Testes or the male gonads – The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Testes or the male gonads
Testes
The testes (singular is testis, or testicle) are the oval shaped reproductive glands of the male and are the equivalent of the ovaries in the female that suspended by spermatic cords into the scrotum where spermatozoa are formed and male sex hormone, testosterone also produced.
The testes develop in the abdominal cavity and usually begin their descent into the scrotum through the right and left inguinal canal in the seventh month of fetal development.

Measurement:
Length: about 4.5 cm
Width: about 2.5 cm
Weight: about 10 to 40 gm

Figure 9.4 Anatomy and histology of the testes. (a) Spermatogenesis occurs in the seminiferous tubules. (6) a transverse section of a seminiferous tubule. (c) The stages of spermatogenesis Arrows in (c) indicate the progression from least mature to most mature spermatogenic cells. The (n) and (2n) refer to haploid and diploid chromosome number, to be described shortly. The male gonads are the testes, which produce haploid sperm.
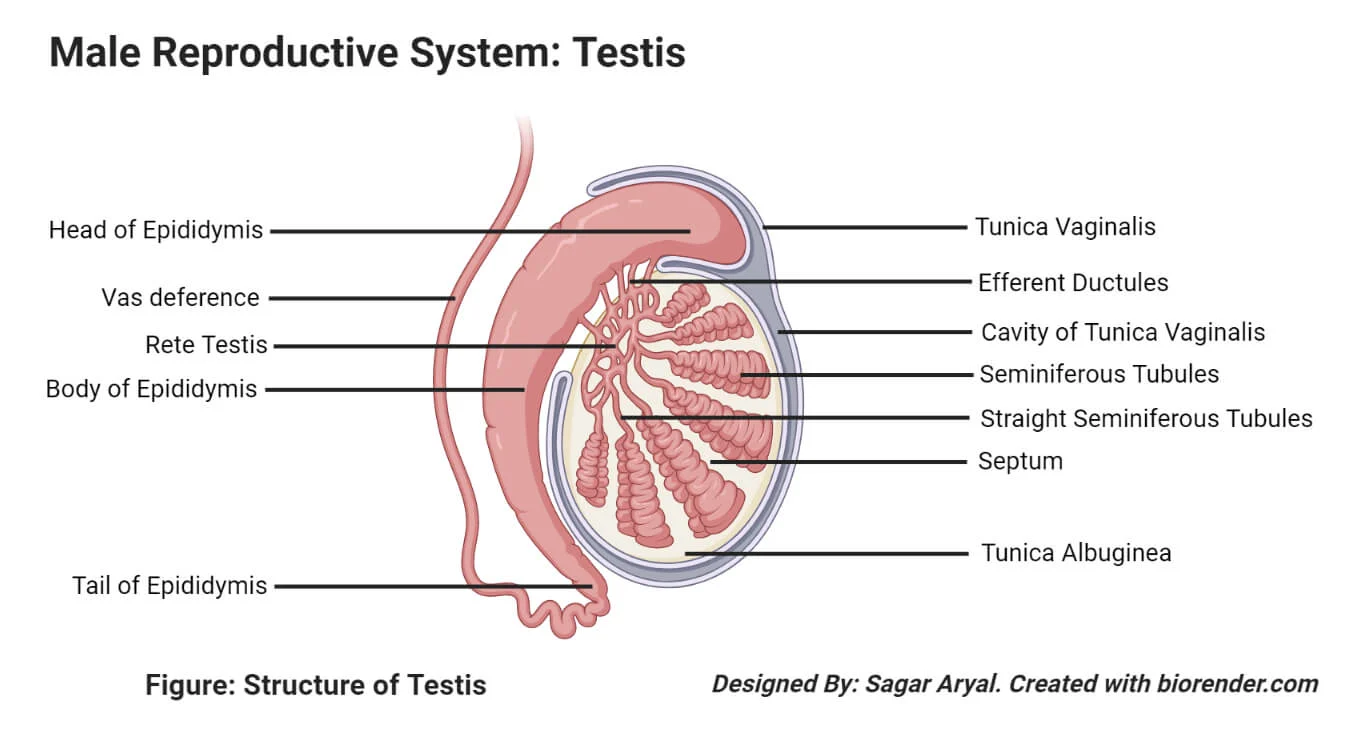
Spermatogenesis, the origin and development of the sperm cells within the male reproductive organs, the testes. The testes are composed of numerous thin tightly coiled tubules known as the seminiferous tubules; the sperm cells are produced within the walls of the tubules
Covering of the testes
The testes are covered by three layers:
- Tunica vaginalis (outer layer)
- Tunica albuginea (meddle layer)
- Tunica vasculosa (inner layer)
Hormones of testes
- Testosterone
- Dihydrotestosterone
- Androsterone
Functions of testes
- Spermatozoa (sperm) are produced in the seminiferous tubules.
- The male hormone, testosterone is produced in the testes. The secretion of testosterone increases during puberty between the age of 10 to 14 yrs and responsible for the development of the secondary sexual characteristics: growth of the extra hair and pubic), deepening of the voice, enlargement of the genitalia. (on face, axilla, chest, abdomen
(Ref: Ross & Wilson 9th /448-450 + K. Indu, 1″ ed,P-385-389 + P.Evelyn, 16th,P-318)
Read more:
