Definition of Glaucoma – This course is designed to understand the concept of community health nursing: nurses’ roles and interventions in family health, school health, occupational health, environmental health, elderly health care, gender issues, disaster management and principles and terminology of epidemiology. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in community health nursing.
Definition of Glaucoma
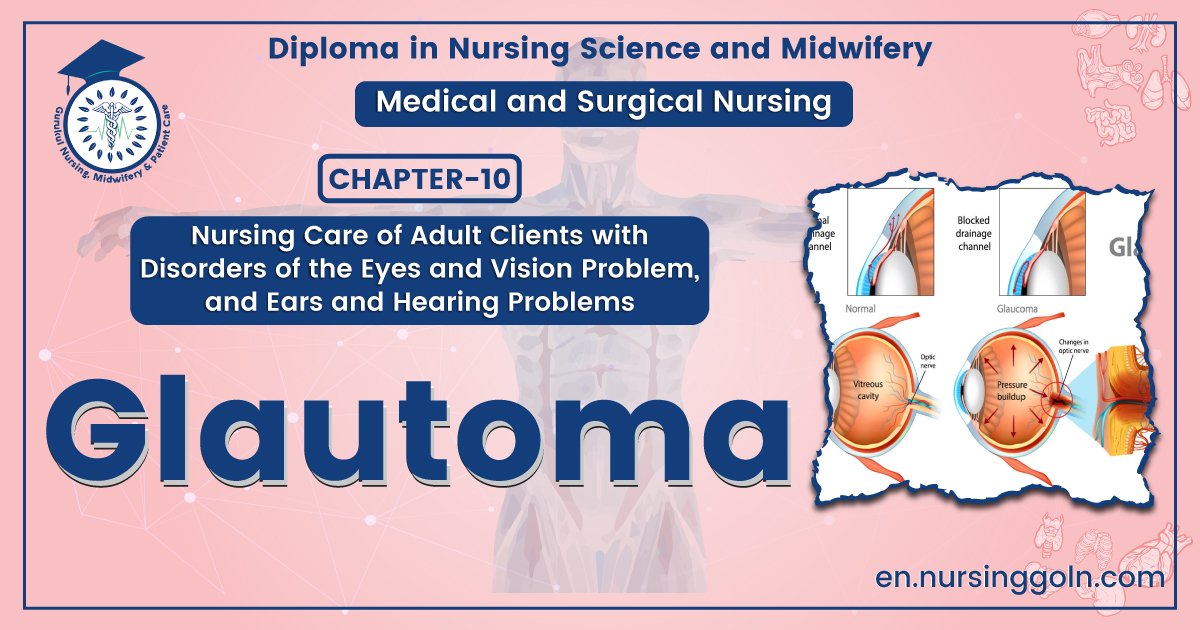
It is a group of disorder where the intraocular pressure of the eye is raised above a certain limit resulting in damage to the optic disc leading to a permanent visual defect.
Or,
It is a condition where the intra ocular pressure of the eye ball increases more than normal which is usually 16-23 mm of Hg.
(Ref-QUIMP-12/142)
Classification:
1. Congenital (infantile glaucoma or buphthalmos)
2. Acquired-
a) Primary
i. Chronic simple glaucoma (wide angle)
ii. Narrow angle or congestive glaucoma
b) Secondary Glaucoma.
- Patient is instructed to avoid precipitating factors like emotional stress exertion
- They must be encouraged for regular follow up.
Corneal Ulcer
Definition of Corneal Ulcer:
Breach of continuity of corneal epithelium due to sloughing out of inflammatory necrotic tissue is called corneal ulcer.
Classification of Corneal Ulcer:
Aetioloeical classification/Causes:
➤ Infective:
- Bacterial.
- Fungal: Filamentous fungi & yeast.
- Viral: Herpes simplex & H. zoster.
- Protozoal: Acanthamoeba.
- Chlamydial.
➤ Non-infective:
- Exposure ulcer.Sum
- Nutritional: Vitamin-A deficiency.
- Neurotrophic.
- Atheromatous.
- Degenerative – e.g. Mooren’s ulcer, Terrien’s ulcer.
- Traumatic
Depending On Purulence:
➤ Purulent ulcer of suppurative keratitis:
- Pyogenic corneal ulcer.
- Hypopyon ulcer.
- Mycotic ulcer.
- Marginal ulcer.
- Ulcer associated with small pox.
➤ Non-purulent ulcer:
- Ulcer due to vitamin-A deficiency.
- Dendritic ulcer
- Lagophthalmic ulcer.
- Ulcer in association with trachoma.
Depending on location:
➤ Central ulcer.
➤ Peripheral ulcer.
Predisposing Factors For Corneal Ulcer:
➤ Contact lens wear.
➤ Trauma to the corneal epithelium, such as accidental injury, surgical and loose sutures.
➤ Ocular surface disease such as –
- Herpetic keratitis.
- Bullous keratopathy.
- Dry eye.
- Chronic blepharitis.
- Trichiasis.
- Exposure.
- Severe allergic eye disease.
- Corneal anaesthesia
➤ Other factors:
- Topical or systemic immunosuppression,
- Diabetes.
- Vitamin A deficiency.
- Measles
Management of Corneal Ulcer:
Clinical features:
Symptoms:
➤ Acute pain, redness & lacrimation.
➤ Photophobia.
➤ Decreased vision.
Signs:
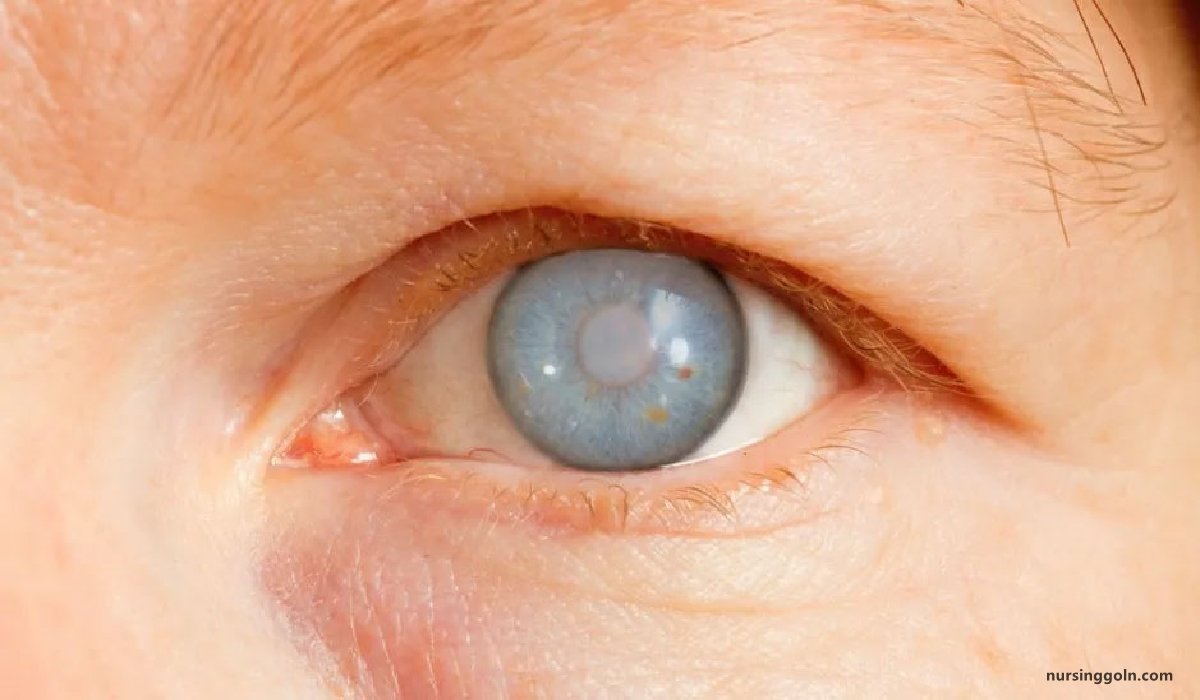
➤ Greyish white disc-shaped ulcer near the center of the cornea.
➤ A cloudy grey area surrounds the disc.
➤ Whole cornea may be hazy.
➤ Violent iridocyclitis with a definite hypopyon.
➤ Conjunctival & ciliary congestion.
➤ Lids are oedematous.
Investigations:
➤ Corneal scraping and then-
- Gram staining.
- Giemsa staining.
- KOH preparation for fungus.
- Culture & sensitivity.
➤ Fluorescein dye test.
Treatment:
➤ Principles of treatment:
- Control of infection.
- Relief of symptoms.
- Promotion of healing.
- Prevention of complications.
- Treatment of complications.
➤ Medical treatment:
- Topical antibiotic:
✔ Ciprofloxacin eye drop 0.3%.
✔ Ciprofloxacin ointment at night.
- Systemic antibiotic: Ciprofloxacin 750 mg BD for 7 days.
- Atropine 1% eye drop.
- Analgesic: Ibuprofen 400 mg, 3 times daily.
- Hot compression.
- Dark glass.
Surgical treatment: If medical treatment failed, then surgical treatment.
- Conjunctival hooding.
- Tarsorrhaphy.
- Amniotic membrane graft,
- Keratoplasty.
Complications of Bacterial Keratitis/Hypopyon Corneal Ulcer:
Before perforation:
- Acute anterior uveitis.
- Hypopyon corneal ulcer.
- Descemetocele or keratocele.
- Ectatic cicatrix.
- Acute iridocycleitis.
- Secondary glaucoma.
- Endophthalmitis.
- Perforation of the cornea & its complications.
- Complicated cataract.
- Corneal opacity (nebula, macula, leucoma).
After perforation:
- Anterior staphyloma.
- Total iris prolapse.
- Anterior polar (capsular) cataract.
- Malignant myopia.
- Secondary glaucoma.
- Panophthalmitis.
- Orbital cellulitis.
- Purulent iridocycleitis.
- Phthisis bulbi.
- Vitreous haemorrhage and prolapse.