Unit of Memory – This book covers the entire syllabus of “Computer & Information Technology” prescribed by the BNMC for B.Sc. in Nursing Science & Diploma in Nursing Science & Midwifery students. We tried to accommodate the latest information and topics.
This book is an examination setup according to the teachers’ lectures and examination questions. We hope in touch with the book students’ knowledge will be upgraded and flourished. The unique way of presentation may make your reading of the book a pleasurable experience.
Definition of Unit of Memory:
The smallest unit in computer memory is known as a bit representing either 0 or 1. 1 byte consist of 8 bits.
- 1 byte = 8 bits
- 1 Kilo Byte = 1,024 bytes
- 1 Mega Byte = 1,048,576 bytes = 1024 K Byte
- 1 Giga Byte = 1,073,741,824 bytes = 1024 Mega Byte
- 1 Tera Byte = 1,099,511,627,776 bytes = 1024 Giga Byte
- 1 Peta Byte = 1,125,899,906,842,624 bytes = 1024 Tera Byte
- 1 a Byte = 1,152,921,504,606,846,976 bytes = 1024 Peta Byte
- 1 Zetta Byte= 1,180,591,620,717,411,303,424 bytes = 1024 Exa Byte
- 1 Yotta Byte= 1,208,925,819,614,629,174,706,176 bytes = 1024 Zetta Byte
Short Note
- Floppy disk
- Hard disk
- CD-DVD-ROM
- Compact Disk/ (CD-ROM)
- Pen Drive
- Magnetic Tap
- Magnetic Disk
- Levels of Memory Hierarchy
Floppy disk
A floppy disk, also called a floppy, diskette, or just disk, is a type of disk storage composed of a disk of thin and flexible magnetic storage medium, sealed in a rectangular plastic enclosure lined with fabric that removes dust particles. Floppy disks are read and written by a floppy disk drive (FDD).

Hard disk
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive or fixed disk is a data storage device that uses magnetic storage to store and retrieve digital information using one or more rigid rapidly rotating disks (platters) coated with magnetic material.

The platters are paired with magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces. Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual blocks of data can be stored or retrieved in any order and not only sequentially. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data even when powered off.
CD-DVD-ROM
A CD-ROM is a pre-pressed optical compact disc which contains data. The name is an acronym which stands for “Compact Disc Read-Only Memory”.

Computers can read CD-ROMs, but cannot write to CD-ROMs, which are not writable or erasable.
Compact Disk/ (CD-ROM)
Compact disc (CD) is a digital optical disc data storage format released in 1982 and co- developed by Philips and Sony. The format was originally developed to store and play only sound recordings but was later adapted for storage of data (CD-ROM).

Several other formats were further derived from these, including write-once audio and data storage (CD-R), rewritable media (CD-RW), Video Compact Disc (VCD), Super Video Compact Disc (SVCD), Photo CD, Picture CD, CD-i, and Enhanced Music CD.
Pen Drive / USB Flash Drive
A USB flash drive, also variously known as a USB drive, USB stick, thumb drive, pen drive, jump drive, disk key, disk on key, flash-drive, memory stick or USB memory, is a data storage device that includes flash memory with an integrated USB interface.

USB flash drives are typically removable and rewritable, and physically much smaller than an optical disc.
Magnetic Tape
Magnetic tape is a medium for magnetic recording, made of a thin, magnetizable coating on a long, narrow strip of plastic film. It was developed in Germany in 1928, based on magnetic wire recording. Devices that record and play back audio and video using magnetic tape are tape recorders and video tape recorders.

A device that stores computer data on magnetic tape is a tape drive (tape unit, streamer).
Magnetic Disk
A magnetic disk is a storage device that uses a magnetization process to write, rewrite and access data. It is covered with a magnetic coating and stores data in the form of tracks, spots and sectors. Hard disks, zip disks and floppy disks are common examples of magnetic disks.

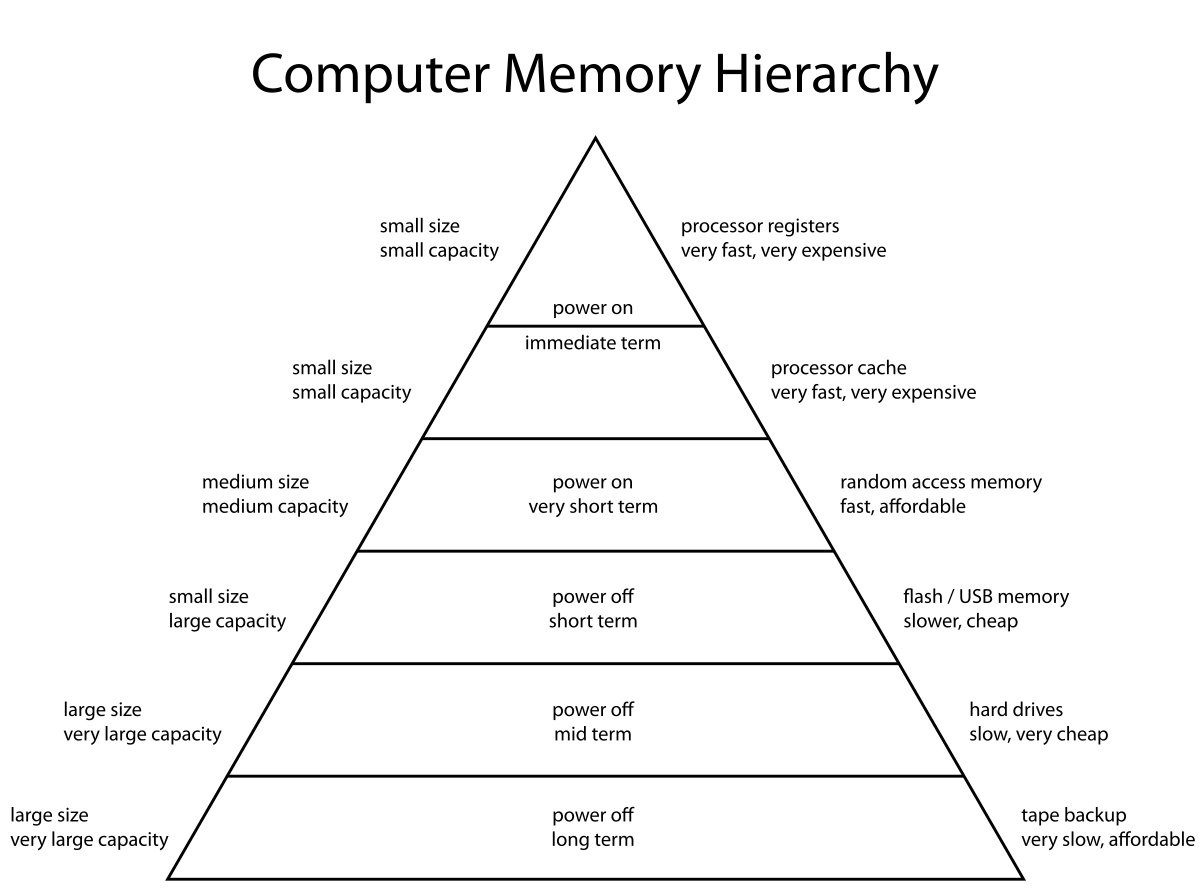
Levels of Memory Hierarchy.
In computer architecture, the memory hierarchy separates computer storage into a hierarchy based on response time. Since response time, complexity, and capacity are related, the levels may also be distinguished by their performance and controlling technologies.[1] Memory hierarchy affects performance in computer architectural design, algorithm predictions, and lower level programming constructs involving locality of reference.
There are four major storage levels.
- Internal – Processor registers and cache.
- Main – the system RAM and controller cards.
- On-line mass storage – Secondary storage.
- Off-line bulk storage – Tertiary and Off-line storage.