Urinary Elimination – Nursing is a profession within the healthcare sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other healthcare providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialisms with differing levels of prescriber authority.
Many nurses provide care within the ordering scope of physicians, and this traditional role has shaped the public image of nurses as care providers. However, nurses are permitted by most jurisdictions to practice independently in a variety of settings depending on training level. In the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced and specialized credentials, and many of the traditional regulations and provider roles are changing.
Nurses develop a plan of care, working collaboratively with physicians, therapists, the patient, the patient’s family, and other team members, that focus on treating illness to improve quality of life. Nurses may help coordinate the patient care performed by other members of an interdisciplinary healthcare team such as therapists, medical practitioners, and dietitians. Nurses provide care both interdependently, for example, with physicians, and independently as nursing professionals.
Definition of Urinary Elimination:
Urinary elimination is the expulsion of waste products from the body through the urinary system.
or
Urinary elimination is the process of releasing excess fluid and metabolic water from the body by the urethra.
Common Alteration/Problems of Urinary Elimination:
A. Altered urine production:
a) Polyuria: Polyuria, or diuresis, refers to the production of abnormally large amounts of urine by the kidneys, about 2500 ml or more/day.
b) Oliguria: It refers to voiding scanty amount of urine such as 100 to 500 ml / day.
c) Anuria: It refers to voiding less than 100 ml /day. The terms complete kidney shutdown, renal failure and urinary suppression have the same meaning. Anuria can result from-
- Kidney diseases.
- Severe heart disease
- Burn and
- Shock.
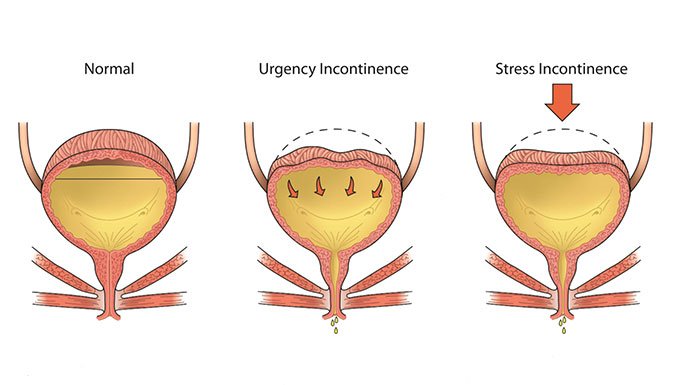
B. Altered voiding pattern:
a) Frequency
b) Nocturia
c) Urgency
d) Dysuria.
e) Enuresis.
Factors Affecting Urine Elimination:
1. Children up to the age of 2 years cannot control urinary functioning.
2. Aging impairs urination.
3. Chronic neurological diseases such as Parkinsonism or cerebro vascular accident impair urination. Frequency is increased and also sometimes incontinence.
4. Anxiety and emotional stress cause a sense of urgency and increase frequency of urination.
5. Emotional tension makes it difficult to relax abdominal and perineal muscles. In this case, voiding may be incomplete due to lack of relaxation of external urethral sphincter.
6. Privacy and adequate time to urinate are important for some people.
7. Weak abdominal and pelvic floor muscles, due to lack of muscle tone, impaire urination, e.g.- after child birth, menopausal muscle atrophy.
8. Use of continuous indwelling catheters.
9. Increase in fluid intake causes increase in urine production.
10. Alcohol consumption increase urine production.
11. Febrile conditions increase urine production
12. During day, urine production is more, during night, it is less,
Indications of Urinary Elimination:
- Unconscious patient or comatose patient.
- Poisoning patient.
- After surgery.
- Cardiac patient.
- Paralysis patient
- Acute retention of urine following prolonged anesthesia, benign enlargement of prostate
- Chronic retention of urine
- After prostatectomy
- After supra-pubic cystolithotomy to allow healing of bladder wound
- Surgery in pelvic region