the lower border of the 1″ lumbar vertebra.
The roots of these spinal nerves angle down the vertebral canal like wisps of flowing hair. They are appropriately named the cauda equina, meaning horse’s tail.
Measurement:
Length: Approximately 45 cm (adult male)
Thickness: About of the little finger.
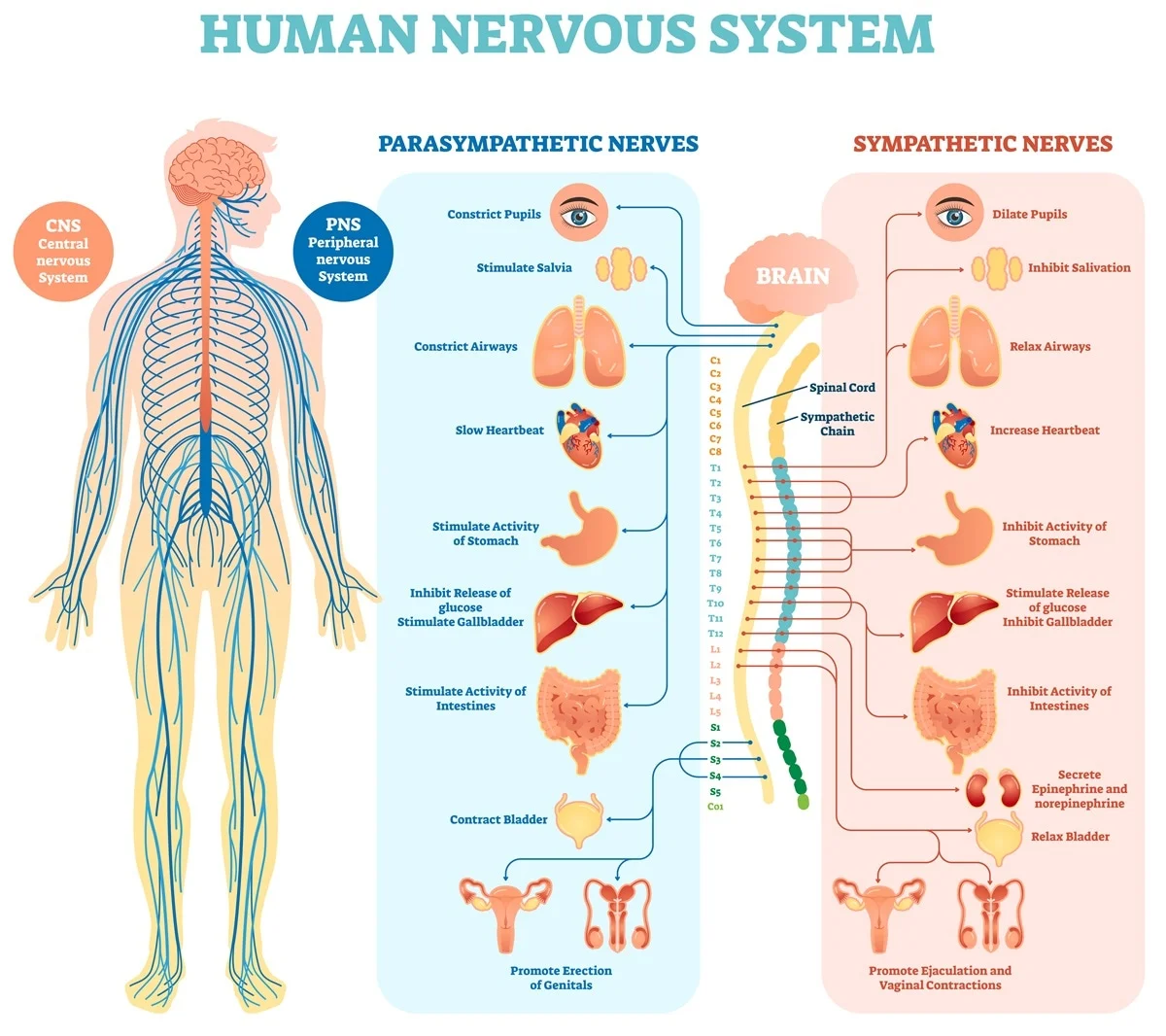
Spinal Nerves:
There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves. These nerves are groupedinto
8 pairs cervical,
12 pairs thoracic,
5 pairs lumbar,
5 pairs sacral, and
1 pair coccygeal
Total 31 pairs
They are named and grouped according to the region of the vertebral column from which they arise. Each spinal nerve is a mixed nerve composed of sensory and motor fibers. These fibers are packaged togetherin the nerve, but they separate near the attachment ofthe nerve to the spinal cord.
This produces two “roots”to each nerve. The dorsal root is composed of sensoryfibers, and the ventral root is composed of motor fibers. An enlargement of the dorsal root, the dorsalroot ganglion, contains the cell bodies of the sensory neurons.
(Ref:- Ross & Wilson 9th ed, P-155-156 +J. Tortora, 8th edition, P-256,257)
