Today our topic of discussion is ” The Pineal Gland “. The human body is a marvel of intricate systems, and within the vast realm of the endocrine network lies the enigmatic pineal gland. Often referred to as the “third eye,” this tiny endocrine gland plays a pivotal role in regulating sleep patterns and has, over the ages, been associated with mysticism and spirituality. This article will delve deep into the anatomy, functions, significance, and disorders of the pineal gland.

The Pineal Gland: The Endocrine System
Introduction: Unraveling the Pineal Enigma
Perched deep within the brain, the pineal-gland may be small, but its impact on physiological and potentially spiritual well-being is monumental. Primarily responsible for the synthesis and secretion of melatonin, the pineal-gland helps regulate our circadian rhythms and sleep-wake cycle.
Anatomy: A Closer Look
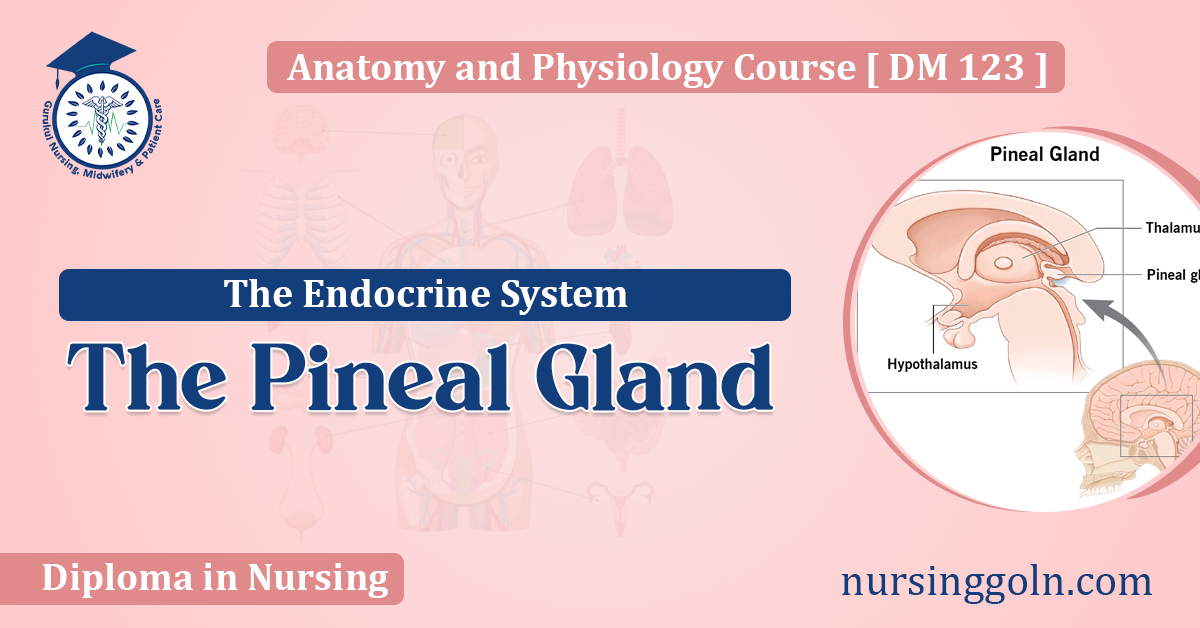
Location: The pineal gland is nestled between the two hemispheres of the brain, positioned near the center, tucked away in a groove where the two halves of the thalamus meet.
Size & Shape: Roughly the size of a grain of rice, the pineal-gland is shaped like a pinecone, which is believed to be the origin of its name.
Melatonin: The Nighttime Messenger
- Synthesis & Secretion: The pineal gland synthesizes melatonin from the amino acid tryptophan. The synthesis and release of melatonin are heavily influenced by light exposure. Darkness stimulates its production, while light inhibits it.
- Functions:
- Sleep Regulation: Melatonin sets the internal body clock, governing sleep patterns and the circadian rhythm.
- Antioxidant Properties: Melatonin is also known for its potent antioxidant properties, helping combat cellular damage.
- Immune System Regulation: There is evidence suggesting melatonin’s role in bolstering the immune system.

Pineal Gland: The Seat of the Soul?
Historically and culturally, the pineal-gland has been attributed with profound spiritual significance:
- Third Eye: Many ancient civilizations, including the Egyptians and Hindus, considered the-pineal gland as the “third eye,” a spiritual gateway to higher consciousness or enlightenment.
- Descartes’ Belief: René Descartes, the 17th-century philosopher, believed the pineal-gland to be the “principal seat of the soul.”
- Modern Spirituality: In contemporary spirituality, the pineal-gland is often associated with intuition, clairvoyance, and states of deep meditation or transcendence.
Disorders & Dysfunctions: When Balance is Lost
- Pineal Cysts: These are benign cysts, often detected incidentally during brain scans. Typically, they don’t present any symptoms. However, if large, they might cause headaches or vision problems.
- Pineal Tumors: These are rare but can be benign or malignant. Symptoms may include sleep disturbances, vision problems, or hydrocephalus (fluid build-up in the brain).
- Melatonin Imbalance: Overproduction can lead to excessive sleepiness, while underproduction may cause insomnia.
- Calcification: Over time, the pineal-gland may calcify. While this is a normal part of aging, excessive calcification, often attributed to environmental toxins or diet, has been theorized (though not conclusively) to reduce the gland’s efficiency.
Decalcifying and revitalizing the Pineal Gland
While not entirely based on rigorous scientific evidence, several methods are popularly believed to revitalize and decalcify the pineal-gland:
- Dietary Adjustments: Consuming organic foods, eliminating processed items, reducing fluoride intake (found in many toothpaste brands and tap water), and incorporating chlorella, spirulina, and wheatgrass in the diet.
- Meditation & Yoga: Practices that focus on the third eye or crown chakra are believed to stimulate and rejuvenate the-pineal gland.
- Sun Gazing: This ancient practice involves looking at the sun during the first or last hour of daylight. Proponents believe it stimulates the-pineal gland, although it’s essential to approach with caution to ensure eye safety.
The Link with Modern Lifestyle
The modern lifestyle, filled with artificial lighting and screen exposure, can disrupt the pineal-gland’s natural rhythm. Blue light from devices, especially before bedtime, can suppress melatonin production, leading to sleep disturbances.
The pineal-gland, though minuscule in size, holds a place of reverence in both physiology and spiritual paradigms. Its crucial role in regulating sleep and potential ties to consciousness make it an organ of great fascination. While modern life poses challenges to its optimal functioning, awareness and certain practices can help in harnessing its full potential. As we continue to explore the intricacies of the human body, the-pineal gland remains a symbol of the profound interplay between the physical and the metaphysical.