Stating Hypothesis – In its most common sense, methodology is the study of research methods. However, the term can also refer to the methods themselves or to the philosophical discussion of associated background assumptions. A method is a structured procedure for bringing about a certain goal, like acquiring knowledge or verifying knowledge claims. This normally involves various steps, like choosing a sample, collecting data from this sample, and interpreting the data. The study of methods concerns a detailed description and analysis of these processes. It includes evaluative aspects by comparing different methods.
In this way, their benefits and drawbacks are evaluated, as well as the research goals for which they may be used. These descriptions and evaluations are predicated on philosophical background assumptions; examples include how to conceptualize the phenomena under study and what constitutes evidence in favor of or against them. In its broadest sense, methodology encompasses the discussion of these more abstract issues.
Stating Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. A hypothesis is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in your study. For example, a study designed to look at the relationship between sleep deprivation and test performance might have a hypothesis that states, “This study is designed to assess the hypothesis that sleep deprived people will perform worse on a test than individuals who are not sleep deprived.
Definition of Hypothesis
According to Charles:
“Hypothesis is a statement or declaration of the expected outcome of a research study. It is based on logical rationale and has empirical possibilities for testing.”
According to Webster:
“Hypothesis is a tentative assumption made in order to draw out and test its logical or empirical consequences.”
According to Nancy Burns:
“Hypothesis is a formal statement of the expected relationships between two or more variables in a specified population.”
(Ref by- Seenidurai Paulraj/Introduction to Nursing Research/1/30)
Sources of Hypothesis
- Hypothesis can be derived from various sources as follows:
- Logical deduction from theory leads to new hypothesis
- Hypothesis can be derived from observation
- Analogies are another source of useful hypothesis
- Intuition and personal experience may also contribute to the formulation of hypothesis
- Hypothesis can be developed out of the findings of other studies in order to replicate and test
- State of knowledge is an important source of hypothesis
- Culture is also a source of hypothesis
- Continuity of research is an important source of hypothesis
(Ref by- Seenidurai Paulraj/Introduction to Nursing Research/1st/30)
Components/ Elements of Hypothesis
Normally, there are four elements in a hypothesis.
1. Dependent and independent variables
2. Some type of relationship between independent and dependent variable
3. The direction of the change
4. It mentions about the subjects, i.e. population being studied.
(Ref by-Seenidurai Paulraj/Introduction to Nursing Research/1st/30)
Standard principles used in formulating a hypothesis
- It should be empirically testable, whether it is right or wrong
- It should be specific and precise
- The statements in the hypothesis should not be contradictory
- It should specify variables between which the relationship to be established
- It should describe one issue only.
(Ref by- Seenidurai Paulraj/Introduction to Nursing Research/1st/31)
Criteria to Formulation of Hypothesis
- Identify the independent and dependent variables to be studied.
- Specify the nature of the relationship that exists between these variables.
- It is better to be concise than to be long-winded. It is also better to have several simple
- hypotheses than one complicated hypothesis.
- Does not include reference to specific measures.
- Does not refer to specific statistical procedures that will be used in analysis.
- Implies the population that you are going to study.
(Ref by-handout)
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
- It should be conceptually clear
- It should be specific and should explain the expected relations between variables
- It should be simple
- It should be free from juugment
- It should be related to available technique
- It should be testable
- It should be logically consistent
- It is directly related of the research problem
- It is factually or theoretically based
- It states a relationship between variables
- It is stated in such a form that it can be accepted or rejected.
(Ref by-Seenidurai Paulraj/Introduction to Nursing Research/1st/31)
.
Purposes of Hypothesis
- It offers explanations for the relationships between those variables that can be empirically
- It furnishes proof that the researcher has sufficient background knowledge to enable him/her to make suggestions in order to extend existing knowledge.
- It gives direction to an investigation.
- It structures the next phase in the investigation and therefore furnishes continuity to the examination of the problem.
Types of Hypothesis
Hypothesis can be classified based on its origin, formulation, complexity, anticipated relationship between the variables and cause and effect relationship between the variables:
| Based on origin: |
|
| Based on formulation: |
|
| Based on anticipated relationship: |
|
| Based on complexity: |
|
(Ref by- Nirmala V/Research Methodology in Nursing/1st/61)
Relationship of Research Questions and Hypothesis:
Hypothesis is nothing but the logical assumed answer to the research questions under exploration. Formulation of hypothesis require researcher to predict an answer to the research question based on relevant knowledge and logical analysis.
The formulation of hypothesis should be-
- Suggest explanations for certain facts.
- Guide in investigation of related facts.
- Investigate characteristics that determine the occurrence of disease.
(Ref by-Selim reza/The essentials of community medicine/16th/700)
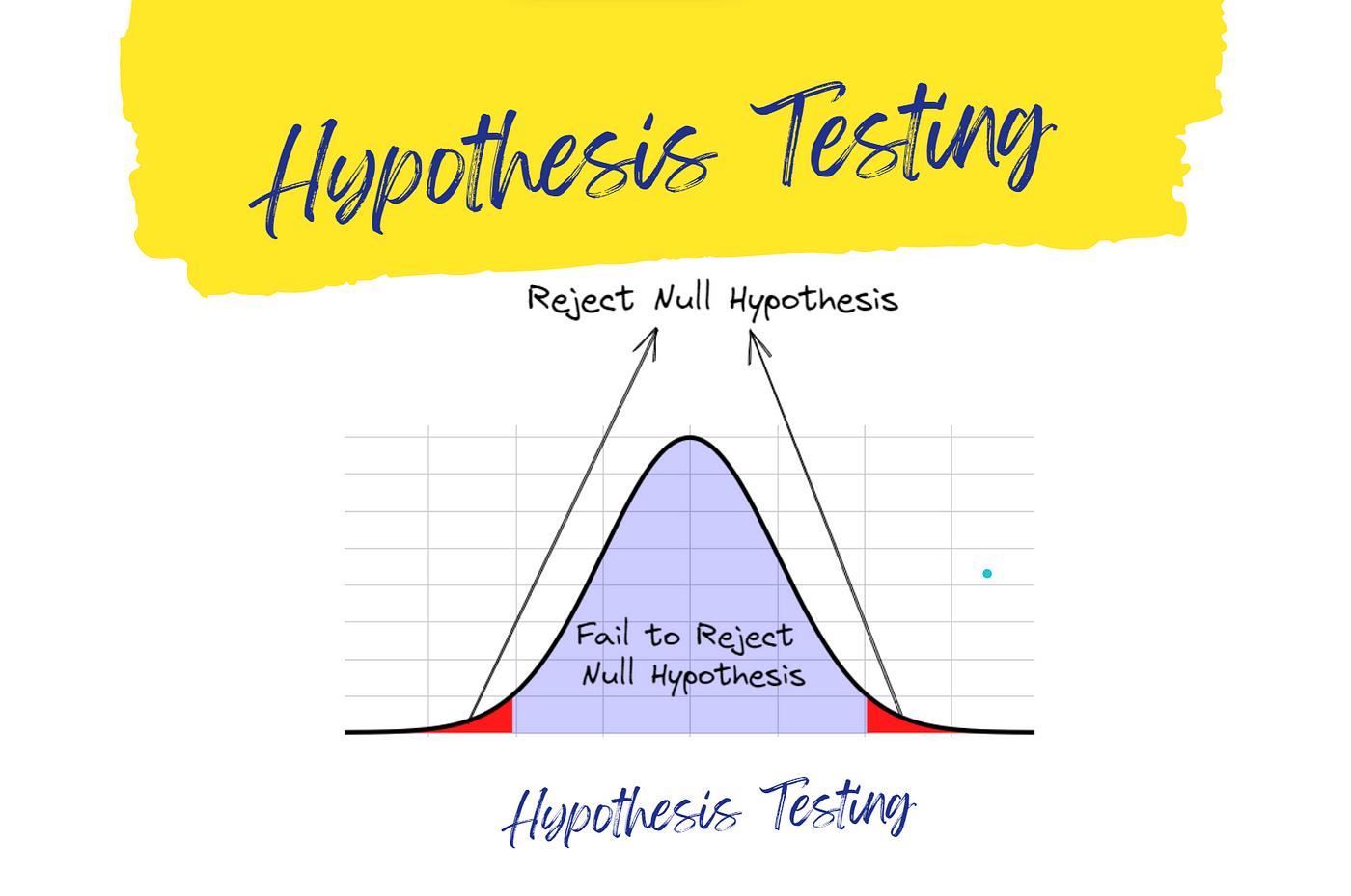
Steps of Testing of Hypothesis
The testing of hypothesis involves the following steps:
| Step-1: Formulate hypothesis | Formulate two hypothesis, i.e. the alternative or research and the null hypothesis. |
| Step-2: Data analysis and interpretation | For testing, the data will be analyzed and compared with the results against the null hypothesis, so the research is designed keeping this in mind. It is vitally important that the research you design produces results that will be analyzable using statistical tests. |
| Step-3: Easy understanding of the process with no fear factor | Most people are very afraid of statistics, due to obscure mathematical symbols, and worry about not understanding the processes or messing up the experiments. There really is no need to fear |
| Step-4: Understanding basic principles of statistics | Most scientists understand only the basic principles of statistics, and once you have these, modern computing technology gives a whole battery of software for hypothesis testing. |
| Step-5: Designing the research | Designing your research only needs a basic understanding of the best practices for selecting samples, isolating testable variables and randomizing groups. |
