Abbreviation and Converting from One Number System to Another – This book covers the entire syllabus of “Computer & Information Technology” prescribed by the BNMC for B.Sc. in Nursing Science & Diploma in Nursing Science & Midwifery students. We tried to accommodate the latest information and topics.
This book is an examination setup according to the teachers’ lectures and examination questions. We hope in touch with the book students’ knowledge will be upgraded and flourished. The unique way of presentation may make your reading of the book a pleasurable experience.

Abbreviation and Converting from One Number System to Another
- PC-Personal Computer
- COMPUTER-Commonly Operating Machine Particularly Used For Technology Entertainment And Research
- ACL-Access Control List
- ADC-Analog-to-Digital Converter
- ADF-Automatic Document Feeder
- ADSL-Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line
- AGP-Accelerated Graphics Port
- AIFF Audio Interchange File Format
- AIX – Advanced Interactive Executive
- ALU-Arithmetic Logic Unit
- ANSI-American National Standards Institute
- API – Application Program Interface
- APU-Accelerated Processing Unit
- ARP Address Resolution Protocol
- ASCII – American Standard Code for Information Interchange
- ASP-Active Server Page or Application Service Provider
- ATA-Advar ced Technology Attachment
- ATM – Asynchronous Transfer Mode
- ATX-Advanced Technology eXtended
- AUP-Acceptable Use Policy
- Bash-Bourne-Again Shell
- BASIC – Beginner’s All-purpose Symbolic Inston Code
- Bee – Blind Carbon Copy
- BIOS – Basic Input/Output System
- Blob-Binary Large Object
- BMP – Bitmap
- BSOD-Blue Screen of Death
- CGI-Common Gateway Interface
- CCD-Charged Coupled Device
- CD – Compact Disc
- CD-R-Compact Disc Recordable
- CDFS-Compact Disc File System
- CDMA – Code Division Multiple Access
- CDN- Content Delivery Network
- CISC-Complex Instruction Set Computing
- CLOB – Character Large Object
- CPU Central Processing Unit
- RAM Random Access Memory
- ROM= Read Only Memory
- PROM = Programmable Read Only Memory
- EPROM-Erasable PROM
- EEPROM = Electrically EPROM
- HDD Hard Disk Drive
- CD-ROM-Compact Disc Read-Only Memory
- CD-RW Compact Disc Re-writable
- FDD = Floppy Disk Drive
- KBD = Key Board
- I/O = Input & Output.
- CAD-Computer-Aided Design
- Ce-Carbon Copy
- CD = Compact Disk
- DVD = Digital Video Disk
- SMPS = Switch Mode Power Supply
- POST = Power ON Self-Test
- CMOS – Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor
- CMS – Content Management System
- BIOS = Basic Input Output System
- VDU Visible Display Unit
- LED Light Embedded Diode
- LCD Liquid Crystal Display
- USB Universal Serial Bus
- VGA = Video/Visual Graphic Adapter
- LAN Local Area Network
- WAN Wide Area Network
- MAN = Metropolitan Area Network
- HLL = High Level Language
- LLL= Low Level Language
- MIPS Million of Instruction Per Second
- Mbps Mega Bytes Per second
- Kbps = Kilo Bytes per second
- HTTP = Hyper Text Templates
- WWW = World Wide Web
- IP = Internet Protocol
- ISP Internet Service Provider
Computer Related Abbreviations
A
- Al-Artificial intelligence
- ALGOL- Algorithmic Language
- ARP Address resolution Protocol
- ASCII – American Standard Code for Information Interchange
B
- BINAC – Binary Automatic Computer
- BCC-Blind Carbon Copy
- Bin – Binary
- BASIC- Beginner’s All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code
- BIOS-Basic Input Output System
- Bit – Binary Digit
- BSNL-Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited
C
- CC-Carbon Copy
- CAD-Computer Aided Design
- COBOL-Common Business Oriented Language
- CD-Compact Disc
- CRT-Cathode Ray Tube
- CPU Central Processing Unit
- CDR-Compact Disc Recordable
- CDROM-Compact Disc Read Only Memory
- CDRW-Compact Disc Rewritable
- CDR/W-Compact Disk Read/Write

D
- DBA-Data Base Administrator
- DBMS – Data Base Management System
- DNS-Domain Name System
- DPI-Dots Per Inch
- DRAM-Dynamic Random Access Memory
- DVD-Digital Video Disc/Digital Versatile Disc
- DVDR-DVD Recordable
- DVDROM – DVD Read Only Memory
- DVDRW-DVD Rewritable
- DVR-Digital Video Recorder
- DOS-Disk Operating System
E
- EBCDIC-Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code
- e-Commerce – Electronic Commerce
- EDP-Electronic Data Processing
- EEPROM – Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory
- ELM/e-Mail-Electronic Mail
- ENIAC – Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer
- EOF-End Of File
- EPROM – Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory
F
- FAX-Far Away Xerox/ facsimile
- FDC-Floppy Disk Controller
- FDD-Floppy Disk Drive
- FORTRAN-Formula Translation
- FS-File System
- FTP-File Transfer Protocol
G
- Gb-Gigabit
- GB – Gigabyte
- GIF-Graphics Interchange Format
- GSM Global System for Mobile Communication
H
- HDD-Hard Disk Drive
- HP-Hewlett Packard
- HTML – Hyper Text Markup Language
- HTTP – Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
I
- IBM International Business Machine
- IM-Instant Message
- IMAP – Internet Message Access Protocol
- ISP-Internet Service Provider
J
- JPEG-Joint Photographic Experts Group
K
- Kb – Kilobit
- KB-Kilobyte
- KHz-Kilohertz
- Kbps – Kilobit Per Second
L
- LCD-Liquid Crystal Display
- LED-Light Emitting Diode
- LPI-Lines Per Inch
- LIS-Large Scale Integration
M
- Mb – Megabit
- MB – Megabyte
- MPEG-Moving Picture Experts Group
- MMS-Multimedia Message Service
- MICR-Magnetic Ink Character reader
- MIPS-Million Instructions Per Second
N
- NIC-Network Interface Card
- NOS-Network Operating System
O
- OMR – Optical Mark Reader
- OOP-Object Oriented Programming
- OSS-Open Source Software
P
- PAN-Personal Area Network
- PC-Personal Computer
- PDA – Personal Digital Assistant
- PDF-Portable Document Format
- POS-Point Of Sale
- PNG- Portable Network Graphics
- PPM-Pages Per Minute
- PPP-Point-to-Point Protocol
- PROM-Programmable Read Only Memory
- PSTN-Public Switched Telephone Network
- POST-Power On Self-Test
- PING-Packet Internet Gopher
R
- RAM-Random Access Memory
- RDBMS – Relational Data Base Management System
- RIP-Routing Information Protocol
- RTF-Rich Text Format

S
- SMTP – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
- SQL-Structured Query Language
- SRAM – Static Random Access Memory
- SNMP-Simple Network Management Protocol
- SIM-Subscriber Identification Module
T
- TCP-Transmission Control Protocol
- TB – Tera Bytes
U
- UPS – Uninterrupted Power Supply
- URI-Uniform Resource Identifier
- URL-Uniform Resource Locator
- USB Universal Serial Bus
- ULSI-Ultra Large Scale Integration
- UNIVAC-Universal Automatic Computer
V
- VAR – Variable
- VGA – Video Graphics Array
- VSNL-Videsh Sanchar Nigam Limited
- VDU-Visual Display Unit
W
- Wi-Fi Wireless Fidelity
- WLAN-Wireless Local Area Network
- WPA-Wi-Fi Protected Access
- WWW-World Wide Web
- WORM-Write Once Read Many
X
- XHTML-eXtensible Hypertext Markup Language
- XML eXtensible Markup language
Z
- ZB-Zeta Byte
Below are Computer Units to measure data size
- 4 Bits 1 Nibble
- 8 Bits = 1 Byte
- 1024 Bytes 1 Kilo Byte (KB)
- 1024 KB 1 Mega Byte (MB)
- 1024 MB = 1 Gyga Byte (GB)
- 1024 GB 1 Tera Byte (TB)
- 1024 TB=1 Peta Byte (PB)
- 1024 PB = 1 Exa Byte (EB)
- 1024 EB = 1 Zetta Byte (ZB)
- 1024 ZB = 1 Yotta Byte (YB)
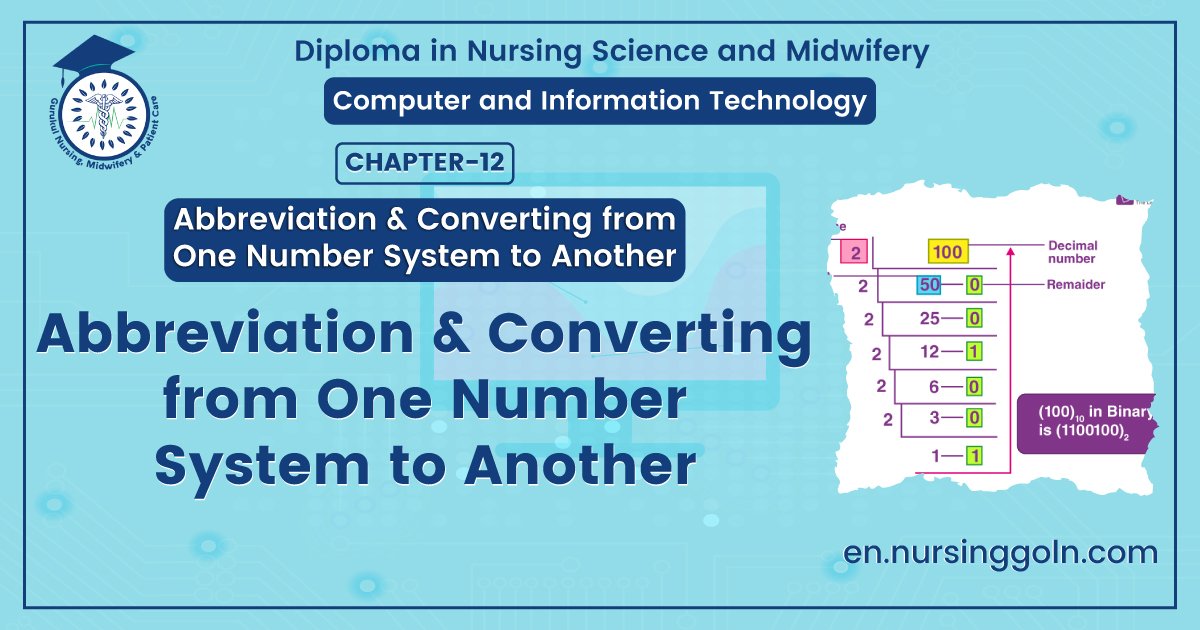
Converting from One Number System to Another.
Number System:
Number systems are the technique to represent numbers in the computer system architecture, every value that you are saving or getting into/from computer memory has a defined number system.
The value of each digit in a number can be determined using
- The digit
- The position of the digit in the number
- The base of the number system (where the base is defined as the total number of digits available in the number system)
Classification of Number System:
Computer architecture supports following number systems.
1. Binary number system
2. Octal number system
3. Decimal number system
4. Hexadecimal (hex) number system
1. Binary Number System: A Binary number system has only two digits that are 0 and 1. Every number (value) represents with 0 and 1 in this number system. The base of binary number system is 2, because it has only two digits.
2. Octal number system: Octal number system has only eight (8) digits from 0 to 7. Every number (value) represents with 0,1,2,3,4,5,6 and 7 in this number system. The base of octal number system is 8, because it has only 8 digits.
3. Decimal number system: Decimal number system has only ten (10) digits from 0 to 9. Every number (value) represents with 0,1,2,3,4,5,6, 7,8 and 9 in this number system. The base of decimal number system is 10, because it has only 10 digits.
4. Hexadecimal number system: A Hexadecimal number system has sixteen (16) alphanumeric values from 0 to 9 and A to F. Every number (value) represents with 0,1,2,3,4,5,6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E and F in this number system. The base of hexadecimal number system is 16, because it has 16 alphanumeric values. Here A is 10, B is 11, C is 12, D is 13, E is 14 and F is 15.

Table of the Numbers Systems with Base, Used Digits, Representation, C language representation:
| Number system | Base | Used digits | Example | CLanguage assignment |
| Binary | 2 | 0,1 | (11110000) | int val=0b11110000; |
| Octal | 8 | 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7 | (360)8 | int val-0360; |
| Decimal | 10 | 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 | (240)10 | int val-240; |
| Hexadecimal | 16 | 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,A,B,C,D,E,F | (FO)16 | int val=0xF0; |
CONVERTING OCTAL TO BINARY
Below are the steps which will help you to understand how to convert octal to binary number –
- Step 1: Consider the given octal number
- Step 2: Let the given number have n number of digits
- Step 3: Multiply each digit of the number with 8 ^ (n – 1) when the digit is in the nth position from the right end of the number. If the number has decimal part the multiply each digit in the decimal part by 1/(8 ^ m) when the digit is in the mthi position from the decimal point.
- Step 4: Add all terms after multiplication
- Step 5: The obtained value is the equivalent decimal number
- Step 6: Consider the decimal number, divide it by 2
- Step 7: Note the remainder
- Step 8: Continue the above two steps for the quotient till the quotient is zero
- Step 9: Write the remainders in the reverse order
- Step 10: The obtained number is the equivalent binary number for the given octal number.
Let us see some examples for converting an octadecimal number to a binary number.
Examples on converting octal to binary number-
Click here To Download CONVERTING OCTAL TO BINARY Question and solution
CONVERTING OCTAL TO DECIMAL
Below are the steps to convert octal to decimal –
- Step 1: Take the given octal number.
- Step 2: Find out the number of digits in the number
- Step 3: Let it have n digits.
- Step 4: Multiply each digit in the number with 81, when the digit is in the nth position.
- Step 5: Add all digits after multiplication.
- Step 6: The resultant is the equivalent decimal to the given octal number.
- If octal number contains a decimal point
- Step 7: Let m digits are there after the decimal
- Step 8: Multiply each digit after decimal with 8″, when the digit is the mth position.
All other steps are same as above.
Click here To Download CONVERTING OCTAL TO DECIMAL Question and solution
CONVERTING OCTAL TO HEXADECIMAL
Below are the steps on octal to hexadecimal conversion –
Step 1: Let the number of digits in the number be n
Step 2: Multiply the digits with 8 ^ <=-1 1 where n is position of digit from the right end of the
number. If the number has decimal part the multiply digits after decimal by 1/(8 ^ m) where m is position of the number from the decimal
Step 3: Add the terms after multiplication
Step 4: The obtained number is equivalent decimal number to the given octal
Step 5: Consider the decimal number, divide it by 16
Step 6: Note the remainder.
Step 7: Continue the process till the quotient in zero
Step 8: Write the remainder in the reverse order
Step 9: The obtained number is equivalent hexadecimal number to the given octadecimal number.
Now we will understand this conversion more clearly using examples.
Below are the examples on converting octal to hexadecimal –
Click here To Download CONVERTING OCTAL TO HEXADECIMAL Question and solution
Read more: