Spontaneous and Habitual abortion – This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
Spontaneous and Habitual abortion
Definition of Spontaneous Abortion:
Expulsion of embryo or fetus prior to completion of the 20th gestational weeks is called spontaneous abortion. It implies delivery of all or any part of the products of conception, with or without a foetus weighing less than 500 gm.
Possible Causes of Spontaneous Abortion:
1. Chromosomal abnormalities: (maternal age >35 yrs)
- Triosomies (Down’s syndrome)
- Triploidies&tetraploidies c
- Monosomy X (Turner’s syndrome).
- Translocation (hereditary)
2. Endocrine disorders:
- Hypothyroidism
- Luteal phase deficiency
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome.
3. Abnormalities of the uterus:
- Uterine septa (bicornuate uterus)
- Endometrial adhesions (post-curretage or Asherman’s syndrome)
4. Infections:
- Salmonella typhi
- Malaria
- CMV
- Brucella
- Toxoplasmosis DHS hominis
- Cl. trachomatis
- U. uralyticum.
5. Chemical agents:
- Tobacco.
- Anaesthetic gases.
- Arsenic, lead, Hg & cadmium
- Benzene
- Ethylene oxide
- Formaldehyde
- Pesticides
6. Psychological disorders.
7. Immunological disorders:
- Anti-phospholipid syndrome
- Thrombophilia (hereditary)
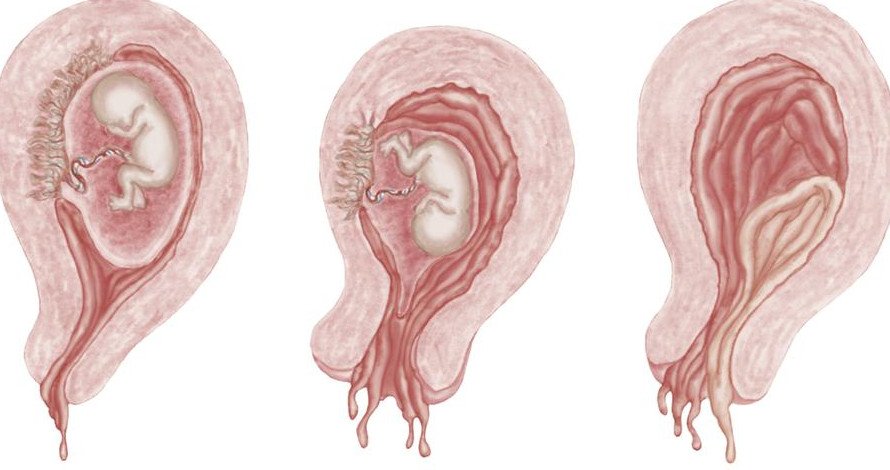
Definition of Habitual Abortion/Recurrent Abortion:
Three or more consecutive pregnancies ending in spontaneous abortion is known as habitualang abortion.
or
This is the spontaneous and recurrent abortion occurring consecutively on 3 or more occasions.
or
The miscarriage of 3 or more consecutive pregnancies. The abortion of 3 or more miscarriages (spontaneous abortions) with no intervening pregnancies is also termed recurrent abortion. Habitual or recurrent abortion is a form of infertility.
Causes of Habitual Abortion:
| A. Uterine (mid trimester abortion): |
|
| B. Systemic diseases: |
|
| C. Hormone deficiency: |
|
| D. Fetal causes: |
|
| E. Idiopathic |
Nice to learn:
A. In 1st trimester:
- Thyroid diseases
- DM, HTN
- Chronic renal disease
- TORCH infection
- SLE
B. In 2nd trimester:
- Cervical incompetence
- Uterine malformation
Q. A 25 years old woman presented to you with history of passage of fleshy mass p.r vaginally 3 days back and now she is suffering from fever, pain in lower abdomen and foul smelling vaginal discharge. How will you investigate her problems?
Answer:
A. Diagnosis:
- Clinical features: In case of cervical incompetence-mid trimester abortion
- Abortion is almost painless
- Suddenly there is leakage of liquor amnii, membranes bulge out and the product of conception comes out as a fleshy mass.
- In other cases: Per vaginal bleeding, lower abdominal pain is followed by abortion
B. Investigation:
- Blood for TC, DC, ESR, Hb%, ABO blood grouping and Rh typing of both husband and wife
- Urine: RME, Sugar for diabetes, C/S for nephritis
- Serological test: for syphilis in both husband and wife
- Renal function test: Where indicted blood urea, S. creatinine
- Glucose tolerance test and fasting blood sugar level for DM
- Thyroid function test
- Ultra sonogram for cervical incompetence
- Dilator test for cervical incompetence
- Hysteroscopy
- Cervical swab for C/S
C. During pregnancy:
- Routine antenatal tests
- VDRL test
- TORCH titre estimation
- Glucose tolerance test
- Ultra sonography
- Hormone assay, as indicated.
Management of Habitual Abortion:
A. General treatment:
a) Before pregnancy:
1. Patient is well advised to wait for 3 months after last abortion
2. In the meantime, steps should be taken to –
✓ Improve physical and mental health
✓ Administer folic acid 5 mg 8 hourly and multi vitamin preparations
b) During pregnancy:
1. Rest: 2 hours in every afternoon and 8-10 hours at night
2. Bed rest for several weeks during critical period
3. Avoid coitus and mechanical vehicle travelling
4. Psychological support
5. Sedatives at night
6. Adequate diet rich in protein, iron and vit. A, B, C, & D throughout pregnancy.
7. Avoid tension and physical activity
8. Empirical therapy with hormones for abortion in early months – Progesterone 20 mg IM 2-3 times weekly till 24 weeks.
9. Immunological therapy: for SLE, Aspirin and cortico steroid therapy
B. Specific treatment:
1. If cervical incompetence: Shirodkor operation or Mc. Donald’s suture
2. If retroverted uterus: Myomectomy
3. Cervical tear: Repair
4. Infection and general diseases, likes syphilis, DM, chronic nephritis – Needs adequate treatment
5. Gross bicornuate deformity of uterus – Utriculoplasty
6. Correction of deficiency states

